December 6th, 2011 by Medgadget in Research
No Comments »
 Obesity is the most significant chronic healthcare crisis facing the United States, as well as other countries. Already 1 out of every 3 adults, and 1 out of every 6 children or adolescents, in the U.S. is obese! Leptin is a hormone that has received considerable attention since its discovery in 1994 for its role in regulating metabolism (like a thermostat, or adipostat) and implications for obesity. High leptin levels are associated with feeling satiated and an active metabolism. Though many overweight people have high levels of circulating leptin, it’s been found that their hypothalamic neurons do not receive the signal – a phenomenon known as “leptin resistance.” An animal model that mirrors this is db/db mice, which lack leptin receptors on the surface of they hypothalamic neurons and are therefore morbidly obese (see image).
Obesity is the most significant chronic healthcare crisis facing the United States, as well as other countries. Already 1 out of every 3 adults, and 1 out of every 6 children or adolescents, in the U.S. is obese! Leptin is a hormone that has received considerable attention since its discovery in 1994 for its role in regulating metabolism (like a thermostat, or adipostat) and implications for obesity. High leptin levels are associated with feeling satiated and an active metabolism. Though many overweight people have high levels of circulating leptin, it’s been found that their hypothalamic neurons do not receive the signal – a phenomenon known as “leptin resistance.” An animal model that mirrors this is db/db mice, which lack leptin receptors on the surface of they hypothalamic neurons and are therefore morbidly obese (see image).
Reporting in Science this past week, researchers at Harvard Medical School transplanted neurons with the leptin receptor into the hypothalami of db/db mice and as a result were able to partially restore leptin sensitivity and ameliorate their obesity. Two to three months after transplanting 15,000 (a relatively small number) fluorescently-tagged, leptin sensitive neurons into the db/db mice hypothalami, they observed statistically significant drops in blood sugar levels, leptin concentration, and fat mass. In terms of the mechanism and implications, the team concludes: Read more »
July 5th, 2011 by GarySchwitzer in News, Research
No Comments »

The Spine Journal has published a special June issue focusing on Medtronic’s INFUSE product, or rhBMP-2, a bone growth product commonly used in spine fusion surgeries. A journal news release states:
A critical review of 13 industry-sponsored studies on a spine surgery product found that the actual risk of adverse events was 10 to 50 times the estimates originally reported. The product in question is recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2), a controversial synthetic bone growth factor often used as a bone graft substitute in spine fusion surgeries. This eye-opening study, “A critical review of rhBMP-2 trials in spinal surgery: emerging safety concerns and lessons learned” is included in a special BMP-focused issue of The Spine Journal.
The comprehensive review found four main areas of concern among the 13 original industry-sponsored studies:
• Conflicts of interest were either not reported or were unclear in each study. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Gary Schwitzer's HealthNewsReview Blog*
July 1st, 2011 by Berci in News
No Comments »

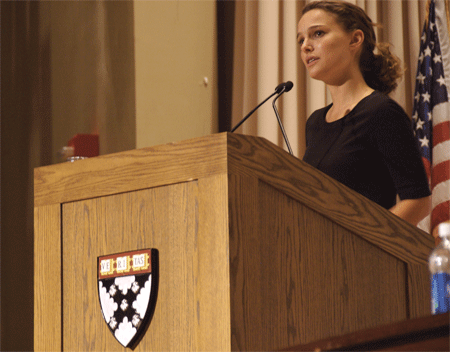 Did you know that Natalie Portman (under the name, Natalie Hershlag) published a paper in a scientific journal in 2002 while at Harvard?
Did you know that Natalie Portman (under the name, Natalie Hershlag) published a paper in a scientific journal in 2002 while at Harvard?
Frontal lobe activation during object permanence: data from near-infrared spectroscopy.
The ability to create and hold a mental schema of an object is one of the milestones in cognitive development. Developmental scientists have named the behavioral manifestation of this competence object permanence. Convergent evidence indicates that frontal lobe maturation plays a critical role in the display of object permanence, but methodological and ethical constrains have made it difficult to collect neurophysiological evidence from awake, behaving infants. Near-infrared spectroscopy provides a noninvasive assessment of changes in oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin and total hemoglobin concentration within a prescribed region. The evidence described in this report reveals that the emergence of object permanence is related to an increase in hemoglobin concentration in frontal cortex.
*This blog post was originally published at ScienceRoll*
June 28th, 2011 by American Journal of Neuroradiology in Research
No Comments »

Gray matter (GM) damage, in terms of focal lesions,1 “diffuse” tissue injury, and atrophy is a well-known feature of multiple sclerosis (MS). Recently, T1-hyperintensity on unenhanced T1-weighted sequences has been found in the dentate nuclei of patients with MS with severe disability and high T2 lesion load.2 Such an abnormality has been interpreted as an additional sign of the neurodegenerative processes known to occur in the course of MS. This report describes a patient who, despite being mildly disabled and having a low T2 lesion load and no evident brain atrophy, showed a bilateral dentate nucleus T1 hyperintensity.
The patient was a 44-year-old man who had a diagnosis of relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) in September 1997, after 3 relapses that occurred in June 1995, March 1997, and September 1997. Brain and cord MR imaging and CSF examination were suggestive of MS. After the diagnosis, he started treatment with interferonβ-1α, with clinical stability until January 2009, when he complained of vertigo, which gradually resolved after 5 days of steroidtreatment (methylprednisolone, 1 g daily intravenously). In September 2010, he entered a research protocol and underwent neurologic and neuropsychologic (Rao Brief Repeatable Neuropsychological Battery) evaluations and brain MR imaging on a 3T scanner. The neurologic examination showed Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at AJNR Blog*
June 10th, 2011 by PJSkerrett in Health Tips, News
No Comments »


If the recent announcement by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) that cell phones may cause brain cancer has you worried, you might want to wait a bit before trashing your mobile phone and going back to a land line.
Last week, the IARC convened experts from around the world to assess what, if any, cancer threat cell phones pose to the 5 billion or so people who use them. After reviewing hundreds of studies, the IARC panel concluded that cell phone use may be connected to two types of brain cancer, glioma and acoustic neuroma.
That sounds mighty scary. But the IARC said the evidence for this conclusion was “limited.” Most studies have shown no connection between cell phone use and brain cancer. In the relatively small number of studies that have observed a connection between the two, the positive result could be due to chance, bias, or confounding.
The decision puts cell phones in IARC’s Group 2B category of agents that definitely or might cause cancer. Group 1 are things like asbestos, cigarette smoke, and ultraviolet radiation. Things in Group 2B are “possibly carcinogenic to humans.” Other denizens of this group include coffee, pickled vegetables, bracken ferns, and talcum powder.
I think the IARC decision puts cell phones on notice—a formal “we’ve got our eyes on you” warning—more than it fingers phones as a cause of brain cancer. For one thing, the evidence so far is pretty weak. Writing on the Cancer Research UK Web site, blogger Ed Yong offers a peak at the data through 2009, taken from a review by Swedish researchers. A graph from the paper shows that only one of 28 studies shows a statistically significant association between cell phone use and cancer. We’ll know more about the strength or weakness of the evidence when the panel publishes its report online later this week and in the July 1 issue of The Lancet Oncology.
For now, I’m far more concerned about being rammed by someone talking on his or her cell phone while driving than I am about getting brain cancer from a phone. If you think the IARC report warrants action, the FDA offers suggestions for reducing your exposure to radiofrequency energy from a cell phone, like using the phone less, texting instead of talking, and using speaker mode or a headset to place more distance between your head and the cell phone.
*This blog post was originally published at Harvard Health Blog*
 Obesity is the most significant chronic healthcare crisis facing the United States, as well as other countries. Already 1 out of every 3 adults, and 1 out of every 6 children or adolescents, in the U.S. is obese! Leptin is a hormone that has received considerable attention since its discovery in 1994 for its role in regulating metabolism (like a thermostat, or adipostat) and implications for obesity. High leptin levels are associated with feeling satiated and an active metabolism. Though many overweight people have high levels of circulating leptin, it’s been found that their hypothalamic neurons do not receive the signal – a phenomenon known as “leptin resistance.” An animal model that mirrors this is db/db mice, which lack leptin receptors on the surface of they hypothalamic neurons and are therefore morbidly obese (see image).
Obesity is the most significant chronic healthcare crisis facing the United States, as well as other countries. Already 1 out of every 3 adults, and 1 out of every 6 children or adolescents, in the U.S. is obese! Leptin is a hormone that has received considerable attention since its discovery in 1994 for its role in regulating metabolism (like a thermostat, or adipostat) and implications for obesity. High leptin levels are associated with feeling satiated and an active metabolism. Though many overweight people have high levels of circulating leptin, it’s been found that their hypothalamic neurons do not receive the signal – a phenomenon known as “leptin resistance.” An animal model that mirrors this is db/db mice, which lack leptin receptors on the surface of they hypothalamic neurons and are therefore morbidly obese (see image).



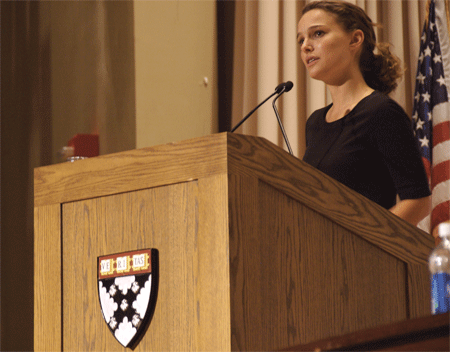 Did you know that
Did you know that 










