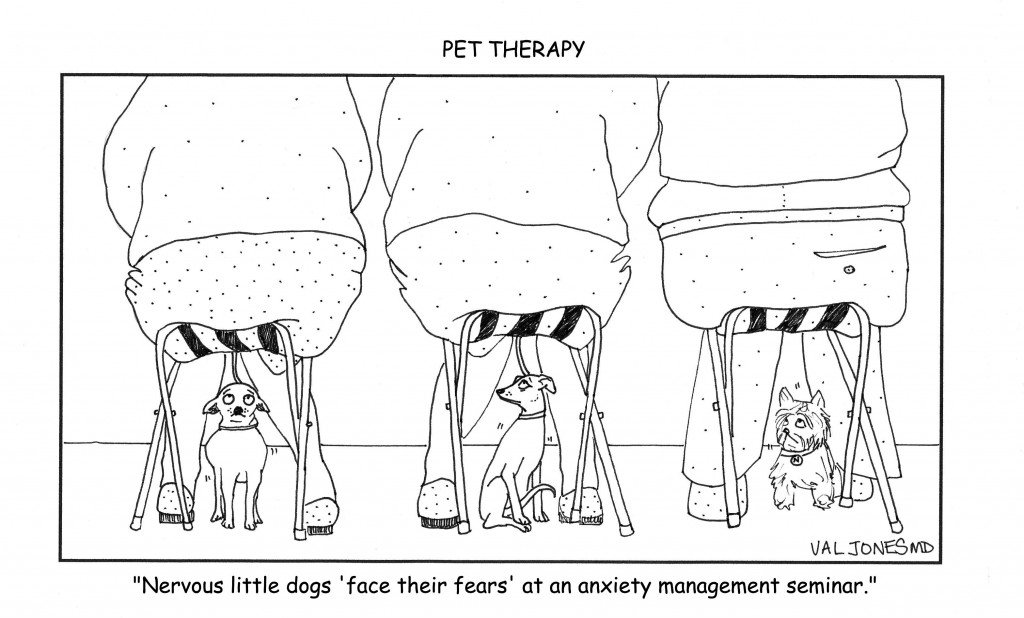
Cartoon: Exposure Therapy For Dogs With Anxiety Disorders

 Over the years that I’ve worked in acute inpatient rehab centers, I have been truly vexed by a particular type of patient. Namely, the stubborn patient (usually an elderly gentleman with a military or armed forces background). I know that it’s not completely fair to generalize about personality types, but it seems that the very nature of their work has either developed in them a steely resolve, or they were attracted to their profession because they possessed the right temperament for it. Either way, when they arrive in the rehab unit after some type of acute illness or traumatic event, it is very challenging to cajole them into health. I suspect that I am failing quite miserably at it, frankly.
Over the years that I’ve worked in acute inpatient rehab centers, I have been truly vexed by a particular type of patient. Namely, the stubborn patient (usually an elderly gentleman with a military or armed forces background). I know that it’s not completely fair to generalize about personality types, but it seems that the very nature of their work has either developed in them a steely resolve, or they were attracted to their profession because they possessed the right temperament for it. Either way, when they arrive in the rehab unit after some type of acute illness or traumatic event, it is very challenging to cajole them into health. I suspect that I am failing quite miserably at it, frankly.
Nothing is more depressing for a rehab physician than to see a patient decline because they refuse to participate in activities that are bound to improve their condition. Prolonged immobility is a recipe for disaster, especially in the frail elderly. Refusal to eat and get out of bed regularly can make the difference between life and death within a matter of days as leg clots begin to form, and infectious diseases take hold of a body in a weakened state. The downward spiral of illness and debility is familiar to all physicians, but is particularly disappointing when the underlying cause appears to be patient stubbornness.
Of course, the patient may not be well enough to grasp the “big picture” consequences of their decisions. And I certainly do not pretend to understand what it feels like to be elderly and at the end of my rope in regards to prolonged hospital stays. Maybe I’d want to give up and be left alone too. But it’s my job to get them through the tough recovery period so they can go home and enjoy the highest quality of life possible. When faced with a patient in the “wet cat” phase of recovery (I say “wet cat” because they appear to be as pleased to be on the rehab unit as a cat is to being doused against their will), these are the usual stages that I go through:

1. I explain the factual reasons for their admission to rehab and what our goals are. I further describe the risks of not participating in therapies, eating/drinking, or learning the skills they need to care for themselves with their new impairments.
2. I let them know that I’m on their side. I understand that they don’t want to be here, and that I will work with them to get them home as soon as possible, but that I can’t in good conscience send them home until it’s safe to do so.
3. I give them a projected discharge date to strive towards, with specific tasks that need to be mastered. I try my best to give the patient as much control in his care as possible.
4. I ally with the family (especially their wives) to determine what motivates them, and request their presence at therapy sessions if that seems fruitful rather than distracting. (Helpful spouse input: “Mike only wants to walk with me by his side, not the therapist.”)
5. I ask loved ones how they think the patient is doing/feeling and if there is anything else I can do to make his stay more pleasant. (Helpful input: “John loves ice cream. He hates eggs” or “John usually goes to bed at 9pm and gets up at 4am every day.”)
6. I meet with nursing and therapy staff to discuss behavioral challenges and discuss approaches that are more effective in obtaining desired results. (For example, some patients will always opt out of a task if you give them a choice. However, they perform the task if you state with certainty that you are going to do it – such as getting out of bed. “Would you like to get out of bed now, Mr. Smith?” will almost certainly result in a resounding “No.” Followed perhaps by a dismissive hand wave. However, approaching with a “It’s time to get out of bed now, I’m helping you scoot to the edge of the bed and we’re going to stand up on 3. One, two, three!” Is much more effective.)
7. If all else fails and the patient is not responding to staff, loved ones, or doctors, I may ask for a psychiatric consult to determine whether or not the patient is clinically depressed or could benefit from a medication adjustment. Typically, these patients are vehemently opposed to psychiatric evaluation so this is almost the “nuclear” option. Psychiatrists can be very insightful regarding a patient’s mindset or barriers to participation, and can also help to tease out whether delirium versus dementia may be involved, and whether the patient lacks capacity to make decisions for himself.
8. If the patient still does not respond to further tweaks to our approach to therapy or medication regimen, then I begin looking for alternate discharge plans. Would he be happier in a skilled nursing home environment where he can recover at a slower rate? Would he be amenable to an assisted living or long term care facility? (The answer is almost always a resounding “no!”) Is the patient well enough to go home with home care services and round-the-clock supervision? Does the family have enough support and can they afford this option?
9. At this point, after exhausting all other avenues, if the patient is still declining to move or eat or be transferred elsewhere, some sort of infection might set in. A urinary tract infection, a pneumonia, or bowel infection perhaps. Then the patient becomes febrile, is started on antibiotics, becomes weaker and less responsive, and is transferred to the medicine floor or higher level of care. Alternatively at this phase (if he is lucky enough not to become infected) the patient might have a cardiac event, stroke, blood clot with pulmonary embolus (especially if he is a large man), kidney failure, or develop infected pressure ulcers. Any of which can be cause for transfer to medicine. In short, if you stay in the hospital long enough, you can find a way to die there.
10. After much hand-wringing, angst, and generalized feelings of helplessness the wives and I review the course of events and ask ourselves if we could have done anything differently. “If I had acted like a drill sergeant, do you think he would have responded better?” I might ask. “No dear, that would only have made things worse.” She’ll reply. I’ll see how disappointed she is in his deterioration, staring off towards pending widowhood, engaging in self-blame and what-ifs (E.g. “If we had only had more money perhaps we could have taken him home with 24 hour nursing care until he was better…” “If I had cooked all his meals, maybe he would have gained enough strength to avoid the infection…” etc.) I try to be reassuring that none of this would have made a difference, myself reeling from the failure to get the patient home.
This 10 step process happens far more often than I’d like, and I certainly wish there were a way to head off the downward spiral with some kind of effective intervention. Would it help to have a volunteer unit of ex-military peer counselors in the hospital who could visit with my patients and help to motivate them to get better? (Operation “wet cat” perhaps?) Should I change my approach and put on my drill sergeant hat at the earliest stages of recovery to force these guys out of bed? Can educating younger law enforcement and military workers about illness help to prepare them to be more compliant patients one day?
I don’t know the cure for stubbornness, but it sure leaves a lot of widows in its wake.

Photograph: Roger Bamber
How far do we travel from our parents’ patterns? A question psychotherapists and their clients have been wrestling with for decades.
We can’t escape the parental imprint. Some of us may not want to. But those of us who did hope to be different often find ourselves in our 40s or 50s unexpectedly leaking parental behaviors or attitudes we thought we had purged ourselves of in our 20s.
I sometimes hear myself saying to Richard, my partner, as he heads out the door for his Tae Kwon Do class, “Be careful.” He has a second degree black belt and has been studying for years. He is always careful. My admonition is a spillover of my father’s anxious voice warning me to be on the lookout for endless, unnamed dangers hiding in plain sight at every turn. Other times I see myself tighten up like a fist when something I thought I had control over twists in an unpredictable direction. It is not my jaw that clenches in agitation; it is my mother’s jaw, on my face.
How our parents do or did illness is a powerful pattern. Did they suffer in silence, while allowing no one to offer tenderness or help? Did they submerge into illness and allow it to define who they were? Did they use illness to control and manipulate? To get attention? Did they remain engaged in living and loving? Did they learn from illness to become more fully who they were? Did they become nastier to each other? Or sweeter? And finally, did they take care of each other — physically and emotionally?
My parents, who kept each other at a distance when well, became even more separated when ill. They went so far as to resent each other for their increasing incapacities. It was not pretty.
There were times when I was in the thick of my pain condition, that I isolated and withdrew from Richard. But more often, I allowed my pain to teach me to reach out for comfort and connection. I had to. For me, the voice of pain was more powerful than my parents’ example.
Dealing with illness can be a consuming job. When you find yourself behaving in ways that don’t create the kind of bridge to your partner that will help lighten the load for both of you, pause and ask yourself: “Am I playing out a pattern that doesn’t really belong to me? Whose voice am I speaking with? Can I do it differently?”
How did your parents deal with illness? What did you learn to do and not to do from them?
***
Barbara Kivowitz is a psychotherapist, business consultant, and book author. She blogs regularly at In Sickness And In Health.

Author Mira Kirshenbaum
I Love You But I Don’t Trust You is national bestselling author, Mira Kirshenbaum’s, 11th book about healing relationships. I had the privilege of working with Mira when she was part of my medical expert team at Revolution Health, so I welcomed the chance to review her latest work. Although I had to endure some curious looks from my fiancé (who wondered why I was reading a book with that title), Mira’s writing sparked some interesting discussions between us and reinforced our own trust in each other.
When I first read the title of the book, I assumed that it would be focused on what to do when your partner has an affair. I was surprised to discover that I was utterly wrong. In fact, relational trust deficits can be caused by anything from broken promises, to misrepresenting financial situations, to lording one’s power over another. I Love You But I Don’t Trust You opened my eyes to all the subtle ways that trust can be eroded, and at the same time offered “actionable” advice for shoring up relationships.
Mira’s writing is particularly engaging because she illustrates her ideas with poignant, real-life examples. For every breach of trust under discussion, she offers a case study. Sometimes the couples she describes make outrageous gaffs, and the emotional train wreck that ensues is both terrifying and riveting. Example after example of poor judgment, bad behavior, and selfish acts could potentially be depressing, if it weren’t for the good news that follows. Many of these couples were able to resolve their conflicts and restore trust against all odds. Illustrating how that happens is part of the reason why Mira’s book is a page-turner.
Beyond advice for couples, I Love You But I Don’t Trust You is actually quite relevant for anyone who has been deeply wronged. Mira describes how she herself was able to offer true forgiveness to a former Nazi soldier who had participated (indirectly) in putting her own parents in a concentration camp. She describes a life-changing moment when she was traveling in Europe as a young woman, and she became very ill and fainted at the train station. A German couple took her to their home and nursed her back to health. Mira learned to trust the “untrustable” and became convinced through this experience that no relationship was beyond help. She devoted the rest of her life to relationship counseling, and her passion fosters hope in each of her books.
Some things you will learn from I Love You But I Don’t Trust You:
*All the ways that mistrust can enter a relationship
*Is your relationship worth saving?
*The typical response to broken trust, and the way to minimize collateral damage
*Suggested timeline for change and trust repair
*How to restore trust by working through 6 key questions
The only downside to Mira’s book is that it is based upon, as far as I can tell, the informed experience of only one therapist. Mira does not refer to the academic literature to support her theses or suggestions, nor does she appear to rely upon outside sources for additional insight. Mira speaks from her gut – she has a brilliant way of positioning arguments, and helping people to approach each other in ways that are minimally inflammatory in what is otherwise an emotional mine field. Beyond that, I can’t say if Mira’s approach to conflict resolution is optimal. My instinct says it’s as fine a methodology as any I’ve seen, but from an evidence-based perspective, there isn’t necessarily a lot of data behind it (just had to add that caveat for my science-loving friends).
Nonetheless, in my opinion, I Love You But I Don’t Trust You would be an excellent workbook for people in couples’ therapy. In fact, the Appendix lists suggested topics and questions for discussion groups, so I’m sure that Mira was thinking the same thing when she wrote it.
But most importantly, I think that reading the book in advance of any trust violations in your relationship, could be the best course of action. Simply learning about all the damage that one impulsive decision can cause to a lover and/or family could make you less likely to make that decision! I Love You But I Don’t Trust You might best be used as a preventive health measure for your relationship(s). I’m sure it has strengthened me against trust violations in my future.
**You can order the book on Amazon.com here **

 When we talk about psychotherapy, one aspect of what we look at is the process of what occurs in the therapeutic relationship. This is an important part of psychodynamic-based psychotherapy, meaning psychotherapy that is derived from the theories put forth by Freud. Psychoanalysis (the purest form of psychodynamic psychotherapy) includes an emphasis on events that occurred during childhood, and a focus on understanding what goes on in the relationship between the therapist and the patient, including the transference and counter-transference.
When we talk about psychotherapy, one aspect of what we look at is the process of what occurs in the therapeutic relationship. This is an important part of psychodynamic-based psychotherapy, meaning psychotherapy that is derived from the theories put forth by Freud. Psychoanalysis (the purest form of psychodynamic psychotherapy) includes an emphasis on events that occurred during childhood, and a focus on understanding what goes on in the relationship between the therapist and the patient, including the transference and counter-transference.
In some of our posts, our friend Jesse has commented about how it’s important to understand what transpires in the mind of the patient when certain things are said and done. Let me tell you that Jesse is a wonderful psychiatrist, he is warm and caring and attentive and gentle, and he’s had extensive training in the analytic method, he’s on my list of who I go to when I need help, so while I want to discuss this concept, I don’t want anyone, especially Jesse, to think I don’t respect him. With that disclaimer…..
On my tongue-in-cheek post on What to Get Your Psychiatrist for the Holidays, Jesse wrote: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Shrink Rap*
It’s no secret that doctors are disappointed with the way that the U.S. healthcare system is evolving. Most feel helpless about improving their work conditions or solving technical problems in patient care. Fortunately one young medical student was undeterred by the mountain of disappointment carried by his senior clinician mentors…
I am proud to be a part of the American Resident Project an initiative that promotes the writing of medical students residents and new physicians as they explore ideas for transforming American health care delivery. I recently had the opportunity to interview three of the writing fellows about how to…
Book Review: Is Empathy Learned By Faking It Till It’s Real?

I m often asked to do book reviews on my blog and I rarely agree to them. This is because it takes me a long time to read a book and then if I don t enjoy it I figure the author would rather me remain silent than publish my…
The Spirit Of The Place: Samuel Shem’s New Book May Depress You

When I was in medical school I read Samuel Shem s House Of God as a right of passage. At the time I found it to be a cynical yet eerily accurate portrayal of the underbelly of academic medicine. I gained comfort from its gallows humor and it made me…
Eat To Save Your Life: Another Half-True Diet Book

I am hesitant to review diet books because they are so often a tangled mess of fact and fiction. Teasing out their truth from falsehood is about as exhausting as delousing a long-haired elementary school student. However after being approached by the authors’ PR agency with the promise of a…