February 22nd, 2011 by Felasfa Wodajo, M.D. in News, Research
No Comments »

The word cancer comes from the greek word for crab “karkinos,” so named by Hippocrates who visualized the tumor and its surrounding vessels looking like a crab, dug stubbornly into the sand with its legs. We know far more about cancer today than the ancient Greeks, but the vision of an entrenched opponent, almost impossible to extract whole, appears to be vividly prescient.
What we have realized over the last half century is that removal of the visible tumor is not enough. Even as we learned how to do bigger and more destructive surgeries, the cancer still managed to sneak back in, growing later at different locations. The crab’s legs are still embedded in the patient.
Thus the discovery that certain chemicals could extinguish these rogue cells opened the modern era of cancer therapy and led to the first “cures” from cancer. Many of these compounds were exquisitely toxic. Early experimenters even used nitrogen mustard, quite literally a poison, as Siddhartha Mukherjee tells in his excellent history of cancer, “The Emperor of All Maladies.”

To many, the battle looked grim. For the founder of CollabRx, who himself was living in the shadow of advanced melanoma, this was the signal to take his expertise in internet information technologies and apply it to cancer. Thus a “biomedical software company” was founded, with the mission:
…to save lives by using information technology to personalize cancer treatments and accelerate research.
The rapid proliferation of knowledge about the molecular underpinnings of different cancers, has brought hope for a new age of “targeted” therapies. These drugs are designed to find and destroy cells with aberrant biochemical pathways, while bypassing the normal body tissues. Immense hopes rest on them. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at iMedicalApps*
February 18th, 2011 by Berci in Better Health Network, Health Tips
No Comments »

As a part of the TheraFlu campaign, Novartis has developed free Android, Blackberry and iPhone applications for tracking flu outbreaks in the U.S. These days it’s become inevitable to develop free apps on all platforms in order to promote your product. From Novartis:
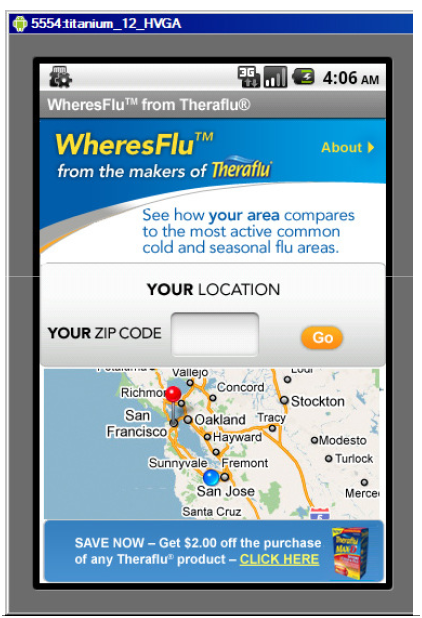 Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
If you’re wondering how it actually works and how it differs from Google Flu Trends, here it is:
WheresFlu™ measures weekly activity for cold and flu based upon real-time reports of symptoms from SDI FAN® (a source used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). As the longest-running respiratory tracking program in the US, SDI FAN® covers illness levels in 135 regions across the country utilizing panel-member reporting along with patient-specific data. Advanced tracking uses illness status levels to predict change in the affected population for the nine US Census Regions.
*This blog post was originally published at ScienceRoll*
February 5th, 2011 by Felasfa Wodajo, M.D. in Opinion, Research
No Comments »

The cost of managing chronic diseases is the largest portion of healthcare expenditures in developed countries. For example, the prevalence of adult acquired diabetes has been rising in the United States, in concert with increasing rates obesity. The CDC has termed it an “epidemic,” especially in light of the massive costs incurred by the healthcare system due to diabetes.
The deleterious health effects of many chronic conditions can be diminished by behavior modifications. While few would underestimate the difficulty of having patients lose weight or exercise more, good management of blood sugar in diabetes is both objectively measurable and strongly correlated with reduced end-organ damage.
This is among the reasons why Research2Guidance has recently nominated diabetes as the condition most likely to be most targeted by mobile medical software and devices (mHealth). This finding is part of their recently published Global Mobile Health Market Report 2010-2015. This is the same report that also predicted that, in the future, medical apps are likely to be distributed by physicians and healthcare institutions.

This time Research2Guidance is highlighting the portion of the survey where they looked into where mobile devices have the most potential to affect health outcomes. While other chronic conditions such as hypertension and obesity have larger populations, the market researchers felt diabetes had the largest market potential due to the huge cost saving potential, the demographic and geographic overlap between smartphone users and people with diabetes, and the real potential to improve blood sugar management using mobile devices. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at iMedicalApps*
December 30th, 2010 by Iltifat Husain, M.D. in Better Health Network, News, Research
No Comments »

 Imagine walking into the room of a patient with ascites and pulling out your iPad (which you were just using to put in orders on another patient), pulling an ultrasound probe out of your pocket, connecting the two, and finding a fluid pocket from which to drain the abdominal fluid.
Imagine walking into the room of a patient with ascites and pulling out your iPad (which you were just using to put in orders on another patient), pulling an ultrasound probe out of your pocket, connecting the two, and finding a fluid pocket from which to drain the abdominal fluid.
We’ve already shown how iPad’s can be useful in the OR. Now they, along with other tablets and smartphones, can be applied to bedside diagnostics and therapeutics to enhance patient safety while reducing costs. It’s a pretty exciting prospect being put forth by an mHealth startup called Mobisante. And having won awards at an MIT Enterprise Forum as well as the Mobile Health Expo, others certainly seem to buying in as well.
Mobisante, an mHealth company based in Redmond, WA, has recently been showing a new smartphone peripheral at conferences across the country: An ultrasound probe. According to the MIT Technology Review, the current prototype connects to a Toshiba TG01 smartphone and was originally developed as a laptop peripheral by David Zar, a computer engineer at Washington University in St. Louis. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at iMedicalApps*
December 16th, 2010 by Berci in Better Health Network, Health Tips, News
No Comments »

 There are more and more premature babies, and the situation for their parents is dramatic. They would love to be with their newborn 24 hours a day, but in most cases they obviously can’t.
There are more and more premature babies, and the situation for their parents is dramatic. They would love to be with their newborn 24 hours a day, but in most cases they obviously can’t.
At the Dutch UMC Ultrecht, they’ve launched a project under the name Telebaby, in which cameras were installed at the incubators and parents can watch their child live 24 hours a day — even through a mobile device.
The system is password protected, of course, so only the parents can access the specific video channels. Isn’t it great? A very human but not that expensive idea — a really Dutch approach.
*This blog post was originally published at ScienceRoll*





 Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.










