December 9th, 2011 by BarbaraFederOstrov in Health Policy, News
Tags: Birth Control, Emergency Contraception, HHS, Kathleen Sebelius, OB/GYN, OTC, Pediatrics, Plan B, Prescription, Reproductive Health, teens
No Comments »
There’s plenty of of analysis, criticism and praise of HHS Secretary Kathleen Sebelius’ controversial decision to prevent the “morning after” contraceptive pill Plan B from being sold over the counter at drugstores and to girls under 17 without a prescription. The top question: how much did election-year politics affect the decision?
President Barack Obama, father of two daughters, defended Sebelius today and said he was not involved in her decision. The New York Times quotes him:
The reason Kathleen made this decision is that she could not be confident that a 10-year-old or an 11-year-old going to a drug store should be able — alongside bubble gum or batteries — be able to buy a medication that potentially, if not used properly, could have an adverse effect.
Here’s a roundup of the national conversation so far:
NPR’s Julie Rovner reports today on the angry reactions from women’s health advocates, who note that Sebelius’ reasoning – that young girls might not use the OTC birth control correctly – sets a double standard for birth control. She quotes former assistant FDA commissioner Susan Wood: Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Reporting on Health - Barbara Feder Ostrov's Health Journalism Blog*
December 9th, 2011 by Dr. Val Jones in News, Patient Interviews
Tags: Apps Against Abuse Technology Challenge, Award, HHS, iTunes, Jill Campbell, Mobile Health, Office Of Science And Technology, OnWatch, Panic Button, Personal Alarm, Safety, Technology, WatchMe 911, Winner, Women's Health
1 Comment »
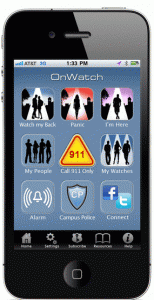 There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the mHealth Summit yesterday. Jill is a 60 year-old woman from Texas who has been actively concerned for the safety of herself and her daughter over the years.
There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the mHealth Summit yesterday. Jill is a 60 year-old woman from Texas who has been actively concerned for the safety of herself and her daughter over the years.
“My daughter took a self-defense class,” Jill explained, “And she was taught the ‘fight or flight’ response to escape harm. I’m 60 years old. I’m not good at fighting and not very fast at fleeing. So what’s my third option?” Jill created the WatchMe 911 app to provide the solution.
“I first started thinking about a personal alarm system before smart phones even existed. I saw that there were car alarms and house alarms, and wondered why there weren’t personal alarms. At the time I imagined that the personal alarm would go through an answering service system, but since smart phones were created, it can all be tied together in an app format.”
Jill demonstrated the WatchMe 911 app to me during our interview. It contains features such as a panic button that can be armed in advance. Two taps on the smart phone screen and a circle of friends and 9-1-1 are contacted immediately with your GPS location and an alert message. The panic button is a favorite for women who are concerned for their safety when walking late at night or in dimly lit parking lots or alleys. Read more »
December 8th, 2011 by RyanDuBosar in News
Tags: Market Share, Nurses, Nursing, Outpatient Medicine, PA, Physician Assistant, Primary Care
No Comments »

The percentage of hospital outpatient department visits seen only by a physician assistant or advanced practice nurse rose from 10% to 15%, while the percentage of joint physician/nonphysician clinician visits remained at about 3%, health researchers found.

Among other findings in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report:
–About three-fourths of the more than 103 million hospital outpatient department visits in 2008-2009 were seen by a physician and 18% were seen by a physician assistant or advanced practice nurse;
–Among visits to a non-physician, 65% were seen by an advanced practice nurse and 35% were seen by a physician assistant;
–The percentage of outpatient department visits attended only by physicians declined from 77% in 2000-2001 to 72% in 2008-2009; and
–The percentage of visits not seen by a physician, physician assistant, or advanced practice nurse remained the same (10%).
Following previous trends, physician assistants or advanced practice nurses are the only provider for visits more often in rural areas, and with younger patients. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at ACP Hospitalist*
December 7th, 2011 by DrRich in Health Policy, News, Opinion, Research
Tags: Cardiac Events, Healthcare Policy, Optimal Levels, Salt Intake, Sodium Restriction
No Comments »

This past summer, DrRich wrote a post on the utter arrogance of the public health experts who are urging the FDA – and international bodies of busybodies – to mandate a policy of strict sodium restriction across the globe.
DrRich attempted to show how such a broad-based salt restriction at this juncture is ill-advised for three reasons. First, the conclusion that a population-wide salt restriction would actually do any good is not based on any actual prospective studies, but on a contrived extrapolation of observational data. Second, there is some evidence that a salt restriction would be harmful to at least a substantial minority of people, even if the overall effect on the population turns out to be positive. And third, there is good reason to believe that the degree of sodium restriction which is being recommended by the public health experts is below the level which is dictated by human physiology.
Perhaps salt restriction for the entire population will turn out to be a good idea. But perhaps not. So in his previous post, DrRich was advocating a prospective, randomized controlled trial to test this proposition before just going ahead and inflicting it upon hundreds of millions of Americans.
And now, as it happens, in recent weeks new studies have been published which question the safety of salt restriction for the whole population. In fact, five studies have been published just this year suggesting that salt restriction might be unsafe.
The latest, published this week in the Journal of the American Medical Association, suggests that when you compare cardiovascular events (such as heart attack and stroke) to sodium intake, the incidence of those events follows a “J” curve. That is, cardiovascular events are lowest at an “optimal” level of sodium intake. But if sodium intake goes above that optimal level – or if it goes below it – the incidence of cardiovascular events increases. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at The Covert Rationing Blog*
December 7th, 2011 by RyanDuBosar in News, Research
Tags: End Of Life, Heart Failure, Longevity, Palliative Care, Patient Communication, Priorities, Quality of Life
1 Comment »

Don’t assume elderly heart failure patients are assumed to prefer improved quality of life over longevity, study authors noted. The majority of them prefer longevity over quality of life, half expressed a desire for resuscitation if needed, and it was difficult to predict individual preferences.
Researchers looked at patients’ willingness to trade survival time for quality-of-life and the preferences for among 622 heart failure patients aged 60 or older participating in the Trial of Intensified vs. Standard Medical Therapy in Elderly Patients with Congestive Heart Failure.
End-of-life preferences were assessed by using a time trade-off tool and one question concerning CPR preference. To assess time trade-off, patients were asked whether they preferred living 2 years in their current state of health or living 1 year in excellent health. If 1 year in excellent health was chosen, the patients were asked whether they would prefer 2 years in their current state of health or 6 months in perfect health. If 2 years in the current state were chosen, then they were asked whether they would prefer 2 years in their current state of health or 18 months in perfect health. The series continued until the choices were the same. This time point subtracted from 24 months derived the number of months of survival time that the patient would be willing to trade.
End-of-life preferences were assessed at baseline, and at 12 and 18 months. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at ACP Hospitalist*



 There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the
There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the 










