December 25th, 2011 by GarySchwitzer in News, Opinion
No Comments »


©iStockphoto.com/Alexander Raths
Last week, the Cleveland Clinic sent out the following “News Tips”:
“Top 5 Medical Tests for 2012
As we head into 2012, healthy New Year’s resolutions will abound. People will pledge to work out more, eat healthy foods and finally go to see their doctor for a physical.
Cleveland Clinic experts note that there are a few tests that everyone should have during their yearly physical. For men, the following tests are recommended by many physicians:”
Included in the list were: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Health News Review*
December 18th, 2011 by Toni Brayer, M.D. in Health Tips, News
2 Comments »

 Women have been told they should have screening for cervical cancer with a pap test every year. The visit to the gynecologist or internal medicine physician has been a right of passage for most young women and most are very compliant with that annual visit throughout their lives.
Women have been told they should have screening for cervical cancer with a pap test every year. The visit to the gynecologist or internal medicine physician has been a right of passage for most young women and most are very compliant with that annual visit throughout their lives.
Well, the times they are a-changin’ because new guidelines issued by the US Preventative Services Task Force and the American Cancer Society say women should undergo screening NO MORE OFTEN than every 3 years starting at age 21. To further strengthen this recommendation, even the American Society for Clinical Pathology (those folks that read the pap smears) agrees with the recommendation. They also recommend stopping routine pap smears after age 65 for women who have had 3 negative Pap test results in the past 10 years. These women are just not at high risk.
So why the change? Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at EverythingHealth*
December 3rd, 2011 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Opinion, Research
No Comments »

The latest issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine contains 2 noteworthy papers on cervical cancer screening. The first, a systematic review of studies commissioned by the USPSTF, looked at 3 methods for evaluating abnormalities in women over 30 years:
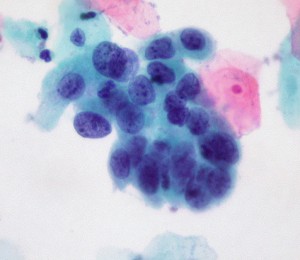
high-grade cervical cell dysplasia (Dr. E. Uthman, Wikimedia Commons)
1. Conventional cytology (as in a Pap smear; the cervix is scraped and cells splayed onto a microscope slide for examination);
2. Liquid-based cytology (for LBC, the NHS explains: the sample is taken as for a Pap test, but the tip of the collection spatula is inserted into fluid rather than applied to slides. The fluid is sent to the path lab for analysis);
3. Testing for high-risk HPV (human papillomavirus). Currently 3 tests have been approved by the FDA in women with atypical cervical cells or for cervical cancer risk assessment in women over the age of 30: Digene Hybrid Capture 2 (manufactured by Quiagen), Cobas 4800 HPV (Roche) and Cervista HR HPV (Hologic); another Roche Diagnostics assay, Amplicor HPV, awaits approval.
These HPV assays use distinct methods to assess DNA of various HPV strains.
There’s a lot of jargon here, and I have to admit some of this was new to me despite my nearly-due diligence as a patient at the gynecologist’s office and my familiarity as an oncologist with the staging, clinical manifestations and treatment of cervical cancer. Who knew so many decisions were made during a routine pelvic exam about which manner of screening? Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
















