June 8th, 2009 by KerriSparling in Better Health Network, Patient Interviews
No Comments »

Even though I do not like the disease, there are some diabetes-related simple pleasures that make me smile:
- I like when I change the battery and the insulin reservoir at the same time. Having my Medtronic 522 “full” on both sides makes me happy.
- I like when the carb count on something is exactly 10 grams of carbs because it matches my insulin to carb ration precisely. One snack, one unit, one oddly happy Kerri.
- I like the sound of the pump counting up a bolus. Boop boop beep!
- I like when the sound of the bolus is caught by Chris and he ends up whistling it back to me, almost without thinking. It’s a little soundtrack snippet of our life.
- I like when the cats wait patiently for me to remove the pump tubing from my body before they lunge for it.
- I like when new boxes of diabetes supplies show up and I can organize them in my little OCD supply closet.
- I like when the number on my meter is two digits, but higher than 89 mg/dl. It’s a tight range, I’m not usually in it, but it brings me weird joy.
- I like when the Dexcom beeps and my coworker (who works a wall away from me) IMs me quietly to check, “Low?” because she’s ready to get juice if necessary.
- I like not having to wear a watch.

- I like when I get to dump all the used test strips that have piled up throughout the day. Knowing I’ve tested a bunch makes me feel like I really stayed tuned in.
- I like the smell of white glucose tabs.
- I like when the new infusion set doesn’t sting at all.
- I like having someone in my life who is willing to get their hands covered in SkinTac in an attempt to stick a Dexcom sensor to random places on my body.
- I like that the hope of the parents of kids with diabetes rubs off on me, and makes me feel good for even just a few minutes.
- I like that diabetes gives two people, who wouldn’t otherwise have a thing to say to one another, a whole dinner’s worth of conversation.
- I like having coworkers who understand but don’t push.
- I like when my best friend clinks her beer to mine and says, “Bolus, baby.”
- I like when the cat licks my hand after I test.
- I like “free shower:” a shower without a pump site or a CGM sensor attached.
- I like having a whole network of people who understand – and do not judge – my diabetes life.
I like when I can focus on the silly, simple things when I feel a little overwhelmed by the tough stuff.
*This blog post was originally published at Six Until Me.*
May 20th, 2009 by Harriet Hall, M.D. in Better Health Network
No Comments »

There is no question that patients on insulin benefit from home monitoring. They need to adjust their insulin dose based on their blood glucose readings to avoid ketoacidosis or insulin shock. But what about patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes, those who are being treated with diet and lifestyle changes or oral medication? Do they benefit from home monitoring? Does it improve their blood glucose levels? Does it make them feel more in control of their disease?
This has been an area of considerable controversy. Various studies have given conflicting results. Those studies have been criticized for various flaws: some were retrospective, non-randomized, not designed to rule out confounding factors, high drop-out rate, subjects already had well-controlled diabetes, etc. A systematic review showed no benefit from monitoring. So a new prospective, randomized, controlled, community based study was designed to help resolve the conflict.
O’Kane et al studied 184 newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes who had never used insulin or had any previous experience with blood glucose monitoring. They were under the age of 70 and recruited from community referrals to hospital outpatient clinics, so they were likely representative of patients commonly seen in practice. They were randomized to monitoring or no monitoring. Patients in the monitoring group were given glucose meters and were instructed in their use and in appropriate responses to high or low readings, such as dietary review or exercise. They were asked to take four fasting and four postprandial readings every week for a year. Patients in the no monitoring group were specifically asked NOT to acquire a glucose monitor or do any kind of self-testing. Otherwise, the two groups were treated alike with diabetes education and an identical treatment algorithm based on HgbA1C levels.
Their findings:
We were unable to identify any significant effect of self monitoring over one year on HbA1c, BMI, use of oral hypoglycaemic drugs, or reported incidence of hypoglycaemia. Furthermore, monitoring was associated with a 6% higher score on the well-being depression subscale.
So home monitoring not only did no good but it made patients feel worse. Why? Perhaps because they were constantly reminded that they had a disease and worried when blood glucose levels rose, especially when the recommended responses of dietary review and exercise didn’t rapidly lead to lower readings.
We would not accept the results of one isolated study without replication, but in this case the new study adds significantly to the weight of previous evidence and arguably tips the balance enough to justify a change in practice.
The American Diabetes Association still says “Experts feel that anyone with diabetes can benefit from checking their blood glucose.” But they only recommend blood glucose checks if you have diabetes and are:
• taking insulin or diabetes pills
• on intensive insulin therapy
• pregnant
• having a hard time controlling your blood glucose levels
• having severe low blood glucose levels or ketones from high blood glucose levels
• having low blood glucose levels without the usual warning signs
Diabetes experts see the severe, complicated cases and have a different perspective from that of the family physician seeing mostly mild and uncomplicated cases. An article in American Family Physician said
Except in patients taking multiple insulin injections, home monitoring of blood glucose levels has questionable utility, especially in relatively well-controlled patients. Its use should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient.
An editorial in the BMJ pointed out that
Home blood glucose monitoring is a big business. The main profit for the manufacturing industry comes from the blood glucose testing strips. Some £90m was spent on testing strips in the United Kingdom in 2001, 40% more than was spent on oral hypoglycaemic agents.2 New types of meters are usually not subject to the same rigorous evaluation of cost effectiveness, compared with existing models, as new pharmaceutical agents are.
If the scientific evidence supporting the role of home blood glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes was subject to the same critical evaluation that is applied to new pharmaceutical agents, then it would perhaps not have been approved for use by patients.
Conclusion
Home glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes is not justified by the evidence. It does not improve outcome, it is expensive, and it may decrease the quality of life of patients.
Common sense suggested monitoring should improve outcome. We had assumed it would work. Scientists thought to question that assumption. They found a way to test that assumption. New evidence showed that it was a false assumption. In response to that evidence, the practice is now being abandoned. This is how science is supposed to work. Another small triumph for science-based medicine.
*This blog post was originally published at Science-Based Medicine*
November 14th, 2008 by Dr. Val Jones in Patient Interviews
3 Comments »
 |
|
Kerri Morrone-Sparling
|
Kerri Morrone-Sparling is a whirlwind of energy. Not only is she the founder of one of the first diabetes blogs on the Internet: SixUntilMe, but she has devoted her career to helping others with diabetes. She works full time at dLife.com, a delightful and practical diabetes website and community. Kerri recently offered me some Halloween survival tips for people with diabetes, and today I had the chance to interview her about her life, her work, and the meaning of World Diabetes Day.
**Listen to the Podcast**
I’ve summarized some of our talking points below for those who don’t wish to listen to the dulcet tones of two very friendly ladies dishing about diabetes.
Dr. Val: Tell me a little bit about your blog.
Kerri: My blog is called SixUntilMe and I started it in May of 2005. I was looking for other people like me who were living with diabetes and since I couldn’t find a community like that I decided to start one myself. As it turns out I wasn’t the only one – there were 2 or 3 other diabetes bloggers out there at the time, and now there are more than 250 of us.
Dr. Val: What does “six until me” mean?
Kerri: My diabetes started when I was six years old – I had a viral illness on my birthday which probably triggered an autoimmune response, causing the disease. My blog is about my diabetes – which started when I was six and is ongoing until now. So I called it “sixuntilme.”
Dr. Val: How are you involved in diabetes advocacy?
Kerri: I work for a diabetes media company, (dLife in Westport, Connecticut) so my entire day is built around reaching out to people with diabetes, trying to make a difference in their life, and connecting them with up-to-date health information. Since I grew up without knowing any other kids who had diabetes, this job is like the holy land. I mean, this whole company was built to help people like me.
Dr. Val: What are some of the worst diabetes myths and what do you have to say about them?
Kerri: First of all, most people don’t know the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and to make matters worse, they believe that people “give themselves diabetes” by eating too much sugar. So they make it seem like it’s all our fault. Secondly, people often believe that insulin is the cure for diabetes. They don’t realize that a glucose meter, an insulin pump, or a continuous glucose monitor are just technology, not a cure. Sometimes people think there’s no need to donate to diabetes research anymore because these technologies are available. And finally, Halle Berry has promoted a myth that has done a lot of harm to the diabetes community. She claimed that she was able to wean herself off her insulin, and that other type 1 diabetics could do the same if they tried hard enough. Of course, that’s blatantly false.
Dr. Val: What’s your favorite new technology for diabetes management?
Kerri: My continuous glucose monitor (CGM). It doesn’t replace finger stick checks, but it helps you to see the trends in your blood sugar. For example, when you’re about to go to bed and you see that your glucose is 90, the CGM will give you some idea if that’s 90 on its way up, or 90 falling towards hypoglycemia, or 90 holding steady – you can go to bed and not worry about a thing. It’s like swinging on a trapeze only now I have a net.
Dr. Val: How does the machine work?
Kerri: It’s a small device that has a needle in it, and you stick it to a fleshier part of your body. There’s a small wire (introduced through the needle) that continuously samples the sugar level in your interstitial fluid. It’s easy to remove and should be rotated every 3-7 days.
Dr. Val: Is it painful?
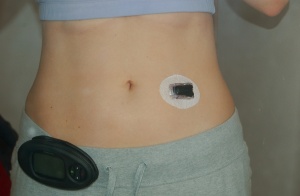
Kerri: No, I don’t think so. I use the Dexcom Seven CGM. Occasionally I feel a little prick when I insert it but then I don’t even notice that I’m wearing it. Here’s a photo of me wearing it:

Dr. Val: Tell me about World Diabetes Day.
Kerri: It’s a global awareness campaign that was started in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation. The United Nations recognized the event for the first time in 2007. It’s a day that directs the world’s attention to diabetes and the epidemic its become and the effort it takes to manage it. On World Diabetes Day bloggers want to spread the word that diabetes is not an invisible disease. It affects lives every day, and it deserves the world’s attention.
Dr. Val: What’s the most important thing for Americans to know about diabetes?
Kerri: They need to know that diabetes is not cured by insulin, and it’s not going away without their help. It’s a very difficult disease to manage. No matter how well you control your sugar levels, the effects of the disease take their toll eventually, and the effects can be devastating. We must not ease up on our research efforts, especially when the numbers of people living with diabetes are growing exponentially.
References
www.diabeticfeed.com
http://the-bad-blog.blogspot.com/
http://www.diabetesdaily.com/johnson/
Kerri writes a column at dLife called Generation D (www.dlife.com/generation_d) and maintains a pretty extensive Flickr account at http://www.flickr.com/photos/sixuntilme/. And lastly, if you’d like to follow Kerri on Twitter, you can find her at www.twitter.com/sixuntilme.
November 11th, 2008 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Tips
5 Comments »
Several people have asked me if corn syrup is the root of all evil. This cheap, high calorie sweetener is adding hidden calories to everything from spaghetti sauce to condiments to peanut butter. But is it actually worse for you than “regular” cane sugar? Is there something special about corn syrup that makes it worthy of national vilification?
The truth is that corn syrup isn’t any “worse” than any other highly refined sugar – there’s nothing special about corn that makes it harmful to consume (unless maybe if you’re allergic to corn, but that’s another story). The real issue is that we humans love sweet things, and that food product manufacturers are simply adding sweetener to their products to cater to our taste buds. In so doing, hidden calories add up… and waist lines expand in response.
Folks with diabetes understand how difficult it is to find unsweetened products these days, and they have to work extra hard to avoid the high fructose corn syrup in so many foods. For those of us who don’t have diabetes (yet?) we’d probably do well to follow their example and consciously cut down on our sugar intake if not to manage our insulin levels, but at least to avoid unnecessary calorie consumption.
I myself am a bit of a sugar addict by nature – I resolved to cut down on carbs a few months ago and have dropped 10 pounds already. I have learned to like unsweetened almond milk, unsweetened organic ketchup, and I make my own sauces and avoid refined flour products.
In my next post I’ll speak with Penny M. Kris-Etherton, Ph.D., R.D., Distinguished Professor of Nutrition, Penn State University about what she learned at the recent American Dietetic Association Food & Nutrition Conference & Expo (FNCE) in Chicago. She’ll explain why all the fear mongering about corn is a bit exaggerated.
October 29th, 2008 by Dr. Val Jones in Health Tips, Medblogger Shout Outs
No Comments »
 My friend and fellow blogger Kerri Morrone Sparling (at the Six Until Me blog) was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes when she was in second grade. The diagnosis came a few short weeks before Halloween, and back then she didn’t realize the risks of sneaking candy bars behind her mom’s back.
My friend and fellow blogger Kerri Morrone Sparling (at the Six Until Me blog) was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes when she was in second grade. The diagnosis came a few short weeks before Halloween, and back then she didn’t realize the risks of sneaking candy bars behind her mom’s back.
Now that Kerri’s grown up, she has some excellent tips for parents of children with type 1 diabetes (or frankly, for anyone who wants to enjoy Halloween and manage their diabetes). You should check out her video blog on the subject here.
Some tips include:
1. Focus on the costume part of the holiday, not the candy part.
2. Make some “candy” corn with Splenda, Equal or a sugar substitute. Enjoy the salty-sweet treat instead of a Snicker’s bar (for example).
3. Work in a small amount of candy into your diet plan. Eat a half a candy bar during a period of high activity, for example, and the sugar spike will not be so bad.
Please check out Kerri’s post for more tips!
***
And for a good laugh about candy, check out The Onion’s headline here.

















