February 27th, 2011 by Glenn Laffel, M.D., Ph.D. in Better Health Network, Research
No Comments »

Most people know that the U.S. is struggling to contain a surging epidemic of obesity, and that the problem is most acute among African-Americans. Whereas about 27 percent of all adult Americans are obese (defined as having a body mass index of 30 or more), fully 37 percent of African-American adults are obese, and that number jumps to an appalling 42 percent among African-American women.
Over the years, public health officials have provided evidence that socioeconomic and cultural factors drive this racial disparity. Now, a new study suggests there is another reason as well: Obese African-Americans receive less obesity-related counseling than their white counterparts, and it matters not whether the physicians they see are African-American or white.
To reach these conclusions, Sara Bleich and colleagues from the Johns Hopkins School of Public Health used clinical encounter data from the 2005–2007 National Ambulatory Medical Care Surveys (NAMCS). The sample included 2,231 visits involving African-American and white obese people who were at least 20 years old and who visited family practitioners and internists that were either African-American or white. Asian and Hispanic patients and physicians were excluded from the study because their numbers were too small to permit hypothesis testing.
For each encounter in the study, the scientists determined whether the patient received guidance on weight reduction, diet and nutrition, or exercise from his or her physician. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Pizaazz*
December 26th, 2010 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Better Health Network, News, Opinion, Research
No Comments »

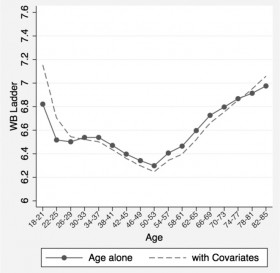
This evening, when I finished cleaning up the kitchen after our family dinner, I glanced at the current issue of the Economist. The cover features this headline: the Joy of Growing Old (or why life begins at 46). It’s a light read, as this so-influential magazine goes, but nice to contemplate if you’re, say, 50 years old and wondering about the future.
The article’s thesis is this: Although as people move towards old age they lose things they treasure — vitality, mental sharpness and looks — they also gain what people spend their lives pursuing: Happiness.
Fig. 1 (above): “A snapshot of the age distribution of psychological well-being in the United States,” Stone, et al: PNAS, May 2010 (y-axis: “WB” stands for well-being.)
Young adults are generally cheerful, according to the Economist’s mysterious author or authors. Things go downhill until midlife, and then they pick up again. There’s a long discussion in the article on possible reasons for the U-shaped curve of self-reported well-being. Most plausible among the explanations offered, which might be kind of sad except that in reality (as opposed to ideals) I think it’s generally a good thing, is the “death of ambition, birth of acceptance.” The concept is explained: “Maybe people come to accept their strengths and weaknesses, give up hoping to become chief executive or have a picture shown in the royal Academy…” And this yields contentedness. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
November 2nd, 2010 by Jennifer Shine Dyer, M.D. in Better Health Network, Health Policy, Opinion, Quackery Exposed, Research
No Comments »
I recently read an article by Heather MacDonald entitled “Public Health Quackery” that has not left my thoughts since. The truth in regards to what determines health is being argued in the article.
At the heart of the article, MacDonald seeks to contrast the traditional science approach with the miasmatician approach to the fundamental question of the role of individual behaviors vs. socioeconomics on the determinants of health. MacDonald summarizes the miasmaticians’ beliefs of health determinants as being exclusively influenced by socioeconomics thereby dismissing any and all influences on health by individual behaviors.
Her primary argument in favor of the traditional science belief in individual behaviors as determinants of health is as follows: Traditional science bases assumptions of truth on data that is valid by scientific standards vs. miasmaticians’ assumptions of truth from biased, “flimsy” data. In other words, “quacky” ideas come from “quacky” data thus are not likely to be true. Read more »
October 12th, 2010 by Jennifer Shine Dyer, M.D. in Better Health Network, Health Policy, Opinion, True Stories
No Comments »
A common question that I get as a practicing physician with a public health background is: “Why is healthcare reform so complicated?” I feel that the question of who’s responsible for healthcare payment is not always an easy one to answer. An example from my most recent weekend on call covering an academic pediatric endocrinology practice demonstrates this point:
“Bill” is a 16-year-old African American male on state Medicaid insurance with type 1 diabetes since the age of 10. He is followed regularly every three months by another colleague in the endocrinology clinic. Review of his last several clinic notes on the electronic medical record reveal that he has been in moderate control of his diabetes on NPH/Novolog twice-daily insulin regimen. Approximately one year prior he was changed to this insulin regimen due to concerns with missed insulin shots on another insulin regimen that provided superior control but which required four shots of insulin daily rather than the two shots daily on his current regimen. Read more »
August 7th, 2010 by KevinMD in Better Health Network, News, Opinion, Research
No Comments »

A recent study from the Annals of Internal Medicine found that doctors often discounted a patient’s social situation when making a medical diagnosis.
Lead researcher Saul Weiner “arranged to send actors playing patients into physicians’ offices and discovered that errors occurred in 78 percent of cases when socioeconomic concerns were a significant factor.”
Evan Falchuk, commenting on the results, provides some context:
It’s hard to expect even the most gifted clinician, trying to make it through yet another week of a hundred or more patient encounters, to get these difficult decisions right. Too much of the context of a patient’s care gets lost in the endless churn of patient visits that the health care system imposes on doctors.I suspect this is enormously frustrating for doctors, although it’s worse for patients. What the researchers call a failure to “individualize care,” a patient might call “not being paid attention to.” It’s a dynamic that anyone who’s been ill has probably seen firsthand.
These findings are entirely unsurprising. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at KevinMD.com*














