August 28th, 2015 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Tips, True Stories
1 Comment »

A Cat Playing Whack-A-Mole
Medication non-adherence is a hot button topic in healthcare. Physicians lament patient “non-compliance” with their medical advice, and policy wonks tell us that more than half of patients do not take their medications as directed. Missed opportunities to control chronic illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer surely do cost us untold billions of dollars and millions of quality life years lost annually in the U.S. But there is a flip side to the equation that no one is talking about. The costs of polypharmacy (over medication).
In my opinion, many Americans, especially those over 65, are taking far too many medicines. The unwanted side effects and medication interactions (both known and unknown) can be devastating. In my line of work (inpatient rehabilitation) I receive a steady stream of patients who have fallen and injured themselves or have been involved in serious accidents. An astonishing number of these incidents are related to drug side effects.
Take, for example, the elderly woman who had mild hypertension. Unbeknownst to her physicians, she was not compliant with the diuretics she had been prescribed. Each successive visit it was presumed that she was taking her medicines as directed, and that they were not sufficient to control her blood pressure. So the dosing was increased. Her husband dutifully picked up the new prescriptions from the pharmacy, and she collected them (unopened) in her desk drawer.
One day this spirited lady caught pneumonia and required a couple of days of inpatient monitoring and antibiotics at the local hospital. Her son decided to assist with her transition back home and stayed with her for a week, taking on both cooking and medication administration duty from his dad. He found all of her pills in her desk drawer and began to give them to her as directed.
Several days later the distraught son told me that his mother’s health had taken a nose-dive, and that she was hallucinating and acting uncharacteristically hostile. He took her to a more distant specialty hospital, where their initial impression was that she had advanced dementia, which had probably gone unnoticed by a son who hadn’t lived nearby for years. She would benefit from hospice placement.
The reality was, of course, that this poor woman was as dehydrated as a raisin and was becoming delirious from excessive diuretic use. Once I figured out that her son’s sudden, and very well-intentioned, medication adherence program was to blame, we stopped the blood pressure medications, gave her some water and she returned to her usual self within 24 hours.
On another occasion, I admitted a closed-head injury patient who had lost her front teeth after fainting and falling head first onto the asphalt in a grocery store parking lot. This was her third head injury in 6 months. A review of her medications revealed no less than six medications (that she was dutifully taking for various diseases and conditions) that carried a known side-effect of “dizziness.” We were able to discontinue all of them, and to this day I have not heard of another fall.
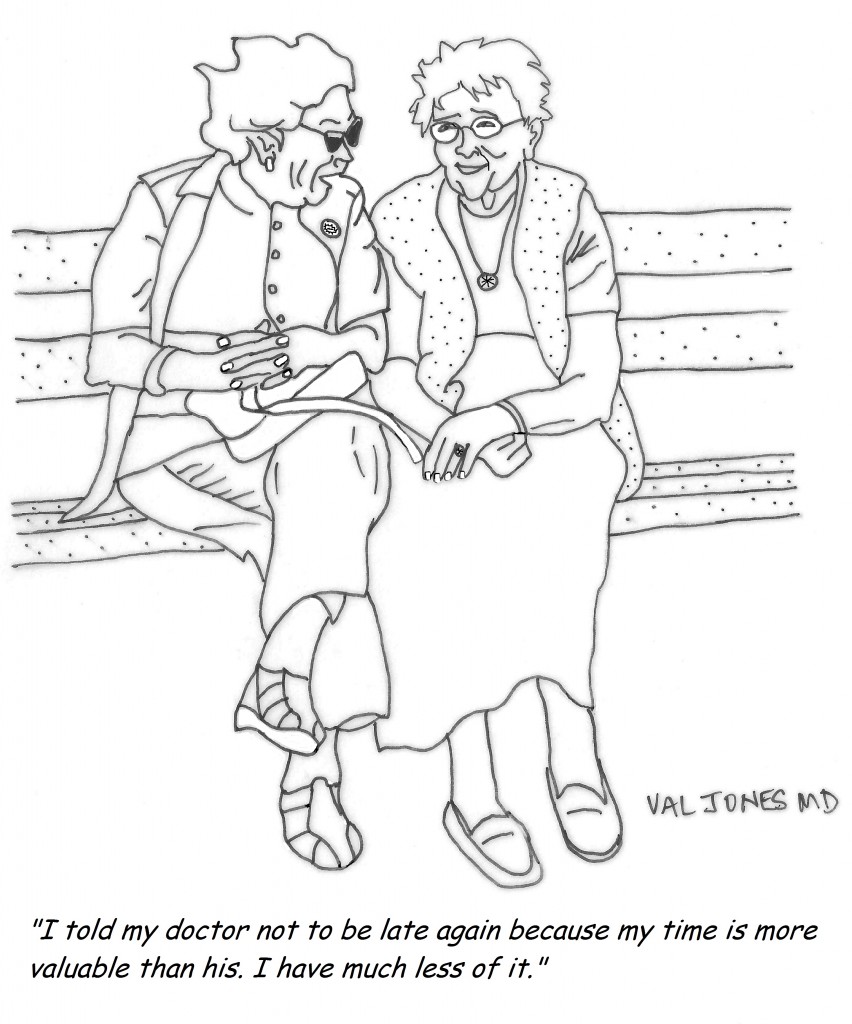
Just last week a wise, elderly patient of mine declined to take her blood pressure medicine. I explained to her that her blood pressure was higher than we’d like and that I wanted to protect her from strokes with the medicines. She smiled kindly at me and said, “I know my body, and I get dizzy when my blood pressure is at the levels you doctors like. The risk of my falling and hurting myself when I’m dizzy is greater than the benefit of avoiding a stroke. I’ve been running at this blood pressure for 80 years. Let’s leave it be.”
What I’ve learned is that although there are costs to not taking medicines, there are costs to taking them too. It is hard to say how many injuries are accidentally prevented by patient non-adherence. But we all need to take a closer look at what’s in our desk drawers, and pare down the prescriptions to the bare minimum required. I consider it a great victory each time I reduce the number of medications my patients use, and I would urge my peers to join me in the pharmaceutical whack-a-mole game that is so sorely needed in this country.
***
The American Geriatrics Society provides a helpful list of medications that should be avoided whenever possible in older individuals.
October 14th, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Policy, True Stories
3 Comments »
Physicians looking for part-time jobs to supplement their income may have run across advertisements for “lucrative” Medicare Advantage evaluation opportunities at CenseoHealth. Here’s a typical ad:
|

CenseoHealth is the leading Risk Adjustment provider for Medicare Advantage plans – with a network of more than 1,800 credentialed providers conducting over 20,000 member health evaluations a month. Due to our continued growth, we are currently looking to hire in-home physician evaluators to work in these states.
As a CenseoHealth physician, you will meet with Medicare Advantage members in their homes to conduct their annual medical history and physical evaluation.
Additional Information:
-
Conduct evaluations when it’s convenient for you
-
Ongoing physicians can make $3,500 to $4,000 per week
-
Physicians who work 1-3 days per week can make $800 – $2,000
-
Travel and lodging expenses are covered, plus we provide a per diem reimbursement
-
Malpractice insurance is included
-
This position does not require you to prescribe medicine, order lab tests, do blood work, or alter the member’s current treatment regimen
Please contact us, for more information.
Bryan Cooke
Director of Physician Recruiting
P: 972.715.3772
E: physicians@censeohealth.com
|
|
Sounds pretty good, right? Well here’s what they won’t tell you:
1. Low Hourly Pay. Compensation is $100 per completed evaluation – but you have to drive to each member’s house (sometimes an hour each way) to complete a 31 page history and physical exam. Members are often medically complex, cognitively impaired, and/or non-English speaking. In the end (after counting travel time, cancellations, scheduling snafus, and long hours completing paperwork and FedEx shipping) the hourly wage works out to be about $30.
2. Poor Logistics. Members are scheduled back-to-back without regard to distance between their locations. That means you are chronically late, and some members cancel their meeting with you. No-show and cancellation rates (in my experience) are about 20%. You are not compensated for any of the time associated with driving to their location, talking to them on the phone, or otherwise trying to locate them when they are not home upon your arrival. Once a member cancels, you cannot fill their slot with someone else on the same day.
3. Threat of harm. Members mostly come from low to middle class income levels. Some of them live in truly horrific living situations (no electricity, a home overrun with cockroaches, no food or running water), and others are psychologically unstable. As a female physician driving alone into a very rural area to conduct a physical exam on a male patient who is actively psychotic… this can be dangerous. You never know what or who you will face. I have had to call social services on numerous occasions and have narrowly escaped inappropriate sexual advances.
4. Limited Support. There is no guarantee that anyone from the parent company will be available via phone when you call during an emergency. I have called on several occasions during critical situations where I had to leave a voice message and was assured that “my call was very important” and someone from provider services “would get back to me within 1/2 a business day.”
5. Questionable ethics. Schedulers do not explain to the members why you are coming to their home to evaluate them. Because the schedulers seem to work on commission, they often use questionable tactics to get the members to agree to the evaluation – such as telling them that the meeting is “mandatory” and will “take 20 minutes” or is “just a wellness visit.” For this reason, many members receive you with suspicion, wondering if you’re there to try to “throw them off the Medicare plan” or are angry that they were mandated to meet with you. Lengthy conversations and apologies to set the stage for your evaluation are commonplace.
6. Payment denials and exaggerated pay potential. Evaluations must be completed meticulously or the quality assurrance reviewers will reject your forms and you will not be compensated for your work (if you, for example, forget to check a box or use a non-approved abbreviation). Although the advertisements state that some physicians complete 35-45 evaluations per week, that is nearly impossible in areas where clients are not clustered together tightly. It is an extremely misleading statement, in my experience. Apparently online reviewers agree.
7. Glitchy and costly technology. In order to save on costs, electronic evaluations can be completed via an iPad rather than paper forms. Unfortunately, the software often crashes, resulting in a return to paper in the middle of an evaluation. This ends up increasing the amount of time required to complete evaluations as your evenings are spent copying paper records into the iPad program. In addition, you are required to purchase your own stylus for data entry, as well as all the equipment required during your physical exam (e.g. blood pressure cuff, bathroom scale, ophthalmoscope, stethoscope, and more).
8. Low-budget travel and accommodations. While the agency boasts that they will pay for your accommodations and rental car, that typically translates into a room at a low-budget hotel and a Toyota Yaris with roll-down windows and no GPS.
9. The truth is hidden. The real reason for the evaluations is to help health insurers obtain larger reimbursements from the government. A physician (or NP) is required to verify all of the patient’s current medical conditions to justify their “risk score.” Medicare Advantage plans get paid more to manage patients with higher risk scores, so they are very motivated to document the complete list of diseases and conditions per at-risk senior. Patients may benefit from having an objective third party review their health record, but this is not the main goal. Also, it is unclear if the higher risk scores ultimately translate to more benefits and services for the patients.
10. Treated like a number. Sadly, my experience with my recruiter (the person who matches your availability with evaluation needs in various states where you hold a medical license) has been underwhelming. I took the time to make suggestions about how to improve the process for evaluators, but my recommendations fell on deaf ears. Not only were my phone calls and emails not returned, but when I suggested that it didn’t make sense for me to continue seeing members when I had a 66% no-show rate he simply replied, “I took you off the schedule – we have an abundance of FL doctors so it is not an issue.”
Take a look at the lovely marketing promotional images for the job:
And this video of what it’s like to do a home evaluation:
Now take a look at some photos that I took while on assignment (note: these are not actual patient homes, but are very similar to ones I encountered):
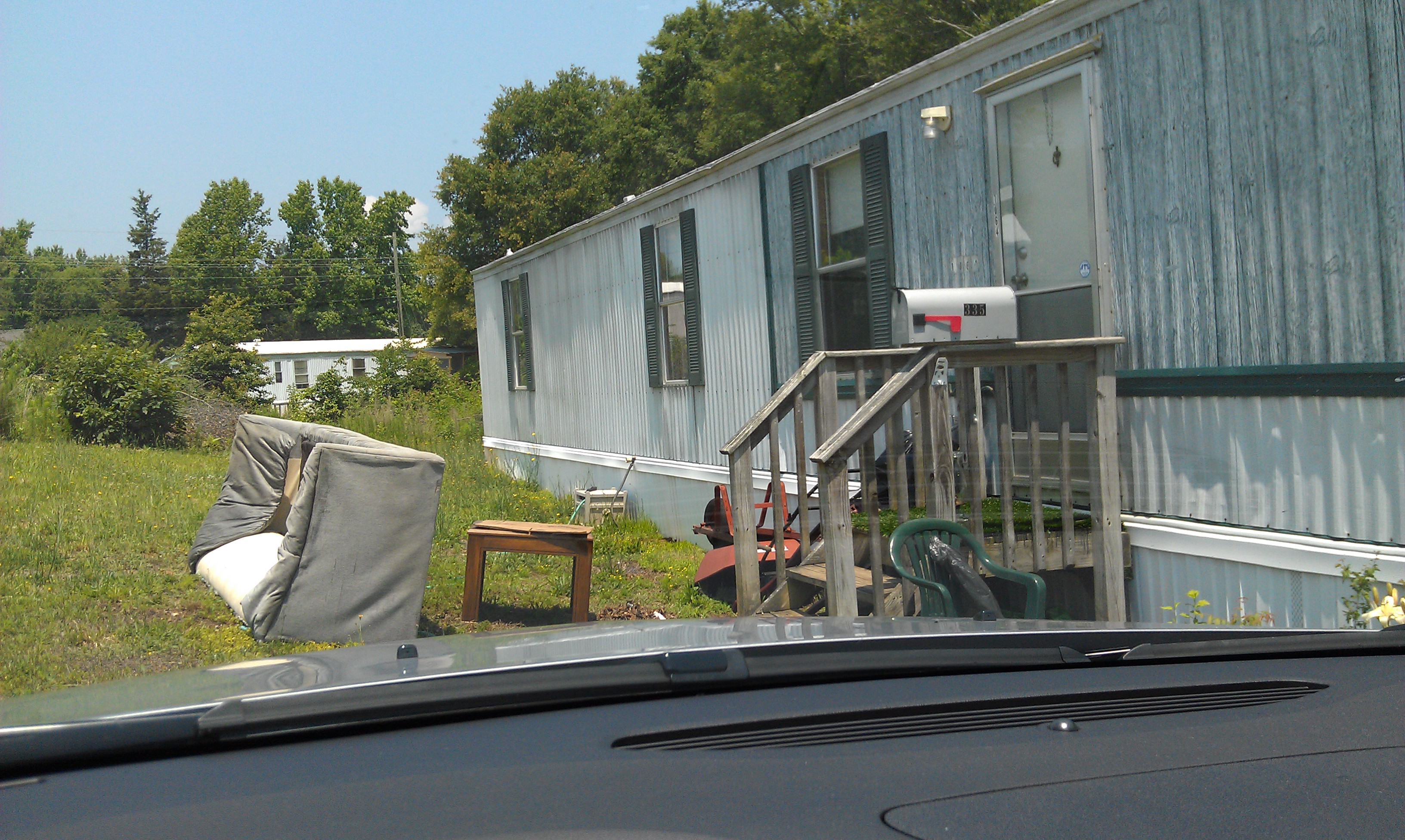
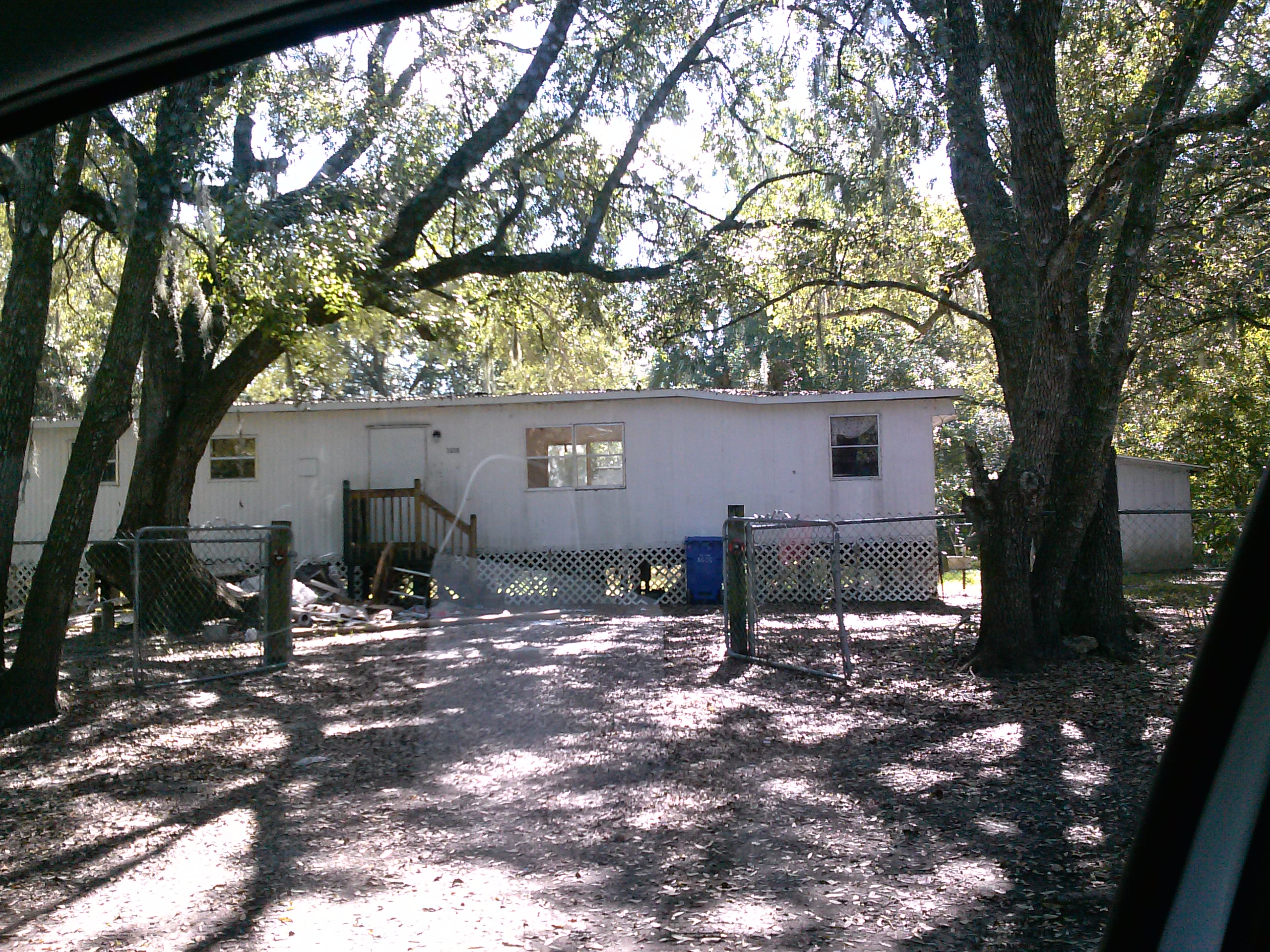
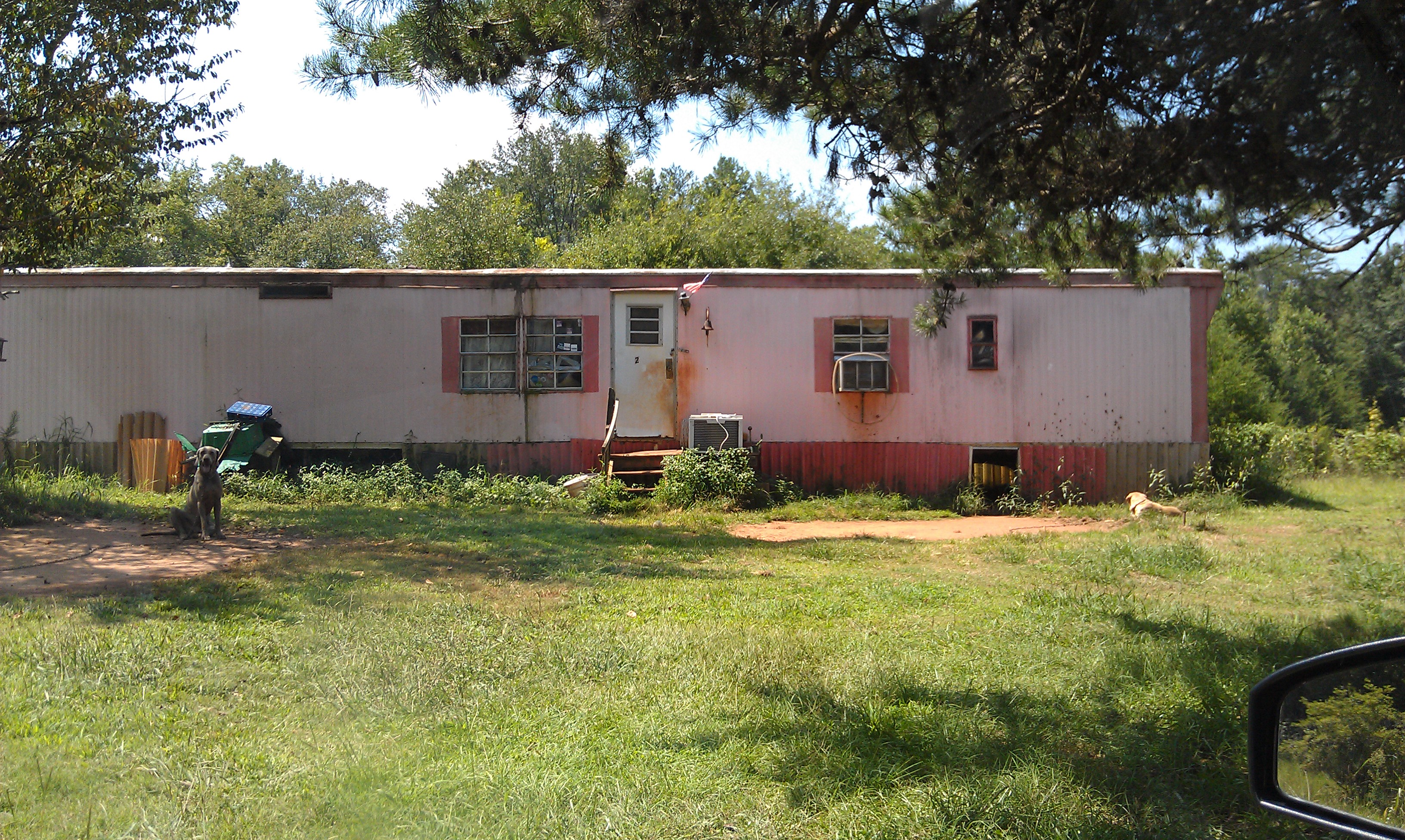



Taking a job as a Medicare Advantage evaluator was a real eye-opener. Poverty and chronic illness in America takes on a whole new light when you experience patients’ actual home environments. It’s like being a medical missionary in your own country. I’ve met patients who hadn’t seen a physician in decades, diagnosed life-threatening illnesses, and made sure that care (or case management) was initiated for countless people living on the fringes of society.
I’m glad for the experience – but think that my peers considering similar work should be told the truth about what they will be doing. Being a Medicare Advantage evaluator is not like the shiny “care anywhere” ad suggests – and “lucrative” is not exactly the right adjective for $30/hour for an MD’s time. But if you don’t mind being treated poorly by your employer, investing a lot of your own money in equipment costs, and putting your life at risk in dangerous home environments – you may actually do some good for the forgotten, frail elderly of this nation, (while helping middle men like Censeo Health to profit from health insurance behemoths, alas). Now you know the truth behind the advertising and can make an informed decision about whether or not you’d like to sign up for this work.
Any takers?
December 4th, 2012 by admin in Health Tips, Humor, Research
No Comments »
 In my last post I told you that I would reveal the one thing you can do to have a significant, positive and lasting effect on your brain health as you get older. See if you can spot it in the following list:
In my last post I told you that I would reveal the one thing you can do to have a significant, positive and lasting effect on your brain health as you get older. See if you can spot it in the following list:
a) Learn to dance Gangnam style
b) Join a choir
c) Catch a wave
d) Pump some iron
Ok, that was a trick question. All of these answers are somewhat correct, but I was looking for the “most” correct answer (flashbacks to undergrad, anyone?): Pump some iron.
I realize I sound like a broken record – I’ve already written about how aerobic exercise can promote healthy aging here and here, and I’ve even already written about resistance training, or lifting weights, here.
So why am I at it again? Because it’s important!
I’m fresh out of the 2012 Aging and Society Conference, where researchers came together to discuss what works and what doesn’t when it comes to healthy aging. It turns out everyone pretty much agrees that exercise is hands down the most effective intervention to keep your brain cells happy into old(er) age. All sorts of different types of exercise, ranging from simply walking to attending resistance training classes, are associated with different types of improvements in cognition, memory, and even brain size.
Of course, there are different levels of effort involved with different types of exercise, or even when talking about a single form of exercise. When my friend Jess asks me to go for a walk, she means a power walk: it usually involves going up hills, sweating like a pig (even though pigs, ironically, don’t sweat much), and barely having enough breath for girl talk (though somehow we always seem to find it). When my friend Al and I go for a walk, what he means is a “mosey”: we stop to look at the view, pet the dog, chit chat with strangers, and have more than enough breath for lengthy discussions about life, work, and the possibility of alien lifeforms. When it comes to brain health, whether you’re walking or pumping iron, a little sweating and effort can go a long way. For example, resistance training has been proven to be most effective when the load, or how much weight you are working with, increases over time. So kick the intensity up a notch: there will still be plenty of time for chit chat around a post-exercise, antioxidant-rich mug of matcha (my new obsession – stay tuned).
Now that the obvious has been (re)stated, I want to take this opportunity to discuss the idea that perhaps lifestyle interventions such as exercise could be prescribed by your doctor. We know that exercise can improve cognition in aging but also conditions like depression. Should physicians prescribe lifestyle changes? Or are diet, exercise, and other lifestyle activities choices we should make ourselves? How would you feel if your doctor prescribed you exercise instead of pills? Would you be more motivated to exercise if the prescription came from your doctor instead of from your friendly Internet science blogger? Your thoughts in the comments!
***
Dr. Julie Robillard is a neuroscientist, neuroethicist and science writer. You can find her blog at scientificchick.com.











 In my
In my 









