June 23rd, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Announcements, Quackery Exposed
1 Comment »
Comedian John Oliver did an excellent job explaining everything that’s wrong with the Dr. Oz show and the dietary supplement industry. Please watch this video for a good laugh:
I’ve been warning folks about Dr. Oz for many years – and I hope that John reaches more people with his message.
To be fair, there are reputable companies who manufacture safe and effective vitamins and supplements too, as I have noted here.
June 16th, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Policy, Health Tips
No Comments »

Occupational Therapy Environment, Saint Luke's Hospital, WA
For most physicians who practice inpatient medicine, acute inpatient rehabilitation facilities are mysterious places with inscrutable admissions criteria. This is partly because physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) has done the poorest job of public relations of any single medical specialty (Does anyone know what we do?), and also because rehab units have been in the cross hairs of federal funding cuts for decades. The restrictive CMS criteria for inpatient rehabilitation have resulted in contortionist attempts to practice our craft in an environment where clinical judgment has been sidelined by meticulous ICD-9 coding.
But I will not bore you with the reasons behind our seemingly capricious admissions criteria. Instead I will simply tell you what they are in the simplest way possible. After much consideration, I thought it would be easiest to start with the contraindications to acute rehab – I call these “red lights.” If your patients have any of these, then they will not qualify for transfer to the acute inpatient rehab unit. I followed the absolute contraindications with relative contraindications (you guessed it, “yellow lights”) – these patients require some clinical and administrative judgment. And finally, I’ve listed the official green lights – the diagnosis codes and medical necessity rules for the ideal inpatient rehab candidate.
I hope that these rules demystify the process – and can help discharge planners, rehab admissions coordinators, and acute care attending physicians alike help to get the right patients to acute inpatient rehab.
RED LIGHT (Patient does not meet criteria, admission is not currently indicated):
- Inability to Participate: Patient cannot tolerate 3 hours of therapy per day.
- Unwillingness to participate: The patient does not wish to participate in PT/OT/speech therapies and/or shows no evidence of motivation in previous attempts to perform therapy
- Poor rehabilitation potential: The patient’s functional status is currently no different than their usual baseline. (Confirmed by previous history, medical records, or reliable source.)
- Dementia: The patient has a chronic brain deficiency that is not expected to improve and makes carryover of training unlikely or impossible.
- Doesn’t need help from at least 2 different rehab disciplines: The patient must demonstrate likely benefit from working with at least 2 of these: PT, OT, Speech.
- Acute illness or condition: The patient has an acute illness/condition requiring medical intervention prior to transfer to an acute rehab facility – these include:
- septicemia (infection with fever and elevated white count)
- delirium (medication effect, dehydration, infectious, toxic-metabolic)
- unstable vital signs (severe hyper or hypotension, severe tachy or brady arrhythmia, hypoxia despite oxygen supplementation)
- acute psychotic episode (including active hallucinations or delusions)
- uncontrolled pain (the patient’s pain is not sufficiently controlled to allow participation in therapy)
- severe anemia
- extreme fatigue or lethargy due to medical condition
- Procedure or workup pending: The patient is in the middle of a work up for DVT, cardiac disorder, stroke, infection, anemia, chest pain, bleeding, etc. or is about to undergo a procedure (surgery, imaging study, interventional or lab test) that could alter the immediate course of his/her medical/surgical management.
YELLOW LIGHT (The patient may not be a good rehab candidate, clinical/administrative judgment required regarding admission):
- Possible poor rehabilitation potential: The patient’s prior level of function (PLOF) is likely low or similar to current level, however there is no clear documentation of the patient’s PLOF. It is unclear if aggressive rehabilitation will substantially improve the patient’s functional independence.
- Unclear benefit of ARU versus SNF: The patient is unlikely to avoid future placement at a skilled nursing facility. Would it be in the patient’s best interest to transfer there directly?
- Mild dementia or chronic cognitive impairment: The patient has carryover challenges but is able to participate and follow directions. There may be family members who could benefit from PT/OT/Speech training so they can take the patient home and be his/her caregiver(s).
- Unclear safe discharge plan: The patient lives alone or has no family support or has no financial means to improve their living conditions or their home is unfit for living/safe discharge or patient refusing SNF but qualifies otherwise.
- Insurance denial: The patient’s insurer declines their inpatient rehab stay. Physiatrist may attempt to overturn decision or facility may wish to take patient on a pro bono status. Uninsured patients may be candidates for emergency Medicaid. Facility must decide if they will lobby for it.
- Severe behavioral disorders (unrelated to acute TBI): Verbally abusive, violent, inappropriate or disruptive to other patients.
- The patient meets medical necessity criteria for acute inpatient rehab but their impairment is not represented by one of the 13 impairment categories approved by CMS. (E.g. medical debility, cardiac impairment, pulmonary disease, cancers, or orthopedic injury without required comorbidities). Admission may depend upon individual facility’s case mix and its current annual compliance rate with 60% rule.
GREEN LIGHT (The patient is a good candidate for acute inpatient rehab if they have no red or yellow lights, meet criteria for medical necessity AND meet the impairment categories listed below):
MEDICAL NECESSITY DEFINITION:
Acute inpatient rehabilitation services are medically necessary when all of the following are present:
- Individual has a new (acute) medical condition or an acute exacerbation of a chronic condition that has resulted in a significant decrease in functional ability such that they cannot adequately recover in a less intensive setting; AND
- Individual’s overall medical condition and medical needs either identify a risk for medical instability or a requirement for physician and other personnel involvement generally not available outside the hospital inpatient setting; AND
- Individual requires an intensive inter-disciplinary, coordinated rehabilitation program (as defined in the description of service) with a minimum of three (3) hours active participation daily; AND
- Individual is medically stable enough to no longer require the services of a medical/surgical inpatient setting; AND
- The individual is capable of actively participating in a rehabilitation program, as evidenced by a mental status demonstrating responsiveness to verbal, visual, and/or tactile stimuli and ability to follow simple commands. For additional information regarding cognitive status, please refer to the Rancho Los Amigos Cognitive Scale (Appendix B); AND
- Individual’s mental and physical condition prior to the illness or injury indicates there is significant potential for improvement; (See Note below) AND
- Individual is expected to show measurable functional improvement within a maximum of seven (7) to fourteen (14) days (depending on the underlying diagnosis/medical condition) of admission to the inpatient rehabilitation program; AND
- The necessary rehabilitation services will be prescribed by a physician, and require close medical supervision and skilled nursing care with the 24-hour availability of a nurse and physician who are skilled in the area of rehabilitation medicine; AND
- Therapy includes discharge plan.
13 Diagnosis Codes Approved by CMS for Acute Inpatient Rehab
1. Stroke
2. Spinal cord injury
3. Congenital deformity
4. Amputation
5. Major multiple trauma
6. Fracture of femur (hip fracture)
7. Brain injury
8. Neurological disorders, including:
• Multiple sclerosis
• Motor neuron diseases (Guillain Barre, ALS)
• Polyneuropathy
• Muscular dystrophy
• Parkinson’s disease
9. Burns
10. Arthritis: Active polyarticular rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and seronegative arthropathies
resulting in significant functional impairment of ambulation and other activities of daily living;
11. Vasculitis: Systemic vasculidities with joint inflammation resulting in significant functional impairment of ambulation and other activities of daily living
12. Severe or advanced osteoarthritis (osteoarthrosis or degenerative joint disease) involving two or more weight bearing joints (elbow, shoulders, hips, or knees but not counting a joint with a prosthesis) with joint deformity and substantial loss of range of motion, atrophy of muscles surrounding the joint, and significant functional impairment of ambulation and other activities of daily living
13. Knee or hip joint replacement, or both, during an acute care hospitalization immediately preceding the inpatient rehabilitation stay and also meets one or more of the following specific criteria:
- The patient underwent bilateral knee or bilateral hip joint replacement surgery during the acute care hospital admission immediately preceding the IRF admission
- The patient is extremely obese with a Body Mass Index of at least 50 at the time of admission to the IRF or
- The patient is age 85 or older at the time of admission to the IRF.
References:
http://www.anthem.com/medicalpolicies/guidelines/gl_pw_a051177.htm
https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNProducts/downloads/InpatRehabPaymtfctsht09-508.pdf
http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2013-08-06/pdf/2013-18770.pdf
June 3rd, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Policy, Opinion
6 Comments »
 In an effort to promote transparency in healthcare, the Association of Health Care Journalists (AHCJ) has published a database of recent hospital deficiencies discovered by Medicare and Medicaid inspectors. They then highlighted 168 reports containing the phrase “immediate jeopardy.” This, of course, piqued my interest as I presumed that hospitals who were putting putting patients in “immediate jeopardy” must be some pretty bad actors.
In an effort to promote transparency in healthcare, the Association of Health Care Journalists (AHCJ) has published a database of recent hospital deficiencies discovered by Medicare and Medicaid inspectors. They then highlighted 168 reports containing the phrase “immediate jeopardy.” This, of course, piqued my interest as I presumed that hospitals who were putting putting patients in “immediate jeopardy” must be some pretty bad actors.
After sifting through the hospital names, I saw no record of ones who should probably be on the list based on my personal experiences. I did find some surprises, including well respected academic centers (including Stanford, UCSD, and Intermountain Health). I did a “deep dive” on a hospital for which I have a good deal of respect and some familiarity. What I discovered was both funny and sad.
In the case of the hospital that I knew, the very grave concerns expressed by the inspectors turned out to revolve around patient signatures on HIPAA documentation, and physicians refreshing their electronic restraint orders on patients with traumatic brain injuries. These documentation mishaps had landed the hospital on the ominous list of institutions who are “putting patients lives in immediate jeopardy.”
What a waste of inspector time and hospital resources! Apparently, a hospital who passes CMS muster simply means that they are providing documentation correctness to patients. Forget the real sources of life-threatening dangers – medication errors, poor physician handoffs, unnecessary testing and treatment, and unsanitary conditions. What the safety police are focused upon is whether or not the sick and delirious signed their health information privacy paperwork.
Now don’t get me wrong, I think it’s important to let patients know their rights, etc. But I’ve yet to see more than 10% of patients even read the HIPAA-related documentation that they sign. Surely an absent signature or two shouldn’t land a hospital on a humiliating federal watch list.
True patient safety cannot be regulated. It is far too complex and nuanced, requiring collaboration between all members of a hospital’s staff. From frequent nursing surveillance, to careful medication review, to laboratory critical value alerts, to conscientious sanitation practices – hospital culture dictates whether or not a patient receives excellent care. Watch lists would be far more accurate if they were simply based on hospital employee questionnaires. As Dr. Marty Makary has discovered, complicated care quality algorithms are no more accurate at predicting hospital excellence than simply asking staff if they’d recommend the place to family members.
So next time you see your hospital flagged by the feds, don’t assume that there is a serious problem going on – better to ask someone who works there if it’s a safe place for care.
May 29th, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Policy, Opinion
4 Comments »
 In an effort to save on human resources costs, some hospitals have decided to make locum tenens* doctors and nurses line items in a supply list. Next to IV tubing, liquid nutritional supplements and anti-bacterial wipes you’ll find slots for nurses, surgeons, and hospitalist positions. This depressing commoditization of professional staffing is a new trend in healthcare promoted by software companies promising to solve staffing shortages with vendor management systems (VMS). In reality, they are removing the careful provider recruiting process from job matching, causing a “race to the bottom” in care quality. Instead of filling a staff position with the most qualified candidates with a proven track record of excellent bedside manner and evidence-based practice, physicians and nurses with the lowest salary requirements are simply booked for work.
In an effort to save on human resources costs, some hospitals have decided to make locum tenens* doctors and nurses line items in a supply list. Next to IV tubing, liquid nutritional supplements and anti-bacterial wipes you’ll find slots for nurses, surgeons, and hospitalist positions. This depressing commoditization of professional staffing is a new trend in healthcare promoted by software companies promising to solve staffing shortages with vendor management systems (VMS). In reality, they are removing the careful provider recruiting process from job matching, causing a “race to the bottom” in care quality. Instead of filling a staff position with the most qualified candidates with a proven track record of excellent bedside manner and evidence-based practice, physicians and nurses with the lowest salary requirements are simply booked for work.
In a policy environment where quality measures and patient satisfaction ratings are becoming the basis for reimbursement rates, one wonders how VMS software is getting traction. Perhaps desperate times call for desperate measures, and the challenge of filling employment gaps is driving interest in impersonal digital match services? Rural hospitals are desperate to recruit quality candidates, and with a severe physician shortage looming, warm bodies are becoming an acceptable solution to staffing needs.
As distasteful as the thought of computer-matching physicians to hospitals may be, the real problems of VMS systems only become apparent with experience. After discussing user experience with several hospital system employees and reading various blogs and online debates here’s what I discovered:
1. Garbage In, Garbage Out. The people who input physician data (including their certifications, medical malpractice histories, and licensing data) have no incentive to insure accuracy of information. Head hunter agencies are paid when the physicians/nurses they enter into the database are matched to a hospital. To make sure that their providers get first dibs, they may leave out information, misrepresent availability, and in extreme cases, even falsify certification statuses. These errors are often caught during the hospital credentialing process, which results in many hours of wasted time on the part of internal credentialing personnel, and delays in filling the position. In other cases, the errors are not caught during credentialing and legal problems ensue when impaired providers are hired accidentally.
2. Limitation of choice. The non-compete contracts associated with VMS systems typically prevent hospital physician recruiters from contacting staffing agencies directly to fill their needs. This forces the hospital to rely on the database for all staffing leads. At least 68% of staffing agencies do not participate with VMS systems, so a large portion of the most carefully vetted professionals remain outside the VMS, inaccessible to those who contracted to use it.
3. Extra hospital employee training required. There are hundreds of proprietary VMS systems in use. Each one requires specialized training to manage everything from durable medical equipment to short term surgical staff. In cases where hospital staff are spread too thin to master this training, some VMS companies are pleased to provide a “managed service provider” or MSP to outsource the entire recruitment process. This adds additional layers, further removing the hospital recruiter from the physician.
4. Providers hate VMS systems. As anyone who has read a recent nursing blog can attest, VMS systems are universally despised by the potential employees they represent. VMS paints professionals in black and white, without the ability to distinguish quality, personality, or perform careful reference checks. They force down salaries, may rule out candidates based on where they live (travel costs), and provide no opportunity to negotiate salary vis-a-vis work load. When a hospital opts to use a VMS system as a middle man between them and the staffing agencies, the agencies often pass along the cost to the providers by offering them a lower hourly rate.
5. Provider privacy may be compromised. Once a physician or nurse curriculum vitae (CV) is entered into the VMS database the agency recruiter who entered it has 1 year (I can’t confirm that this is true for all systems) to represent them exclusively. After that, the CV is often available for any recruiter who has access to that VMS to view or pitch to any client. There is a wide variety of agency quality in the healthcare staffing industry, with some being highly ethical and selective in choosing their clients (only quality hospitals) and providers (carefully screened). Others are transactional, bottom-feeders with all the scruples of a used car salesman. When your data is in a VMS, one minute you might be represented by a caring, thoughtful recruiter who understands and respects your career needs, and the next (without your informed consent) you’ll be matched to a bankrupt hospital undergoing investigation by the Department of Health by a gum-chewing salesman who threatens you with a lawsuit if you don’t complete an assignment for half the pay you usually receive.
6. No cost savings, only increased liability. In the end, some hospitals who have tried VMS systems say that their decreased hiring costs have not resulted in overall savings. While they may see a downward shift in salary paid to their temporary work force, they get what they pay for. Just one “bad hire” who causes a medical malpractice lawsuit can eat up salary savings for an entire year of VMS. Not to mention the increased costs associated with a slower hiring process, attrition from poor fits, and the inconvenience of having to re-recruit for positions over and over again. Providers also lose out on career opportunities while they’re “on hold” during a prolonged hiring process. And for those who layer on a MSP, they lose control of the most important hospital quality and safety line of defense – choosing your own doctors and nurses.
In summary, while the idea of using a software matching service for recruiting physicians and nurses to hospitals sounds appealing at first, the bottom line is that reducing care providers to a group of numerical fields removes all the critical nuance from the hiring process. VMS, with their burdensome non-competes, cumbersome technology, and lack of quality control are an unwelcome new middle man in the healthcare staffing environment. It is my hope that they will be squeezed out of the business based on their own inability to provide value to a healthcare system that craves and rewards quality and excellence in its staff.
Job matching requires thoughtful hospital recruiters in partnership with ethical, experienced agencies. Choosing one’s hospital gauze vendor should involve a different selection algorithm than hiring a new chief of surgery. It’s time for physician and nurse groups to take a stand against this VMS-inspired commoditization of medicine before its roots sink in too deeply and we all become mere line items on a hospital vendor list. So next time you doctors and nurses plan to work a temporary assignment, ask your recruiter if they use a VMS system. Avoiding those agencies who do may mean a much better (and higher paying) work experience.
*Locum tenens (filling hospital staffing needs with part time or traveling physicians and nurses) is big business. Here is a run down of the estimated market size and its key industry leaders (provided by CompHealth):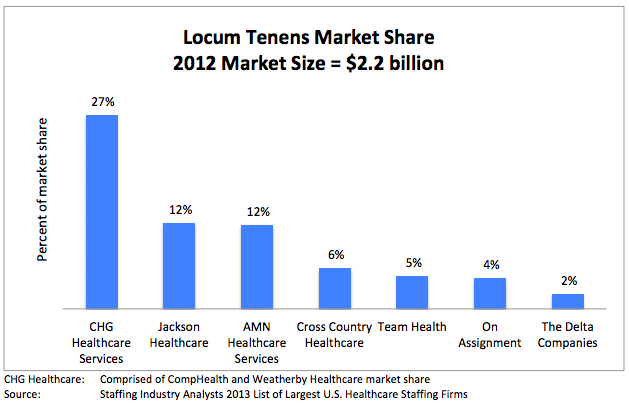
May 5th, 2014 by Dr. Val Jones in Expert Interviews, Health Policy, Opinion
1 Comment »
 It’s no secret that most physicians are unhappy with the way things are going in healthcare. Surveys report high levels of job dissatisfaction, “burn out” and even suicide. In fact, some believe that up to a third of the US physician work force is planning to leave the profession in the next 3 years – an alarming statistic.
It’s no secret that most physicians are unhappy with the way things are going in healthcare. Surveys report high levels of job dissatisfaction, “burn out” and even suicide. In fact, some believe that up to a third of the US physician work force is planning to leave the profession in the next 3 years – an alarming statistic.
Direct primary care practices are touted as the best way to restore patient and provider satisfaction. Those brave enough to cut out the “middle man” (i.e. health insurers, both public and private) find a remarkable reduction in billing paperwork, unrecovered fees, and electronic documentation requirements. I know many physicians who have made the switch and are extremely happy to be able to spend most of their time in direct patient care, unfettered by most rules, regulations, and coding systems. They can solve problems via phone, email, text, video chat, or in-office as the need arises without having to worry about whether or not their manner of interaction will be reimbursed.
Direct primary care is probably the best way to find freedom and happiness in practicing outpatient medicine. But where does that leave physicians who are tied to hospital care due to the nature of their specialty (surgeons, intensivists, anesthesiologists, etc.)? Is there any way for them to find a brighter way forward?
I have found that working as a locum tenens hospital-based physician has dramatically improved my work satisfaction, and it may do so for you too. Here’s why:
1. You can take as much time off as you want, anytime you want. Do not underestimate the power of frequent vacations on your mental health. The frenetic pace of the hospital is much more tolerable in short doses. My attitude, stamina, and ability to stay focused is dramatically improved by working only 2-3 week stretches at a time. When I feel good, I can spread the cheerfulness, and I am happy to spend longer hours at work to give my patients more of my time.
2. You can avoid most political drama. Hospitals are incredibly stressful environments filled with hierarchical and territorial land mines. Being a short-timer allows you to avoid many conflicts. Administrators never nag you, or hold you responsible for perceived departmental deficiencies. You don’t need to attend committee meetings or become involved in personality quirk arbitrage. You can stay above the fray, focusing purely on the patients.
3. You learn all kinds of new things. Exposure to different patient populations, hospital expertise and different peer groups exposes you to a broader swath of technology and humanity. No longer will you be tied to the regional practice idiosyncrasies of a single hospital – you’ll learn how to tackle problems from many different angles. That knowledge earns you respect, and serves to cross-pollinate your own specialty, making you – and those you learn from – better doctors.
4. You are free to leave. There’s something refreshing about knowing that you can leave a place that you don’t like without any repercussions. No matter how unpleasant a locums assignment, it will end, and you can saunter off to brighter pastures.
5. You make more money. Believe it or not, locums work can be quite lucrative if you find the right assignments. I know a team of hospitalists who travel the country together, negotiating higher rates since they are a “one stop” solution. Their housing, travel, and cars are paid for by the agency, and they have take home pay (before taxes) around $350K per year. I personally think that working that many hours as a locum tenens physician kind of defeats the purpose of avoiding burn out, but some people like to do it that way.
6. You can live in the warm states in the winter, and the cold ones in the summer. Enough said.
7. You can try before you buy. Maybe you’re not sure where you want to sink down career roots. Or maybe you’re not sure you’ll like living in a certain city or part of the world? Maybe your family isn’t sure they want to move to a new location? Locum tenens assignments are the perfect way to try before you buy.
8. You can use your experience to become an excellent consultant. With long term exposure to various hospital systems, you are in a unique position to develop an encyclopedic knowledge of best practices. Sharing how other hospitals have solved their challenges can spark reform at other institutions. You can become a real force for positive change, not just on a micro level, but system and state-wide.
Working as a locum tenens physician may enhance your career satisfaction and promote professional advancement. What it will not solve, however, is the following:
1. You still have to work within the framework of bureaucracy endemic to hospitals. You’ll need to learn to use multiple different EMR systems and fill out most of the same paperwork that you do as a full-timer. This is painful at first, but once you’ve mastered the most common EMR systems (I’ve only really encountered 5 different ones in 2 years of locum tenens work) you’ll find a clinical rhythm that fits into most frameworks.
2. You will be living out of a suitcase. If the disruption of frequent travel is too much for you (or your family) to bear, then perhaps the locums lifestyle is not for you.
3. You will be annoyed by the process of getting multiple medical licenses and hospital credentialing. Agencies try to help with this burden, but mostly, you’ll need to suffer through this part yourself.
4. You will have to live with some degree of uncertainty. Part of the nature of working as a locum tenens physician is that clients (hospitals) change their minds frequently. They try to fill open positions with local staff or hire additional full-timers, using locums as their more expensive back ups. Assignments fall through frequently, so you’ll need to be ready to change course quickly.
Overall, I believe that locum tenens work can provide the practice freedom that many hospital-based physicians crave. If you’re eager to get off the unrelenting clinical treadmill, this is an easy way to do it. At a recent assignment near New Hampshire, I mused at the license plates that I passed on my way to work: “Live free or die” is their state motto. And I think it captures my sentiments exactly.



 In an effort to promote transparency in healthcare, the Association of Health Care Journalists (AHCJ) has published a database of recent hospital deficiencies discovered by Medicare and Medicaid inspectors. They then highlighted
In an effort to promote transparency in healthcare, the Association of Health Care Journalists (AHCJ) has published a database of recent hospital deficiencies discovered by Medicare and Medicaid inspectors. They then highlighted  In an effort to save on human resources costs, some hospitals have decided to make locum tenens* doctors and nurses line items in a supply list. Next to IV tubing, liquid nutritional supplements and anti-bacterial wipes you’ll find slots for nurses, surgeons, and hospitalist positions. This depressing commoditization of professional staffing is a new trend in healthcare promoted by software companies promising to solve staffing shortages with vendor management systems (VMS). In reality, they are removing the careful provider recruiting process from job matching, causing a “race to the bottom” in care quality. Instead of filling a staff position with the most qualified candidates with a proven track record of excellent bedside manner and evidence-based practice, physicians and nurses with the lowest salary requirements are simply booked for work.
In an effort to save on human resources costs, some hospitals have decided to make locum tenens* doctors and nurses line items in a supply list. Next to IV tubing, liquid nutritional supplements and anti-bacterial wipes you’ll find slots for nurses, surgeons, and hospitalist positions. This depressing commoditization of professional staffing is a new trend in healthcare promoted by software companies promising to solve staffing shortages with vendor management systems (VMS). In reality, they are removing the careful provider recruiting process from job matching, causing a “race to the bottom” in care quality. Instead of filling a staff position with the most qualified candidates with a proven track record of excellent bedside manner and evidence-based practice, physicians and nurses with the lowest salary requirements are simply booked for work.
 It’s no secret that most
It’s no secret that most 







