May 4th, 2011 by Medgadget in Health Tips, News
No Comments »

 “Are you a super-spreader?” That’s the catchphrase for a new study out of the University of Cambridge. However, if you answered “yes”, you may want to stay home and cover your mouth, because the study was designed to track the spread of influenza using cellular phone technology.
“Are you a super-spreader?” That’s the catchphrase for a new study out of the University of Cambridge. However, if you answered “yes”, you may want to stay home and cover your mouth, because the study was designed to track the spread of influenza using cellular phone technology.
The study (and accompanying app) is called FluPhone, and it uses cell phones to collect information on social encounters within the study sample of participants in Cambridge. A phone’s Bluetooth antenna detects encounters with other participants and also records the proximity to each other. The built-in GPS chip tracks each user’s location, but this feature was disabled due to recent ethical concerns. Finally, the phone’s 3G/GPRS antenna sends all the proximity data automatically back to researchers for analysis. Other features include the ability to program a specific disease model by introducing a virtual “pathogen” which can be transmitted via Bluetooth when at least two users are near each other.
In addition to revealing useful data about the spread of disease and how to minimize its effects, the study could also be helpful for creating more effective public health messages.
More from the University of Cambridge: FluPhone: disease tracking by app…
Research project page…
FluPhone participant website…
*This blog post was originally published at Medgadget*
February 18th, 2011 by Berci in Better Health Network, Health Tips
No Comments »

As a part of the TheraFlu campaign, Novartis has developed free Android, Blackberry and iPhone applications for tracking flu outbreaks in the U.S. These days it’s become inevitable to develop free apps on all platforms in order to promote your product. From Novartis:
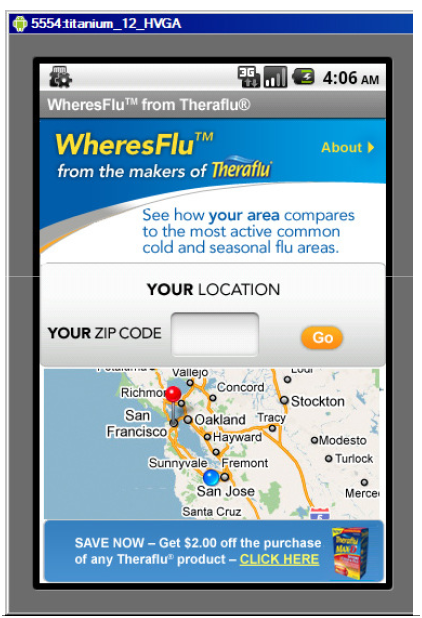 Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
If you’re wondering how it actually works and how it differs from Google Flu Trends, here it is:
WheresFlu™ measures weekly activity for cold and flu based upon real-time reports of symptoms from SDI FAN® (a source used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). As the longest-running respiratory tracking program in the US, SDI FAN® covers illness levels in 135 regions across the country utilizing panel-member reporting along with patient-specific data. Advanced tracking uses illness status levels to predict change in the affected population for the nine US Census Regions.
*This blog post was originally published at ScienceRoll*
January 13th, 2011 by Harriet Hall, M.D. in Book Reviews, Research
No Comments »

 One of our readers suggested that I review the book The Great Influenza: The Epic Story of the Deadliest Plague in History, by John M. Barry. It’s not a new book (it was published in 2004) but it is very pertinent to several of the issues that we have been discussing on this blog, especially in regards to the current anti-vaccine movement. It’s well worth reading for its historical insights, for its illumination of the scientific method, and for its accurate reporting of what science has learned about influenza.
One of our readers suggested that I review the book The Great Influenza: The Epic Story of the Deadliest Plague in History, by John M. Barry. It’s not a new book (it was published in 2004) but it is very pertinent to several of the issues that we have been discussing on this blog, especially in regards to the current anti-vaccine movement. It’s well worth reading for its historical insights, for its illumination of the scientific method, and for its accurate reporting of what science has learned about influenza.
In the great flu epidemic of 1918, influenza killed as many people in 24 weeks as AIDS has killed in 24 years. It’s hard to even imagine what that must have been like, but this book helps us imagine it. It tells horror stories: Children found alone and starving beside the corpses of their parents in homes where all the adults had died, decomposing bodies piling up because there was no one left who was healthy enough to bury them.
Sometimes the disease developed with stunning rapidity: During one three-mile streetcar trip, the conductor, three passengers, and the driver died. In another incident, apparently healthy soldiers were being transferred to a new post by train: During the trip, men started coughing, bleeding, and collapsing; and by the time it arrived at its destination, 25 percent of the soldiers were so sick they had to be taken directly from train to hospital. Two-thirds of them were eventually hospitalized in all, and 10 percent of them died. The mind boggles. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Science-Based Medicine*
October 21st, 2010 by Harriet Hall, M.D. in Better Health Network, Health Policy, Health Tips, News, Opinion, Research, True Stories
No Comments »

Dr. Novella has recently written about this year’s seasonal flu vaccine and Dr. Crislip has reviewed the evidence for flu vaccine efficacy. There’s one little wrinkle that they didn’t address — one that I’m more attuned to because I’m older than they are.
I got my Medicare card last summer, so I am now officially one of the “elderly.” A recent review by Goodwin et al. showed that the antibody response to flu vaccines is significantly lower in the elderly. They called for a more immunogenic vaccine formulation for that age group. My age group. One manufacturer has responded. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Science-Based Medicine*
May 13th, 2010 by Medgadget in Better Health Network, News, Research
No Comments »

 Professor Mark Kendall of the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology and his team have been investigating a novel way to deliver vaccines.
Professor Mark Kendall of the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology and his team have been investigating a novel way to deliver vaccines.
Their method makes use of nanopatches, which are fingernail-sized dermal patches with microscopic projections on their surface that hand vaccine off directly to the antigen-presenting cells just below the surface of the skin.
The scientists’ recent work in mice has shown that an immune response equivalent to that achievable by needle and syringe can be reached using 100 times less vaccine. Not only does the nanopatch appear to be a more effective delivery method, it’s also cheaper to produce and doesn’t require refrigeration, adjuvants or multiple doses. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medgadget*
 “Are you a super-spreader?” That’s the catchphrase for a new study out of the University of Cambridge. However, if you answered “yes”, you may want to stay home and cover your mouth, because the study was designed to track the spread of influenza using cellular phone technology.
“Are you a super-spreader?” That’s the catchphrase for a new study out of the University of Cambridge. However, if you answered “yes”, you may want to stay home and cover your mouth, because the study was designed to track the spread of influenza using cellular phone technology.



 Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.
Keep up-to-date on the most active cold and flu reports around the country. The WheresFlu™ app follows sickness incidence levels from week to week and keeps track of the current top 5 affected cities in the nation. The WheresFlu™ app will find your current location and provide you with results for that area. Or you can enter a ZIP code to get information for that area.

 Professor Mark Kendall of the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology and his team have been investigating a novel way to deliver vaccines.
Professor Mark Kendall of the Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology and his team have been investigating a novel way to deliver vaccines.







