July 25th, 2011 by ChristopherChangMD in Research, Video
No Comments »

Many people are already aware of nebulizer treatments to help with breathing during asthma attacks and other pulmonary conditions.
What many people may not be aware of is that such nebulizer treatments can also potentially be used for chronic sinus infections. One of the best known companies offering such treatment is Sinus Dynamics.
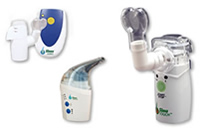 Using one of several different nebulizers, compounded liquid medications (antibiotics and/or steroids) selected by the physician are nebulized/atomized which the patient then breathes into the nasal passages. The small size of the particles allow medication to theoretically move through the tiniest of sinus openings directly onto the infected tissue. Treatments are quick generally lasting 3 – 5 minutes (depending on medication and device). Here’s a video demonstrating how it is used.
Using one of several different nebulizers, compounded liquid medications (antibiotics and/or steroids) selected by the physician are nebulized/atomized which the patient then breathes into the nasal passages. The small size of the particles allow medication to theoretically move through the tiniest of sinus openings directly onto the infected tissue. Treatments are quick generally lasting 3 – 5 minutes (depending on medication and device). Here’s a video demonstrating how it is used.
Sinus Dynamics™ specifically is contracted by over 14,000 insurance companies across the nation, which means that most patients are able to receive their treatment for little to no cost out of pocket.
Most ENT doctors are already familiar with this product.
Personally, I prescribe Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Fauquier ENT Blog*
March 15th, 2011 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Opinion, Research
No Comments »

Lupus, an autoimmune disease, [recently] turned up on the front page of the Wall Street Journal (WSJ). It cropped up, also, on the first page of the New York Times business section, and elsewhere. Scientific American published a nice online review just now. The reason is that the FDA has approved a new monoclonal antibody for treatment of this condition.
The drug belimumab (Benlysta), targets a molecule called BlyS (B-lymphocyte Stimulator). The newspapers uniformly emphasize that this drug marks some sort of triumph for Human Genome Sciences, a biotech company that first reported on BlyS in the journal Science way back in 1999. BlyS triggers B cells to produce antibodies that in patients with lupus tend to bind and destroy their own cells’ needed machinery, causing various joint, lung, liver, kidney, brain, blood vessel and other sometimes life-threatening problems. So if and when Benlysta works, it probably does so by blocking aberrant autoimmune B-cell activity.
The newspapers don’t give a lot of details on the drug’s effectiveness, except that it appears to help roughly one in 11 patients, and the main benefit may be that some lupus patients on Benlysta can reduce their use of steroids, which have long-term and toxic effects on many organs. The most recent major medical publication on a trial on the drug came out in the Lancet two weeks ago.
Some reported caveats are that the drug has not been adequately tested or approved for patients with severe kidney or neurological manifestations of the disease, and that its activity, marginal as it is, appears to be less in patients of African heritage based on trials completed thus far. Additional trials are in the works.
The drug is expensive, to the updated tune of $35,000 per year. According to the WSJ: “Estimates of how many Americans are affected range from 161,000 to 1.5 million.” (How’s that for a wide ballpark figure? Likely a function of how hard it is to define and establish diagnosis for this disease, which anticipates how hard it will be to measure this drug’s effects — see below.) The same WSJ piece says analysts expect the drug to become a blockbuster, with annual sales eventually topping $1 billion. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
January 28th, 2011 by Paul Auerbach, M.D. in Health Tips, Research
No Comments »

 This is a guest post by Dr. Jeremy Windsor.
This is a guest post by Dr. Jeremy Windsor.
**********
Steroids and Acute Mountain Sickness
In recent years, many attempts have been made to identify safe and effective medications to prevent acute mountain sickness (AMS). Acetazolamide (Diamox), currently the “drug of choice” for this purpose, is not perfect and occasionally causes objectionable side effects. Dexamethasone (Decadron), a powerful steroid medication, has become increasingly popular for prevention and treatment in certain circles. While there is ample evidence to suggest that dexamethasone is effective, a recent case report highlights that this drug is not without risk.
In the latest issue of the journal Wilderness & Environmental Medicine [WEM 21(4):345-348, 2010] in an article entitled “Complications of steroid use on Mt. Everest,” Bishnu Subedi and colleagues working for the Himalayan Rescue Association (HRA) described the case of a 27 year-old man who was prescribed a course of three drugs, including dexamethasone, intended to support him during his attempt to climb Mt. Everest. After more than three weeks of taking the medications, the mountaineer noticed the appearance of a rash and decided to stop taking them. Rather than wait for the rash to subside, he chose to continue his acclimatization program and ascend to Camp 3 at 7010m altitude. The patient arrived exhausted and confused; onlookers quickly recognized that something was seriously wrong and so a rescue party was organized to help him back to safety. Read more »
This post, Drug Safety In Preventing Acute Mountain Sickness, was originally published on
Healthine.com by Paul Auerbach, M.D..
August 13th, 2010 by Happy Hospitalist in Better Health Network, Humor
No Comments »

Happy: Ma’am, I noticed you have an allergy to prednisone listed.
Ma’am: Oh, I can never take prednisone again. I’m allergic to it.
Happy: Really? Huh. What happened when you took prednisone?
Ma’am: It made my tongue swell up really bad.
Happy: Huh. What did they give you to reverse the allergic reaction?
Ma’am: Some sort of steroid through my IV.
I’m thinking this qualifies as a raging case of systemic fibromyallergia.
*This blog post was originally published at The Happy Hospitalist*
March 18th, 2010 by StaceyButterfield in Better Health Network, Research
1 Comment »

You might already be aware of this week’s finding if you’ve watched baseball in the past decade or so and noticed that Mark McGwire’s arms are about the circumference of the average ballplayer’s waist in the 70s. But just to be sure, researchers recently compared the BMIs of professional baseball players from 1876 to 2007 to find that, like serving sizes and master bathrooms, they’ve gotten bigger.
Clear, right? But in taking the next step, drawing conclusions from this study, this article from HealthDay gets about as confused as a science article can be. The study authors are concerned because they correlated the ballplayers’ “increased BMIs with an increased risk of death.” (We’re assuming that’s a risk of premature death, since it seems pretty certain that the 1876 team would be dead regardless of their % body fat.)
But a critic of the study argued first that ballplayers’ increasing size is not a health risk, and then that the players might be dying early because they’re using steroids. Um, we’re not scientists, but mightn’t there be a relationship (even a causal one, perhaps?) between steroid use and increased BMI?

*This blog post was originally published at ACP Internist*
 Using one of several different nebulizers, compounded liquid medications (antibiotics and/or steroids) selected by the physician are nebulized/atomized which the patient then breathes into the nasal passages. The small size of the particles allow medication to theoretically move through the tiniest of sinus openings directly onto the infected tissue. Treatments are quick generally lasting 3 – 5 minutes (depending on medication and device). Here’s a video demonstrating how it is used.
Using one of several different nebulizers, compounded liquid medications (antibiotics and/or steroids) selected by the physician are nebulized/atomized which the patient then breathes into the nasal passages. The small size of the particles allow medication to theoretically move through the tiniest of sinus openings directly onto the infected tissue. Treatments are quick generally lasting 3 – 5 minutes (depending on medication and device). Here’s a video demonstrating how it is used.




 This is a guest post by Dr. Jeremy Windsor.
This is a guest post by Dr. Jeremy Windsor.









