June 30th, 2011 by Paul Auerbach, M.D. in Health Tips
No Comments »

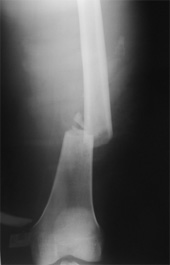 My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
At her age—indeed at any age—a fractured femur is a very significant injury. This past year, I have learned of friends and others who have suffered falls and broken their legs, ankles, or backs, as well as others who suffered “pathological fractures.” The latter group had the bones break from normal daily stresses, without a traumatic incident, because the bones were weak and/or osteoporotic. More than a few of these injuries occurred outdoors, associated with stumbles on the trail or falls.
All of this highlights features of an excellent review article that was published this past year in the New England Journal of Medicine. Authored by Murray Favus, MD, it is entitled “Biphosphonates for Osteoporosis” (New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363:2027-35). Anyone who is contemplating taking or administering this therapy would benefit from reading this article. Read more »
This post, Osteoporosis Treatment With Bisphosphonates: Is Exercise Good Or Dangerous?, was originally published on
Healthine.com by Paul Auerbach, M.D..
January 14th, 2010 by Harriet Hall, M.D. in Better Health Network, Opinion, Research
1 Comment »

A recent story on NPR accused the drug manufacturer Merck of inventing a disease, osteopenia, in order to sell its drug Fosamax. It showed how the definition of what constitutes a disease evolves, and the role that drug companies can play in that evolution.
Osteoporosis is a reduction in bone mineral density that leads to fractures. The most serious are hip fractures, which require surgery, have complications like blood clots, and carry a high mortality. Many of those who survive never walk again. Vertebral fractures are common in the osteoporotic elderly and are responsible for dowager’s hump and loss of height. There is also an increased risk of wrist and rib fractures. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Science-Based Medicine*
September 21st, 2009 by Paul Auerbach, M.D. in Better Health Network, Health Tips
No Comments »

 This is the next post based upon a presentation given at the Wilderness Medical Society Annual Meeting held in Snowmass, Colorado from July 24-29, 2009. The presentation was about trauma and orthopedics. It was delivered by Douglass Weiss, MD of Teton Orthopaedics in Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
This is the next post based upon a presentation given at the Wilderness Medical Society Annual Meeting held in Snowmass, Colorado from July 24-29, 2009. The presentation was about trauma and orthopedics. It was delivered by Douglass Weiss, MD of Teton Orthopaedics in Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
Utilizing some fabulous images, including those of Lanny Johnson, Dr. Weiss made some important points. Many of these are familiar to seasoned medical practitioners, but they merit repeating. First, when approaching a victim, always attend to the “ABCs” first – airway, breathing, and circulation (including bleeding) – so that a life can be saved. Then, if possible, take into account other injuries, including those of bones – save the limb, save the joint, and restore function.
Here are two good pointers. First, your field evaluation of the victim may be the only complete one, so do your best to examine the entire victim, and also to document in writing what you discover. Examine and establish the airway, listen for breath sounds, observe chest movements, feel for pulses and observe skin color, etc. Within the constraints of the situation and environment, “expose” the victim in order to evaluate bony and other injuries. The, move on to the “secondary” survey, which will include examination of the neck, back, pelvis, arms and legs, looking for swelling, bruises, scrapes, cuts, bleeding and deformities. If you feel inappropriate motion (e.g., broken or dislocated bones or joints), be prepared to apply splints.
Always try to roll the patient (using a logroll technique if necessary) to examine the victim’s back.
For the benefit of doctors reading this post, remember that if a fracture is identified, suspect an injury to the joint above and below the fracture, and be sure to splint these for the comfort and protection of the victim.
The application of splints is an art form, so should be practiced prior to your expedition. Any limb that is obviously deformed or that demonstrates excess motion (where there should be none) should be immobilized immediately. If a helper(s) is available, use assistance. Be sure to pad all splints very well to avoid pressure injuries to the tissue underneath. Depending on the rescue, the splint may be in place longer than you anticipate.
If a broken bone (fracture) is “open” (the bone has poked through the skin), then apply a wet (preferably normal saline or disinfected water) dressing and apply a splint. If you have an all-purpose antibiotic (e.g., cephalexin, amoxicillin or ciprofloxacin) and the victim is capable of purposeful swallowing, administer a dose.
Fractures of the pelvis generally imply that a very significant force was applied, so they carry a high risk for associated life threatening injuries. The victim should be evacuated as soon as possible. It is commonly taught that a broken femur (the long bone of the thigh) can cause bleeding in excess of a liter into the limb. This can be dangerous, so these injuries should be promptly splinted, preferably with a pre-fashioned or improvised traction splint.
Compartment syndrome occurs when tissue pressures within inelastic soft tissue compartments of the limbs (commonly the forearm or lower leg exceed perfusion pressure, that is, the pressure necessary to allow blood to circulate freely through the tissues and provide energy and remove waste products. Symptoms include extreme pain, loss of pulses, pale skin color, weakness or paralysis of the muscle, and numbness and tingling. If the pain is severe and the skin feels tight, a compartment syndrome may be developing. If a compartment syndrome is felt to be impending or present, keep the limb elevated and seek immediate medical attention, because an operation may be required to open the compartment and release the pressure before the onset of permanent tissue damage.
Thanks to Dr. Weiss for his contribution to wilderness medicine education.
This post, Tips For Evaluating Injured People In The Outdoors, was originally published on
Healthine.com by Paul Auerbach, M.D..
 My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.












