September 12th, 2011 by RyanDuBosar in Research
No Comments »


Treating 1,000 people with preventive aspirin for five years prevents 2.9 major cardiovascular events (nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death) and causes 2.8 major bleeds, according to a meta-analysis.
Nine primary prevention trials compared results for aspirin alone for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease, and reported data on myocardial infarction, stroke and cardiovascular deaths. Aspirin doses ranged from 100 mg every other day to 500 mg/d, and seven of them studied doses from 75 mg/d to 162.5 mg/d. No dose-dependent effects were noted, the researchers said. Results appeared in the July issue of the American Heart Journal.
A total of 2,029 major cardiovascular events occurred among 52,145 (3.86%) patients allocated to aspirin compared with 2,099 major cardiovascular events among 50,476 (4.16%) patients assigned to placebo or control. Over a mean follow-up of nearly 7 years, aspirin was Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at ACP Internist*
June 30th, 2011 by Paul Auerbach, M.D. in Health Tips
No Comments »

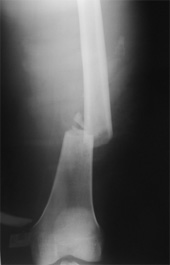 My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
At her age—indeed at any age—a fractured femur is a very significant injury. This past year, I have learned of friends and others who have suffered falls and broken their legs, ankles, or backs, as well as others who suffered “pathological fractures.” The latter group had the bones break from normal daily stresses, without a traumatic incident, because the bones were weak and/or osteoporotic. More than a few of these injuries occurred outdoors, associated with stumbles on the trail or falls.
All of this highlights features of an excellent review article that was published this past year in the New England Journal of Medicine. Authored by Murray Favus, MD, it is entitled “Biphosphonates for Osteoporosis” (New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363:2027-35). Anyone who is contemplating taking or administering this therapy would benefit from reading this article. Read more »
This post, Osteoporosis Treatment With Bisphosphonates: Is Exercise Good Or Dangerous?, was originally published on
Healthine.com by Paul Auerbach, M.D..





 My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.
My 86 year-old mother, who is generally in good health, slipped and fell recently and suffered a fractured femur. She was unfortunate to have suffered the accident, but had the good fortune to be discovered quickly, treated promptly and well by the paramedics who responded to her, and then to have a swift and skillful operation by an orthopedic surgeon to repair the fracture. Almost miraculously, she was standing upright (with a considerable amount of pain) the next day and had begun the rehabilitation process.







