April 5th, 2017 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Tips, Opinion
1 Comment »
This blog post first appeared at: Curious Dr. George
 Rehabilitation medicine is one of the best-kept secrets in healthcare. Although the specialty is as old as America’s Civil War, few people are familiar with its history and purpose. Born out of compassion for wounded soldiers in desperate need of societal re-entry and meaningful employment, “physical reconstruction” programs were developed to provide everything from adaptive equipment to family training, labor alternatives and psychological support for veterans.
Rehabilitation medicine is one of the best-kept secrets in healthcare. Although the specialty is as old as America’s Civil War, few people are familiar with its history and purpose. Born out of compassion for wounded soldiers in desperate need of societal re-entry and meaningful employment, “physical reconstruction” programs were developed to provide everything from adaptive equipment to family training, labor alternatives and psychological support for veterans.
Physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) then expanded to meet the needs of those injured in World Wars I & II, followed closely by children disabled by the polio epidemic. In time, people recognized that a broad swath of diseases and traumatic injuries required focused medical and physical therapy to achieve optimal long term function. Today, cancer patients frequently benefit from comprehensive rehabilitation as they recover from the effects of chemo (neuropathy, weakness, and cognitive impairments), radiation (scarring and range of motion limitations), surgery (flaps, plastics procedures, tumor resection, amputations), and brain injuries (edema, debulking, gamma knife and neurosurgery).
Rehabilitation is a phase of recovery occurring after any major life-changing medical or surgical event. Our bodies are designed to regenerate and repair, though optimizing this process takes skilled guidance. PM&R physicians (also known as physiatrists) are trained to use physical modalities (stretching, strengthening, heat, cold, etc.) to mechanically enhance healing. They prescribe medications to manage pain, spasticity, nerve injury, and cognitive impairments, while also leveraging the power of physical therapy to increase cardiopulmonary fitness, muscle strength and flexibility. PM&R physicians are also experts in neurologic injury, and can adapt exercises to coax spinal cord, brain and peripheral nerve injuries to construct new pathways for movement and repair.
Inpatient rehab’s prime directive is to get patients back home. To succeed at home, patients need to be able to function as independently as possible, using trained assistants for managing the activities that cannot be performed without help. Admission to a rehab hospital or unit offers the patient home practice opportunities – with simulated challenges that can include everything from terrain parks, test kitchens, medication management trials, driving simulators, balance tests, electric wheelchairs and even exoskeletons that allow paralyzed patients to walk again. It is like a robotic Disney World, with endless aquatic and equipment possibilities for restoring movement and independence.
When I discuss admission to inpatient rehab with my cancer patients, I ask them about their goals, motivation, and energy levels. Timing of rehab is important, because it must dovetail with treatment, so that the physical exertion strengthens, not saps, the patient. Often times when a person is newly diagnosed with cancer, they want “everything done” – intensive chemo/radiation/surgery as well as rehab/exercise. But staggering these interventions can be more effective.
In other cases when care is palliative, learning new skills and being fitted with battery or electric-powered equipment can mean the difference between living at home or in an assisted environment. Some successful cancer patients come to inpatient rehab to practice managing their activities of daily living with varied amounts of assistance, preparing for increased needs as time goes on so they can enjoy being at home for as long as possible.
For the physiatrist, cancer is a cause of impairments that can be overcome with creativity and practice, no matter the long-term prognosis. Adaptive equipment, physical exercise, and cognitive retraining may be applied intensively (3 hours a day in the inpatient setting), or at a slower outpatient pace, depending on individual need. Rehab physicians desire to support and sustain patient function at the highest level, and “add life to years.” As such, rehabilitation should be considered an integral part of successful cancer care and management.
August 5th, 2015 by Dr. Val Jones in True Stories
No Comments »
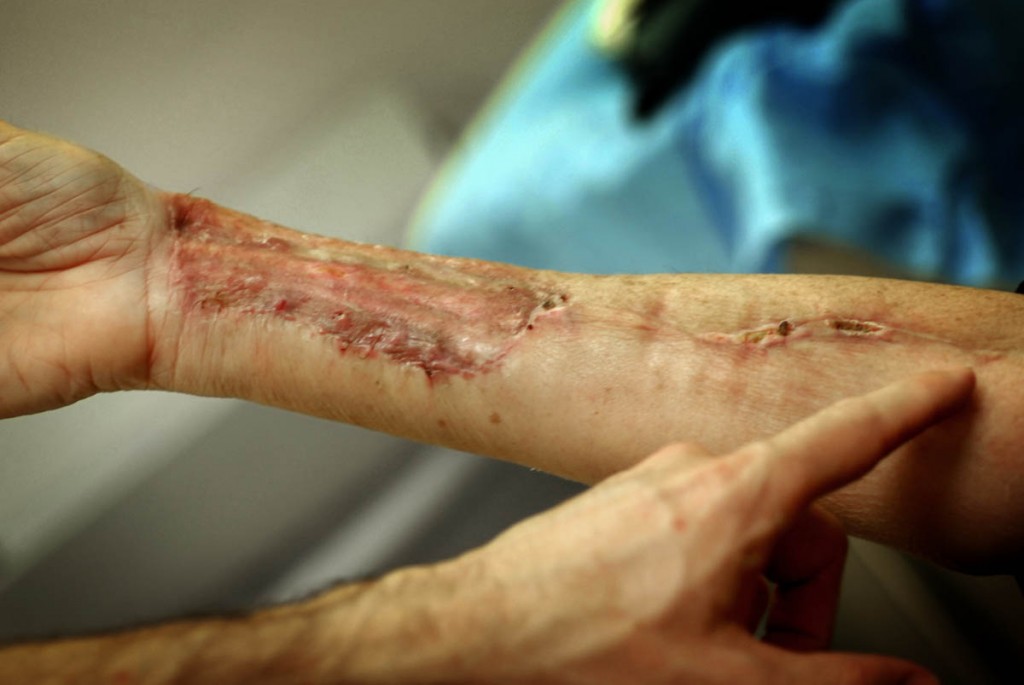
A wrist graft similar to what my friend's husband required.
I watched helplessly as a dear friend went through the emotional meat grinder of a new cancer diagnosis. Her husband was found to have melanoma on a recent skin biopsy, and she knew that this was a dangerous disease. Because she is exceptionally intelligent and diligent, she set out to optimize his outcome with good information and the best care possible. Without much help from me, she located the finest specialists for her husband, and ultimately he received appropriate and state-of-the-art treatment. But along with his excellent care came substantial (and avoidable) emotional turmoil. The art of medicine was abandoned as the science marched on.
First came the pathology report, detailed and nuanced, but largely uninterpretable for the lay person. She received a copy of it at her request, but without any attempt at translation by her physician. In his view, she shouldn’t be looking at it at all, since it was up to him to decide next steps. She brought the report to me, wondering if I could make heads or tails out of it. Although I am not trained in pathology, I did know enough to be able to translate it, line-by-line, into normal speak. This was of great comfort to her as the ambiguity of prognosis (rather than certainty of metastasis and or mortality, etc.) was clearly outlined for the trained eye.
Then came the genetic testing and node biopsy. She was told that the tests could identify variants that would portend poorer outcomes, though it would take 6 weeks to find out if he had “the bad kind of melanoma.” Those 6 weeks were excruciating for her, as she planned out how they would manage financially if he needed treatment for metastatic disease, and if his life were shortened by various numbers of years. At week 6 they received no word from the physician, and so she called the office to inquire about how much longer it would take for the genetic testing to come back. She was rebuffed by office staff and was instructed to be patient because the lab was “processing an unusual number of samples” at this time.
Another week of anguish passed and she decided to contact the lab directly. As it turned out, they were eagerly awaiting the arrival of her husband’s sample, but it had been “lost” in hospital processing somehow. She called the hospital’s facility and someone found the tissue under a pile of other samples and tagged it appropriately and sent it on to the genetics lab. The hospital apologized for the delay via email – and she forwarded the note to her oncologist, so that he could sort out the potential processing bottleneck for other patients going forward.
The result was reported to the oncologist within a week’s time and in turn, the physician called (at 6:30am on a Monday morning) to discuss the result with my friend’s husband. He missed the call as he was in the shower getting ready for work, and wound up playing phone tag with the physician’s office for 3 more days. My friend had her heart in her mouth the entire time. She continued to imagine a world without her husband. If the disease stole him from her, how would she manage? What about the children? Could she make enough money alone to support her family?
“Why didn’t the physician leave any hint of the result in the phone message? If it was good news, surely he would have mentioned that.” She presumed. The physician required his patient to come into the office to discuss the results. And so they booked the next available time slot, another couple of days later. My friend was certain this was a bad sign.
As they arrived at the oncologist’s office, the staff forbade my friend to accompany her husband to the meeting. “Clinic policy” they stated. My friend’s mind was now spinning out of control – maybe my husband needs to be alone with the doctor because the results are so devastating that he must hear it by himself?
She insisted, nonetheless, to accompany him – and the staff felt obligated to clear it with the oncologist before they allowed her to enter the examining room with her husband. They whispered to him in another room before giving her the irritated nod that she could proceed. You could have cut the tension with a knife… she was certain that a death sentence was about to be handed down.
Once the oncologist entered the room, he spent the first 10 minutes making excuses for the delay in genetic tissue results. He argued that the hospital lab was actually not at fault for the delay and listed all the various reasons why nothing had been done incorrectly. His was so single-mindedly focused on the email he received weeks prior (simply describing the delay — as if it were some kind of assault on his own competency) that he almost left the room without telling them the results of the genetic test and biopsy sample.
As an afterthought at the end of the meeting, he announced: “Oh, and the tests suggest that you have a melanoma that is extremely unlikely to metastasize. The wide excisional biopsy is likely curative.”
And off he swished, white coat flowing behind him as he flung wide the door and moved on to the next patient.
The irony is that my friend’s husband got “great” medical care with a large helping of unnecessary suffering. His initial biopsy, wide excision and skin grafting, lymph node testing, and genetic lab studies were all appropriate and helpful in his diagnosis and treatment. But the way in which the information was presented (or not presented) was what made the entire process so painful. Unfortunately, we spend most of our time as physicians focused on the technicalities of what we do, rather than the emotional consequences they have on our patients and their families.
As we continue to “deliver healthcare” to our patients, let’s remember not to serve up any sides of unnecessary mental anguish. Clear and timely communication makes a world of difference in patient anxiety levels. And reducing those is part of the art of medicine that is so desperately needed, and disturbingly rare these days.
November 26th, 2012 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Tips, Opinion, Research
5 Comments »
 A recent mammogram study in the New England Journal of Medicine was so controversial that the authors (Drs. Welch and Bleyer) decided to make a YouTube video to defend and explain their conclusions. Now that’s a first, isn’t it? Well kudos to the study authors for their creative approach to getting ahead of a controversy. However, their video (created for the “general public”) is still a bit too technical in my opinion. I’d like to take a crack at distilling it further.
A recent mammogram study in the New England Journal of Medicine was so controversial that the authors (Drs. Welch and Bleyer) decided to make a YouTube video to defend and explain their conclusions. Now that’s a first, isn’t it? Well kudos to the study authors for their creative approach to getting ahead of a controversy. However, their video (created for the “general public”) is still a bit too technical in my opinion. I’d like to take a crack at distilling it further.
A question on most women’s minds (as they turn 40 and beyond) is whether or not they should get a screening mammogram (x-ray of the breasts). If you have found a lump in your breast or you have a family history of breast cancer the answer is yes. No need to read any further. However, for the majority of us lumpless, family-history-free women, a screening mammogram is far more likely to expose us to unnecessary follow up testing than it is to catch a tumor early. Dr. Welch explains that screening mammograms aren’t very good at identifying aggressive breast cancer early enough to make a difference in whether one lives or dies anyway. That’s very disappointing news.
Dr. Welch goes on to explain that most of the gains we’ve made in breast cancer survival have been because of improved breast cancer treatments, not because of early detection with mammograms. He estimates that every year in the U.S. 1.3 million women are “over-diagnosed” with breast cancer because of screening mammograms, subjecting women to unnecessary biopsies, surgical procedures, and further follow up studies. In the video, Dr. Welch doesn’t explain exactly what these “over diagnosed” cancers end up being exactly (Cysts? Benign calcifications? Early non-aggressive cancers that the immune system kills on its own?) But suffice it to say that they don’t contribute to the cancer death rates.
So, given the fact that you are more likely to suffer through a false alarm than to discover a cancer early (and even if you do find it early, if it’s the “bad” kind you may not survive) are you willing to undergo a screening mammogram? That’s a personal question that we each have to answer for ourselves. As time goes on, however, I suspect that the answer will be made for us since health insurance companies (whether public or private) will begin to balk at paying for tests that do more harm than good overall. I think this issue is really at the heart of the controversy (the perception of rolling back a health benefit that women currently “enjoy”). Eventually screening mammograms may become an out-of-pocket expense for women who simply prefer the peace of mind that a normal test can give – even at the risk of going through a false alarm.
That being said, it sure would be great if we could find a screening test that identifies breast cancer early – especially the aggressive kind. Perhaps a blood test will do the trick one day? At least it is comforting to know that we have made great strides on the treatment side, so that fewer women than ever before die of breast cancer. More research is needed on both the screening and treatment sides of course.
As for me, I do regular breast self exams – though because I have no family history of breast cancer I’ve opted out of screening mammograms because I feel the cost/benefit ratio is not in my favor. I certainly hope that a better screening test is developed before I face a potential diagnosis. I respect that other women will disagree with me – and I think they have the right to be screened with the only option we currently have: the mammogram. I’m not sure how long it will continue to be covered by insurance, but at a price point of about $100, most of us could still afford to pay for it out-of-pocket if desired.
The bottom line of this controversial research study is that screening mammograms don’t actually catch death-causing breast cancers early enough to alter their course. Even though it makes intuitive sense to be screened, long term observations confirm that overall, mammograms do more harm than good. So now we wait for a better test – while some of us continue with the old one (as the National Cancer Institute recommends), and others (like me) don’t bother.
***
Thanks to ePatient Dave and Susannah Fox who brought the issue to my attention on Facebook. Isn’t social media grand?
October 24th, 2012 by admin in Health Tips, Quackery Exposed
No Comments »

Edzard Ernst, M.D., Ph.D.
Cancer patients are understandably desperate to try every treatment that promises a cure. They often turn to the Internet where they find thousands of “alternative” cancer cures being sold often for exorbitant cost. One of them is Ukrain.
Ukrain is based on two natural substances: alkaloids from the Greater Celandine and Thiotepa. It was developed by Dr Wassil Nowicky who allegedly cured his brother’s testicular cancer with his invention. Despite its high cost of about £50 per injection, Ukrain has become popular in the UK and elsewhere.
Ukrain has its name from the fact that the brothers Nowicky originate from the Ukraine, where also much of the research on this drug was conducted. When I say much, I should stress that I use this word in relative terms. In the realm of “alternative” cancer cures, we often find no clinical studies at all. For Ukrain, however, the situation is refreshingly different; there are a number of trials, and the question is, what do they really tell us?
In 2005, we decided to review all the clinical studies which had tested the efficacy of Ukrain. Somewhat to our surprise, we found 7 randomised clinical trials. Even more surprising, we thought, was the fact that all of them reported baffling cure rates. So, were we excited to have identified a cure for even the most incurable cancers? The short answer to this question is NO.
All of the trials were methodologically weak; but, as this is not uncommon in the area of alternative medicine, it did not irritate us all that much. Far more remarkable was the fact that these studies seemed to be odd in several other ways.
Their results seemed too good to be true; all but one trial came from the Ukraine where research governance might have been less than adequate. The authors of the studies seemed to overlap and often included Nowicky himself. They were published in only two different journals of little impact. The only non-Ukrainian trial came from Germany and was not much better: its lead author happened to be the editor of the journal where it was published; more importantly, the paper lacked crucial methodological details, which rendered the findings difficult to interpret, and the trial had a tiny sample size.
Collectively, these circumstances were enough for us to be very cautious. Consequently, we stated that “numerous caveats prevent a positive conclusion”.
Despite our caution, this article became much cited, and cancer centres around the world began to wonder whether they should take Ukrain more seriously; many integrative cancer clinics even started using the drug in their clinical routine. Dr Nowicky, who meanwhile had established his base in Vienna from where he marketed his drug, must have been delighted.
Soon, numerous websites sprang up praising Ukrain: “It is the first medicament in the world that accumulates in the cores of cancer cells very quickly after administration and kills only cancer cells while leaving healthy cells undamaged. Its inventor and patent holder Dr Wassil Nowicky was nominated for the Nobel Prize for this medicament in 2005…” .
Somehow, I doubt this thing with the Nobel Prize. What I do not question for a minute, however, is this press release by the Austrian police: since January, the Viennese police have been investigating Dr Nowicky. During a “major raid” on 4 September 2012, he and his accomplices were arrested under the suspicion of commercial fraud. Nowicky was accused of illegally producing and selling the unlicensed drug Ukrain. The financial damage was estimated to be in the region of 5 million Euros.
I fear, however, that the damage done on desperate cancer patients across the world might be much greater. Generally speaking, “alternative” cancer cures are not just a menace, they are a contradiction in terms: there is no such a thing and there will never be one. If tomorrow this or that alternative remedy shows some promise as a cancer cure, it will be investigated by mainstream oncology with some urgency; and if the findings turn out to be positive, the eventual result would be a new cancer treatment. To assume that oncologists might ignore a promising treatment simply because it originates from the realm of alternative medicine is idiotic and supposes that oncologists are mean bastards who do not care about their patients – and this, of course, is an accusation which one might rather direct towards the irresponsible purveyors of “alternative” cancer cures.
***
Dr. Ernst is a PM&R specialist and the author of 48 books and more than 1000 articles in the peer-reviewed medical literature. His most recent book, Trick or Treatment? Alternative Medicine on Trial is available from amazon. He blogs regularly at EdzardErnst.com and contributes occasionally to this blog.
December 4th, 2011 by Medgadget in Expert Interviews, Research
No Comments »

 Two months ago we reported on the first ovarian cancer surgeries performed with fluorescence guidance. As described in the Nature Medicine paper, the international team of researchers from The Netherlands, Germany, and Indiana used folate coupled to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) to make ovarian cancer cells glow so they could be easily identified.
Two months ago we reported on the first ovarian cancer surgeries performed with fluorescence guidance. As described in the Nature Medicine paper, the international team of researchers from The Netherlands, Germany, and Indiana used folate coupled to fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) to make ovarian cancer cells glow so they could be easily identified.
Now, in this week’s issue of Science Translational Medicine, another international team from Japan and Maryland reports their development of a spray-on probe that may provide even better sensitivity and fluorescent contrast than the folate-FITC counterpart. The editors of STM summarize this work well in the following note: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medgadget*
 Rehabilitation medicine is one of the best-kept secrets in healthcare. Although the specialty is as old as America’s Civil War, few people are familiar with its history and purpose. Born out of compassion for wounded soldiers in desperate need of societal re-entry and meaningful employment, “physical reconstruction” programs were developed to provide everything from adaptive equipment to family training, labor alternatives and psychological support for veterans.
Rehabilitation medicine is one of the best-kept secrets in healthcare. Although the specialty is as old as America’s Civil War, few people are familiar with its history and purpose. Born out of compassion for wounded soldiers in desperate need of societal re-entry and meaningful employment, “physical reconstruction” programs were developed to provide everything from adaptive equipment to family training, labor alternatives and psychological support for veterans.


 A
A 

 Two months ago we
Two months ago we 







