December 26th, 2010 by Toni Brayer, M.D. in Better Health Network, Health Tips, News, Research
Tags: Age-Related Macular Degeneration, AMD, Archives of Ophthalmology, Blindness, Diet and Exercise, Dr. Toni Brayer, Everything Health, Eye Conditions, Eye Health, Good Vision, Healthy Diet, Healthy Eyes, Healthy Lifestyle, Loss of Central Vision, Lost Eyesight, Regular Exercise, Vision Impairment
No Comments »

 We now have another condition that may be prevented by eating a healthy diet, exercising, and abstaining from smoking: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
We now have another condition that may be prevented by eating a healthy diet, exercising, and abstaining from smoking: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Macular degeneration causes a loss of central vision and makes it difficult to recognize faces and read small print. The macula degenerates with age and severe macular degeneration causes blindness. Treatment is costly and doesn’t work very well.
A new study published in the Archives of Ophthalmology looked at 1,313 women aged 55 to 74 years. They reviewed their diet and exercise habits. Eating a “healthy diet” meant 3.5 servings of fruit and vegetables, 2.3 servings of dairy, 2.7 ounces of meet and 3.5 servings of grain a day. Exercise habits and smoking history were also monitored. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at EverythingHealth*
December 26th, 2010 by Glenn Laffel, M.D., Ph.D. in Better Health Network, Health Tips, News, Research
Tags: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, Dr. Glenn Laffel, Emily Holmes, Emotional Health, Flashbacks, Health-Related Video Games, Memory, Mental Health, Mental Illness, Oxford University, Pizaazz, PLoS ONE, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Psychiatry and Psychology, PTSD, Tetris, Traumatic Experience, Unwanted Mental Images, Video Games and Health
3 Comments »

 Flashbacks are vivid, recurring, intrusive, and unwanted mental images of a past traumatic experience. They are a sine qua non of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Although drugs and cognitive behavioral interventions are available to treat PTSD, clinicians would prefer to utilize some sort of early intervention to prevent flashbacks from developing in the first place.
Flashbacks are vivid, recurring, intrusive, and unwanted mental images of a past traumatic experience. They are a sine qua non of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Although drugs and cognitive behavioral interventions are available to treat PTSD, clinicians would prefer to utilize some sort of early intervention to prevent flashbacks from developing in the first place.
Well, researchers at Oxford University appear to have found one. Remarkably, all it takes is playing Tetris. Yes, Tetris!
The team responsible for the discovery was led by Emily Holmes. The writeup appears in the November issue of PLoS ONE. Holmes and colleagues had reasoned that the human brain has a limited capacity to process memories, and that memory consolidation following a traumatic experience is typically complete within six hours after the event. Holmes’ team also knew that playing Tetris involved the same kind of mental processing as that involved with flashback formation. So they figured if they had people play Tetris during that six-hour window after the traumatic event, it might interfere with memory consolidation of the traumatic experience. That, in turn, would reduce or eliminate the flashbacks. The idea worked like a charm. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Pizaazz*
December 26th, 2010 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Better Health Network, News, Opinion, Research
Tags: Aging, Being Content With Life, Being Happy, Contentedness, Dr. Elaine Schattner, Economist, Emotional Health, Emotional Well-Being, Getting Old, GNH, Gross National Happiness, Health Economics, Medical Lessons, Old Age, Older Adults, Pete Townshend, Psychiatry and Psychology, Satisfaction In Life, Socioeconomics, The Joy of Growing Old, The Who
No Comments »

This evening, when I finished cleaning up the kitchen after our family dinner, I glanced at the current issue of the Economist. The cover features this headline: the Joy of Growing Old (or why life begins at 46). It’s a light read, as this so-influential magazine goes, but nice to contemplate if you’re, say, 50 years old and wondering about the future.
The article’s thesis is this: Although as people move towards old age they lose things they treasure — vitality, mental sharpness and looks — they also gain what people spend their lives pursuing: Happiness.
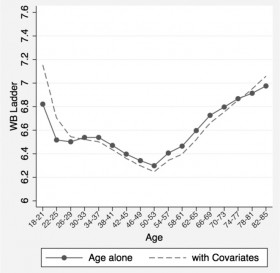
Fig. 1 (above): “A snapshot of the age distribution of psychological well-being in the United States,” Stone, et al: PNAS, May 2010 (y-axis: “WB” stands for well-being.)
Young adults are generally cheerful, according to the Economist’s mysterious author or authors. Things go downhill until midlife, and then they pick up again. There’s a long discussion in the article on possible reasons for the U-shaped curve of self-reported well-being. Most plausible among the explanations offered, which might be kind of sad except that in reality (as opposed to ideals) I think it’s generally a good thing, is the “death of ambition, birth of acceptance.” The concept is explained: “Maybe people come to accept their strengths and weaknesses, give up hoping to become chief executive or have a picture shown in the royal Academy…” And this yields contentedness. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
December 26th, 2010 by JenniferKearneyStrouse in Better Health Network, News, Research
Tags: ACP Internist, American College Of Physicians, Doctor Patient Relationship, Dr. Anthony Lembo, Dr. Ted Kaptchuk, Gastrointestional Medicine, IBS, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Jennifer Kearney Strouse, LA Times, National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Placebo Effect, Placebo Medicine, PLoS ONE
3 Comments »

Placebos helped ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) even when patients knew that was what they were taking, a new study reports.
Researchers randomly assigned 80 patients with IBS to receive placebo pills (openly labeled as such) or no treatment over a three-week period. Patients taking placebos had significantly higher mean scores on the IBS Global Improvement Scale at 11 and 21 days, and also reported significant improvements in symptom severity and relief. The results of the study, which was funded by the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, were published online Dec. 22 by PLoS ONE.
Anthony Lembo, M.D., a study coauthor, said in a press release that he didn’t expect the placebo to work. “I felt awkward asking patients to literally take a placebo. But to my surprise, it seemed to work for many of them,” he said.
Ted Kaptchuk, O.M.D., the study’s lead author, told the LA Times that a larger study needs to be done to confirm the findings, and said that he didn’t believe such effects would be possible “without a positive doctor-patient relationship.”
ACP Internist looked at placebos’ place in clinical practice in a 2009 article. (PLoS ONE, Public Library of Science, LA Times, ACP Internist)
*This blog post was originally published at ACP Internist*
December 24th, 2010 by PeterWehrwein in Better Health Network, Health Tips, News, Research
Tags: Archives of Internal Medicine, Dr. Daniel Solomon, Drug Overdose, Drug Safety, FDA, Food and Drug Administration, Harvard Health Blog, Harvard Health Letter, Harvard Health Publications, Harvard Medical School, Harvard University, Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, NSAIDs, Opioid Analgesics, Opioid Dependence, Opioid Pain Relievers, Opioids, Pain Management, Painkillers, Patient Safety, Peter Wehrwein, Prescription Pain Medication
No Comments »

Perhaps as many as one in every five American adults will get a prescription for a painkiller this year, and many more will buy over-the-counter medicines without a prescription. These drugs can do wonders — getting rid of pain can seem like a miracle — but sometimes there’s a high price to be paid.
Remember the heavily marketed COX-2 inhibitors? Rofecoxib, sold as Vioxx, and valdecoxib, sold as Bextra, were taken off the market in 2004 and 2005, respectively, after studies linked them to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like aspirin, ibuprofen (sold as Advil and Motrin), and naproxen (sold as Aleve) seem like safe bets. But taken over long periods, they have potentially dangerous gastrointestinal side effects, including ulcers and bleeding. Kidney and liver damage are possible, too. More recently, some of the NSAIDs have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Low doses of aspirin (usually defined as 81 mg) is an exception and is often prescribed to lower the risk of heart and stroke.
Even acetaminophen, which is often viewed as the safest pain drug and a low-risk alternative to the NSAIDs because it doesn’t have their gastrointestinal side effects, comes with a caution about high doses possibly causing liver failure. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Harvard Health Blog*
 We now have another condition that may be prevented by eating a healthy diet, exercising, and abstaining from smoking: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
We now have another condition that may be prevented by eating a healthy diet, exercising, and abstaining from smoking: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD).

















