July 22nd, 2011 by Jeffrey Benabio, M.D. in Health Tips
No Comments »


Baby skin is sun-sensitive.
Everyone wishes they had baby skin. It feels so soft and smooth; it’s perfectly adapted to induce us adults to want to clean their diaper, no matter how many times they dirty them. Like their big eyes and cute noses, baby skin is part of the whole package of being adorable. But like their eyes, their skin, however beautiful, is immature. Baby skin is thinner, has less natural moisturizers and has fewer pigment cells, making it more vulnerable to the environment than adult skin.
This is important especially in summer. How often do you see babies running around on the beach with just a diaper on? Although they seem indestructable, they are more vulnerable than the adult holding the pail and shovel.
Studies have shown that up to 83% of babies get sunburned their first year of life. This is our fault, not theirs. Sunburns at an early age can increase the risk for melanoma skin cancer on the trunk later in life. Sun exposure is also a poor way to get vitamin D for infants because most will get far more damaging sun than they need to make vitamin D — we adults tend to over cook them.
Here are five tips to keep your baby safe this summer: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at The Dermatology Blog*
July 1st, 2011 by Dr. Val Jones in Audio, Health Tips
No Comments »
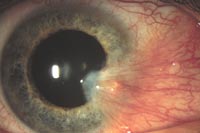
A Pterygium
Dermatologists have done a great job promoting sun safety. We all know that we should use sunscreen or sunblock to avoid burns, and to reapply it religiously when we plan to be outdoors for long periods of time. But how often do we think about protecting our eyes from the same UV rays?
A dear friend of mine has been on a long-term medicine that makes her skin especially sun-sensitive. She did not take sufficient precautions to protect her eyes from UV radiation (though she always wore sunscreen on her skin), and she developed a pterygium that looks just like the photograph above. Her condition reminded me of the importance of eye protection, and I thought I’d offer you 5 excellent reasons to start shielding your eyes from the sun. UV protection is critical for avoiding:
1. Photokeratitis. Photokeratitis is essentially a sunburn of the front layer (cornea) of your eyeball. If you’ve ever had a burning sensation in your eyes after a long day at the beach, or in the snow, you may have burned your eyes. Just as skin sunburns are painful and take a few days to calm down, eye pain can be very uncomfortable. But worse than the temporary discomfort is the increased long-term risks of pterygia, cataracts, and other eye conditions (see below).
2. Pterygia. Pterygia are overgrowths of corneal tissue that can grow across the iris and pupil. They can be cosmetically unsightly, and can block vision if they grow large. They are caused almost exclusively by UV damage, and are most common in people who live near the equator (because their exposure to UV radiation is highest). Surgery is the only known treatment for pterygia, though as many as 50% grow back, and surgical divets in the cornea can cause visual problems.
3. Cataracts. Cataracts are opacities of the eye lenses that lead to partial or total blindness. The exact mechanism by which they occur is unclear, though we know that sun exposure contributes to their development. Cataracts are the number one cause of blindness in the world.
4. Skin Cancers. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a type of skin cancer that primarily develops on skin that has been sunburned, especially in childhood. Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer that is much rarer than BCC, but also most commonly develops on skin that has been burned. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the least invasive type of skin cancer, and usually develops on skin that has had the largest total amount of sun exposure over a lifetime. People who don’t protect the thin eye skin and lids from UV radiation (beginning in childhood) are more likely to develop cancer around the eyes
5. Macular Degeneration. Exposure to the sun’s UV rays can cause damage to the deep structures of the eye, including the retina. Light focused on the macula (the most important part of the retina for vision) can cause damage in the area over time. Macular degeneration results in visual damage and even blindness.
Ok, so I hope I’ve convinced you that UV protection is critically important for your eyes… How can you protect yourself? There are 4 primary strategies:
1. Wear UV protective sunglasses. When buying sunglasses, check out their product labels and avoid glasses that are purely cosmetic – opt for those that block 99-100% of UV A and B rays. Larger glasses and wrap-arounds offer the most coverage. Remember that kids need sunglasses too!
2. Wear a wide-brimmed hat. Although a hat doesn’t always protect you from glare and light reflection from other surfaces, it can reduce the total amount of radiation that reaches your eyes and skin.
3. Wear UV-protective contact lenses. Most people don’t realize that some contact lenses are manufactured with a UV protective layer already built in. Although they are not large enough to protect the entire eye surface (or the skin around the eye) they offer an added layer of protection against harmful UV rays. However, not all contact lenses offer UV protection, and of those that do, not all provide similar absorption levels. An eye care professional can prescribe Class 1 UV-blocking contact lenses, which provide the greatest level of UV protection and which have a Seal of Acceptance for UV Absorbing Contact Lenses from both the American Optometric Association and the World Council of Optometry’s Commissions on Ophthalmic Standards. These lenses block more than 90 percent of UVA rays and 99 percent of UVB rays.
4. Protect your eyes all day. UV radiation for the eyes is actually worse when the sun is lower in the sky. Researchers at the Kanazawa Medical University in Japan found that during early morning and late afternoon, UV exposure to the eyes was about double that of the hours around noon during Spring, Summer and Fall.
For more information about protecting your eyes from the sun, you may enjoy listening to my recent interview with Dr. Stephen Cohen.* He is an optometrist who lives in Arizona – and is therefore well acquainted with UV radiation! Scroll down to the bottom of the page after clicking on the link and you’ll see the podcast.
***
Note that I was paid by Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. to host the radio show with Dr. Cohen.
June 18th, 2011 by Jeffrey Benabio, M.D. in Health Tips
No Comments »


Do you ever wish you didn’t have so many moles? It might be too late for you, but it doesn’t have to be for your kids. By reducing their sun exposure, you can reduce the number of moles (also called nevi) they develop.
Sunburns and excess sun exposure are triggers for moles to develop. Having lots of moles can be unsightly and increases their risk of developing melanoma later in life. Reducing excess sun will limit the number of moles they have and reduce their risk for melanoma many years from now.
Protect against sun to reduce moles.
Many of us grew up without good sunscreens (baby oil and iodine anyone?), but you can do so much more for your children: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at The Dermatology Blog*
May 18th, 2011 by Jeffrey Benabio, M.D. in Health Tips
No Comments »


“I hate needles.” Patients say this to me everyday. When you think about it, who “likes” needles?
Skin biopsies are relatively painless, but they still involve the dreaded needle and always leave scars. The trouble is we dermatologists cannot guarantee that a mole isn’t skin cancer without sending a biopsy for pathology. That is, until now.
Although it is not available in clinic yet, an almost incredible new innovation might allow us to determine if a mole is cancerous by testing the DNA of the mole. It sounds like it’s from an episode of CSI, but it’s real.
Melanomas have DNA (messager-RNA to be exact, but it’s a little complicated) that differentiate them from normal moles, so testing the mole for melanoma requires only a tiny sample of skin. Fortunately, no needles are needed — in fact, no sharp objects are necessary at all. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at The Dermatology Blog*
April 13th, 2011 by AndrewSchorr in Opinion, Patient Interviews
No Comments »

How is it that a person with an illness forgets to take their medicine, or refuses to get a treatment, or forgoes important monitoring? I’ve been thinking about that because someone close to me has hit that “medical fatigue” wall. There has been no effective treatment for their digestive system illness and they are tired of the prods, pokes, and special exams. They just want to live their life and “cope.”
One can understand – especially in a child or teenager. Imagine someone with diabetes. Diet, exercise, monitoring, medication. It can be so tiring. If only the illness – the boogieman or what some call “the beast” could just go away!
But it can’t and it doesn’t. And medical treatments may well be imperfect. They probably are. So do you give up? There is no “right answer,” only a right answer for you. Here are some examples: This week I am interviewing Kathy Sparks of suburban Seattle. Kathy is a nurse who was diagnosed with melanoma on her forearm. It was cut out. Then more was cut out. Then it came back. She had chemotherapy with lots of side effects. A remission followed, and then it came back again, this time in her breast. As time passed doctors gave her only months to live. Unwilling to try to fairly toxic chemo again, she spent time making peace with her impending demise. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Andrew's Blog*
















