May 31st, 2009 by Dr. Val Jones in True Stories
6 Comments »
My primary care physician has a cash-only medical practice, and he is paid by the hour for whatever he does – be it a phone call, email, office visit, house call, or outpatient surgical procedure. He doesn’t charge higher prices for procedure complexity – that’s factored into the time it takes to complete the procedure. It’s a wonderful model for those of us who’ve chosen high deductible health insurance plans, and pay cash for primary care services. My husband and I save thousands of dollars/year with our plan, and spend a few hundred of that savings to cover our primary care needs. We also have our family physician available to us 24-7 via phone/email, and can generally see him for an in-person visit within hours of a request for one.
Yesterday was a perfect example of the incredible convenience of this model of care – I called Dr. Dappen at 10:30am and asked if we could come in to have a sebaceous cyst removed from my husband’s back. Dr. Dappen said he’d be happy to see us at 11:30am that day, so we hopped in a car and were finished with the procedure by 12:00. I even had fun taking photos for the blog (see below)…
Cost of the procedure: (surgery plus supplies): $150
Days spent waiting for an appointment: 0
Time spent in a waiting room: 0 minutes
Convenience of having a cash-only family physician: priceless
*For more information, check out: Doctokr Family Medicine, Vienna, Virginia*
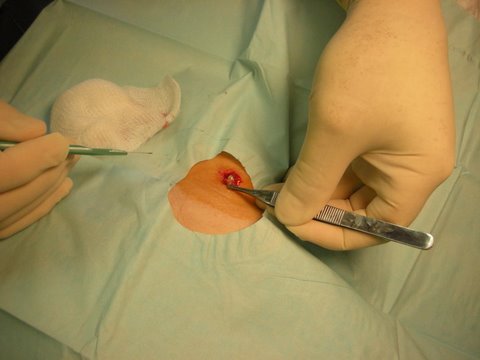
Pearly appearance of small sebaceous cyst
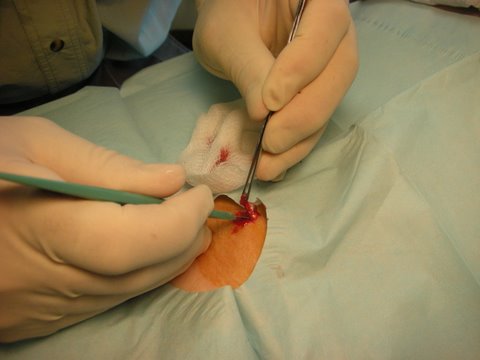
Excision of sebaceous cyst
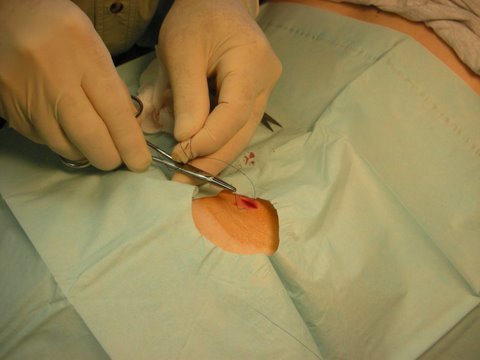
Wound closure with simple sutures
May 30th, 2009 by DrRich in Better Health Network, Opinion
No Comments »

Earlier this year, DrRich offered several potential strategies for doctors and patients to consider, should healthcare reformers ultimately decree it illegal for Americans to seek medical care outside the new universal system. This eventuality (i.e., making it a crime to spend your own money on your own healthcare) may not be as far fetched as one might think at first glance, since in societies where social justice is the ultimate goal, such individual prerogatives must be criminalized.
At that time, DrRich offered several creative solutions to this problem, including offshore, state-of-the-art medical centers on old aircraft carriers, and combination Casino/Hospitals on the sovereign soil of Native American reservations. A reader subsequently offered the possibility of simply establishing institutions something like the “Cleveland Clinic Tijuana,” i.e., cutting-edge medical centers just south of the border. (This solution would have the added advantage of encouraging the government to finally close the borders once and for all, employing whatever means it might take, including military patrols, minefields, and missle-armed drone aircraft.)
As entertaining as it might be to imagine such solutions, a readily available, though much more mundane, solution exists today – medical tourism.
Medical tourism, where one travels outside one’s country in order to obtain medical care elsewhere, is a booming business. A number of superb state-of-the-art medical centers expressly aimed at attracting medical tourists have been established in the Middle East, Singapore, India, China and elsewhere in Asia. These institutions cater to citizens of the world whose own healthcare systems cannot (or will not) provide in a timely fashion (or at all) the level of care patients may desire. They offer modern hospitals, numerous amenities, luxurious accommodations, attentive nursing care, top-notch doctors – and they do it all for a tiny fraction of what the same care might cost (if you can even find it) in the U.S. and other “first world” nations.
Obviously medical tourism is not particularly feasible for medical emergencies such as heart attack or stroke, or for chronic illnesses such as diabetes, congestive heart failure, or Parkinson’s disease, which require frequent visits and long-term management. What is feasible is to become a medical tourist for those one-time medical services that can be scheduled and planned, for which there is a long waiting period at home, or which is simply too expensive in one’s own country. Such medical services often include coronary artery bypass surgery, hip replacements, knee replacements, and numerous minimally-invasive and not-so-minimally-invasive surgical procedures. In other words, medical tourism to a large extent is something one does for elective (i.e., non-emergency) surgery.
It ought not be a surprise, therefore, that the first organization of American physicians to issue a formal policy statement regarding medical tourism is the American College of Surgeons.
The reaction of American surgeons to medical tourism ought to be obvious. They hate it. Elective surgical procedures – the very procedures for which Americans become tourists – are the bread and butter of most surgical specialties. And here go their prospective patients, off to Singapore for their lucrative bypass surgeries. American cardiac surgeons, for instance (already underemployed, thanks to American cardiologists throwing stents at every tiny coronary artery indentation they they can justify as a “blockage”), are nearly apoplectic at the idea.
It’s always fun to read formal policy statements which attempt to deliver an entirely self-serving message whose essence is, “We hate this and if you do it we’ll hate you,” but in which it is necessary to deliver the message in a polite, politically correct, non-judgmental, helpful and even friendly manner.
The surgeons in general have made a good effort, as you can see if you’d like to read the policy statement for yourself. It’s pretty much what you would expect – “Go ahead and have your knee replaced in Timbuktu if you want to. It’s your right, so go ahead and devil take the hindmost. Just don’t come crying to me when things go south a month later.” Only, of course, the surgeons employ the obligatory very polite and professional tone.
DrRich is struck by two aspects of the surgeon’s policy statement on medical tourism.
First, the surgeons begin with a litany of dire warnings regarding all the medical considerations one must take into account before trusting one’s health to foreign medical hands:
“Some of the intangible risks include variability in the training of medical and allied health professionals; differences in the standards to which medical institutions are held; potential difficulties associated with treatment far from family and friends; differences in transparency surrounding patient discussions; the approach to interpretation of test results; the accuracy and completeness of medical records; the lack of support networks, should longer-term care be needed; the lack of opportunity for follow-up care by treating physicians and surgeons; and the exposure to endemic diseases prevalent in certain countries. Language and cultural barriers may impair communication with physicians and other caregivers.”
These are all very important considerations. DrRich notes, however, that these very same considerations (even the warning about endemic diseases, once one allows for the MRSA infections which are secretly “endemic” in some American hospitals) must also be taken into account before agreeing to receive care even in an American institution. It may be that these considerations are more an issue in top-notch foreign hospitals than in your average American hospital, but DrRich is not convinced this is the case, and the surgeons do not provide any evidence that it is. That is, DrRich sees this very good advice as being equally applicable whether one is considering becoming a medical tourist, or just a typical American patient.
Second, and most astoundingly, DrRich notes – not so much with interest, but more with awe – that the surgeons are beseeching their patients to consider just how difficult it might be to launch a malpractice suit against foreign doctors. (DrRich himself does not know how difficult this would be. Given that we are being so strongly urged these days to merge the American legal system with international law, it might not be much of a problem for long.) Indeed, the potential difficulty in suing foreign doctors appears to be the chief differentiator, and the primary argument in favor of good-old-American-surgery. The surgeons, in essence, are saying, “Let us do your surgery, because we’re easier to sue if we screw up.”
This, from the very body of American physicians who are most at risk for malpractice suits, and who traditionally have been most vociferous in favor of malpractice reform.
DrRich can only shake his head in wonderment. If medical tourism is viewed by surgeons as such a dire threat that they are formally embracing medical malpractice suits as their chief weapon against it, then medical tourism must have already caught on far more than most of us realize.
Which means, of course, that when healthcare reform takes place, medical tourism will likely enter a phase of truly explosive growth.
And so, Dear Reader, thanks to this critical clue provided by our friends in the American College of Surgeons, DrRich can confidently offer yet another nugget of investment advice. He formally recommends the medical tourism industry – now in its infancy – as an area ripe for growth.
*This blog post was originally published at The Covert Rationing Blog*
May 29th, 2009 by Nancy Brown, Ph.D. in Better Health Network
No Comments »

The junior year of high school includes a huge number of tests including midterms, finals, AP exams, SAT tests that all contribute to which colleges a teen will get into. The pressure is intense and even the mellowest teen will experience at least some anxiety.
Some stress helps teens do better, work harder, and stay focused. Too much stress will strip them of their confidence and actually make their test-taking skills worse. It is important that parent help teens prepare for tests by:
- Not planning trips or events in the weeks before the tests;
- Encouraging them not to cram the night before;
- Encouraging them to take practice tests to increase their comfort;
- Helping them get a good night sleep the night before the test and eating a healthy breakfast;
- Going early and having what they need (picture ID, admit form, pencils, calculator);
- Reminding them to read through the whole test making notes and then budget time and reading all the directions slowly and completely, as well as organizing their thoughts before writing; and
- Working with them to remember to think positively, calming any anxious thoughts during the test.
No matter how independent our teens can be, testing season calls for extra parenting and comfort provision!
This post, How To Help Teens Handle Test Stress, was originally published on
Healthine.com by Nancy Brown, Ph.D..
May 29th, 2009 by DrWes in Better Health Network
No Comments »
There are some things that Electronic Medical Records do well and there are some things that Electronic Medical Records do poorly. To say that I need Electronic Medical Records to help me type is nothing short of ridiculous. Unfortunately, when engineers meet computer programmers and try to help health care professionals type in the health care record in the name of “safety,” the results can torment those they’re trying to help.
Take auto-spelling, for instance. I have the nasty habit of typing “Lungs: Claer to A&P” and marvel at the auto-correction feature automatically correcting my typing to “Lungs: Clear to A&P.” This is an example of the wonders of electronics.
But when I type “DC Cardioversion” and the computer won’t left me type “DC” because it wants to know if I mean “discharge” or “discontinue,” the computer becomes intrusive, obstructive, and performs a service that should be right up there with water-boarding. I mean, is someone really going to mistaken that I mean “Discontinue cardioversion” or “Discharge cardioversion” when I’m typing my operative report? I could see this being a problem in the order-entry portion of the software, but when I’m typing by progress note or operative note?
Please.
Even better are the wonderfully useful letters “MS.” These might mean “magnesium sulfate,” “mental status,” mitral stenosis, “MS Contin,” “multiple sclerosis,” “musculoskeletal,” “Ms.,” or maybe even “Mississipi.” So, instead of being able to type a logical sentence without interruption, the doctor finds that that a drop-down pick list prevents those magic letters from being typed. It seems the chance that a nurse will wonder if you’re prescribing a drug in a southern state trumps the ability to enter a simple sentence on the computer. This is, after all, how we’re preventing medical errors.
But I wonder if these computer engineering road blocks are doing something much more insidious and detrimental to our health care delivery of tomorrow: like devaluing independent thought, reason, permitting the subtleties of context, and common sense.
No, better to torment instead.
















