December 3rd, 2011 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Opinion, Research
No Comments »

The latest issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine contains 2 noteworthy papers on cervical cancer screening. The first, a systematic review of studies commissioned by the USPSTF, looked at 3 methods for evaluating abnormalities in women over 30 years:
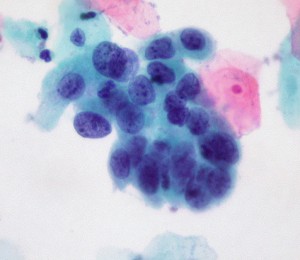
high-grade cervical cell dysplasia (Dr. E. Uthman, Wikimedia Commons)
1. Conventional cytology (as in a Pap smear; the cervix is scraped and cells splayed onto a microscope slide for examination);
2. Liquid-based cytology (for LBC, the NHS explains: the sample is taken as for a Pap test, but the tip of the collection spatula is inserted into fluid rather than applied to slides. The fluid is sent to the path lab for analysis);
3. Testing for high-risk HPV (human papillomavirus). Currently 3 tests have been approved by the FDA in women with atypical cervical cells or for cervical cancer risk assessment in women over the age of 30: Digene Hybrid Capture 2 (manufactured by Quiagen), Cobas 4800 HPV (Roche) and Cervista HR HPV (Hologic); another Roche Diagnostics assay, Amplicor HPV, awaits approval.
These HPV assays use distinct methods to assess DNA of various HPV strains.
There’s a lot of jargon here, and I have to admit some of this was new to me despite my nearly-due diligence as a patient at the gynecologist’s office and my familiarity as an oncologist with the staging, clinical manifestations and treatment of cervical cancer. Who knew so many decisions were made during a routine pelvic exam about which manner of screening? Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
March 24th, 2011 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Research
No Comments »

A recent issue of the New England Journal of Medicine includes an article with the bland title Cytarabine Dose for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. AML is an often-curable form of leukemia characterized by rapidly-growing myeloid white blood cells. Cytarabine — what we’d call “Ara-C” on rounds — has been a mainstay of AML treatment for decades.
The new report* covers a fairly large, multicenter, randomized trial of adult patients with AML. The researchers, based in the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium and Germany, evaluated 860 patients who received either intermediate or high doses of Ara-C in their initial, induction chemotherapy. According to the journal, “this investigator-sponsored study did not involve any pharmaceutical companies.”
The main finding was that at a median follow-up of 5 years there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of complete remission rates, relapses or overall survival. The high-dose Ara-C offered no clear advantage in any prognostic subgroup, including those with genetic changes that bear a poor risk. Not surprisingly, Grade 3 and 4 (severe) toxicities were more common in the patients who received higher doses of Ara-C. Those patients also had lengthier hospitalizations and prolonged reduction in their blood counts.
Why am I mentioning this report, besides that it hasn’t received any press coverage? First, because the findings might matter to people who have AML and are contemplating treatment options. But mainly it’s an example of how carefully dialing down some chemotherapy doses could reduce health care costs and lessen untoward effects of cancer therapy — in terms of early toxicities and, possibly down the line, fewer secondary malignancies – without compromising long-term outcomes.
—
*subscription required: N Engl J Med 364: 1027–36 (2011). The free abstract includes some details on the chemo doses.
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
July 12th, 2010 by GarySchwitzer in Better Health Network, Health Policy, News, Opinion
No Comments »

Kaiser Health News proves its value once again with an under-the-radar story covering some items you won’t see in many other news sources. An excerpt:
“…several lesser-known provisions also take effect in coming months that could have a lasting impact on the nation’s health care system.
These provisions include eliminating patients’ co-payments for certain preventive services such as mammograms, giving the government more power to review health insurers’ premium increases and allowing states to expand Medicaid coverage to low-income adults without children.
While these changes might not have gotten at lot of attention, they could help build support for the law in the run-up to the contentious mid-term elections.”
Their list:
• Prevention For Less
• Knowing Which Treatments Work Best
• Helping Cover Early Retirees’ Health Costs
• Keeping Tabs on Health Insurance Premiums
• Expanded Medicaid Coverage
• Care Coordination for ‘Dual Eligibles’
• FDA Approval For ‘Follow-On Biologics’
Read the full story at the link above for details.
*This blog post was originally published at Gary Schwitzer's HealthNewsReview Blog*













