September 24th, 2009 by David H. Gorski, M.D., Ph.D. in News, Quackery Exposed
Tags: ANA, Complaints, HIPAA, Jail, Medical Ethics, Nursing, Report, Supplements, Texas Medical Board
3 Comments »
Although I have criticized state medical boards for not doing enough to protect patients from physicians who practice pseudoscientific medicine and quackery, they do nonetheless serve a purpose. Moreover, critical to medical boards doing even the limited amount of enforcement that they do is the ability of health care providers or other citizens to submit anonymous complaints against physicians who are not practicing up to the standard of care or who may be in other ways taking advantage of patients.
Unfortunately, the other day I found out about a very disturbing case in Kermit, Texas. Two nurses who were dismayed and disturbed by a physician peddling all manner of herbal supplements reported him to the authorities. Now, they are facing jail:
In a stunning display of good ol’ boy idiocy and abuse of prosecutorial discretion, two West Texas nurses have been fired from their jobs and indicted with a third-degree felony carrying potential penalties of two-to-ten years’ imprisonment and a maximum fine of $10,000. Why? Because they exercised a basic tenet of the nurse’s Code of Ethics — the duty to advocate for the health and safety of their patients.
The nurses, in their 50s and both members of the American Nurses Association/Texas Nurses Association, reported concerns about a doctor practicing at Winkler County Memorial Hospital in Kermit. They were unamused by his improperly encouraging patients in the hospital emergency department and in the rural health clinic to buy his own herbal “medicines,” and they thought it improper for him to take hospital supplies to perform a procedure at a patient’s home rather than in the hospital. (The doctor did not succeed, as reportedly he was stopped by the hospital chief of staff.)
How can this be? This is how:
The nurses Vicki Galle, RN, and Anne Mitchell, RN, say they were just trying to protect patients when they anonymously reported their concerns April 7 to the Texas Medical Board (TMB). The RNs believed a physician wasn’t living up to ethical practice standards at the 15-bed county hospital where they worked.
The report indicated Rolando Arafiles, MD, one of three physicians on contract with the hospital, improperly encouraged patients at the Winkler County Memorial Hospital emergency department and the county’s rural health clinic to buy herbal supplements from him.
However, because the two nurses worked for a county hospital – and included medical record numbers of the patients in their letter to the TMB in April – the county attorney’s office indicted them on “misuse of official information” – a third-degree felony that carries potential penalties of 2-10 years’ imprisonment and a maximum fine of $10,000. Additionally, the prosecution asserts the nurses used patient records as part of the evidence they offered to the TMB to “harass or annoy” Arafiles.
Part of what’s so disturbing about this is that complaints to the medical board are supposed to be confidential. Indeed, this sort of retaliation is exactly why such complaints are confidential. Why do I say “retaliation”? Well, certainly there is the suspicious timing of how they were arrested:
Mitchell and Galle, both long-time nurses at the facility, were fired from their positions and were subsequently arrested June 12, just 5 days past the 60-day window that could have been part of the defense to prove retaliation. The two nurses are free on bond of $5,000 each.
Gee, you don’t think that timing was intentional, do you? If that’s not enough, take a look at this account:
The nurses went up their chain of command with their complaints. They got nowhere with their 25-bed rural hospital. So they anonymously turned the doctor into the Texas Medical Board using six medical record numbers of the involved hospital patients .
When the medical board notified the physician that he was under investigation for mistreatment and poor quality of care, he filed a harassment complaint with the Winkler County Sheriff’s Department.
To find out who made the anonymous complaint, the sheriff left no stone unturned. He interviewed all of the patients whose medical record case numbers were listed in the report and asked the hospital to identify who would have had access to the patient records in question.
At some point, the sheriff obtained a copy of the anonymous complaint and used the description of a “female over 50″ to narrow the potential complainants to the two nurses. He then got a search warrant to seize their work computers and found a copy of the letter to the medical board on one of them.
So let’s get this straight. Two nurses, alarmed that a physician was inappropriately peddling herbal remedies that he sells to patients in the emergency room of a small rural hospital in the middle of Nowhere, Texas, try to report him through the chain of command. From here on out, I’m going to try to read between the lines a bit, but I bet my speculation is not too far from the truth. My guess is that Dr. Arafiles is probably either popular or desperately needed in Kermit–or both–and that he’s well-connected in the town. Well, actually, that last part is almost certainly true, as apparently Dr. Arafiles is buddies with the Sheriff (Robert Roberts) and–who knows?–probably Winkler County Attorney Scott Tidwell as well for all we know. The Sheriff, tipped off by his buddy that someone at the hospital was complaining about his questionable choice of venue to peddle his herbal woo, went after Mitchell and Galle as though they had gone on a four county shooting spree and and then, after he figured out who they were, threw the book at them, even though they had no justification in doing so:
The Texas Medical Board sent a letter to the attorneys stating that it is improper to criminally prosecute people for raising complaints with the board; that the complaints were confidential and not subject to subpoena; that the board is exempt from federal HIPAA law; and that, on the contrary, the board depends on reporting from health care professionals to carry out its duty of protecting the public from improper practitioners.
Excerpts from this letter include:
- Information provided by an individual to the board… is information used by the Board in its governmental capacity as a state agency…Information provided triggering a complaint or furthering and investigation by the Board is information provided for a governmental purpose – the regulation of the practice of medicine.
- …under federal law, the TMB is exempt from the [HIPAA] requirements; therefore, the provision of medical documentation with patient names on them to the Board is not a violation of [HIPAA].
And it’s true. In order to encourage whistleblowing and minimize the chances of retaliation, HIPAA rules don’t apply to complaints to state medical boards. Regardless of the merit of Mitchell and Galle’s complaint, they were well within their rights to report Dr Arafiles to the Texas Medical Board. It doesn’t matter whether they had first gone through the chain of command or not, regardless of what hospital flunkies or apologists for the sheriff say.
This case is bad. Real bad. Nurses and other health care professionals are reluctant enough as it is to report a bad doctor or a doctor peddling dubious therapies as it is. What makes this case particularly outrageous is not only because it appears to be a horrible abuse of power by Sheriff Roberts, but, even worse, it sends the clear and unmistakable message to nurses in Texas: Don’t get out of line or the medical powers that bewill make you pay. They will find out who you are, no matter what it takes to do so, and then they will do everything in their power to retaliate. They’ll even try to throw you in jail if they can figure out a rationale to do so, legal or not. It’s hard enough to go against a doctor as it is, particularly in small towns, where doctors are often considered pillars of the community, making it hard enough to risk the disapproval that would be likely to be directed at any whistleblower. Without legal protections against prosecution for reporting a doctor to the board, confidentiality means nothing if there is someone in a position of power who is determined enough to shred the confidentiality of the complaint (like a county sheriff) and apparently ready to abuse his power to retaliate against the nurses making the complaints.
Even though I’m a bit late to the game, it disgusted me to read about this case. If we are to protect the public from physician misconduct, be it quackery, breaches of ethics, inappropriate sexual behavior, fraud, or whatever, there must be protections for the complainants against retaliation by hospitals or whomever. Quite correctly, the Texas Nurse’s Association is fully backing Mitchell and Galle, and Mitchell and Galle are also filing a civil lawsuit in federal court against the hospital (Winkler County Memorial Hospital), the county attorney, and the sheriff. The complaint alleges:
Specifically, Winkler County had a policy to prohibit any adverse report without first getting the approval of the Board of Control of Winkler County Memorial Hospital and the Medical Staff. This discouraged employees from publicly reporting matters of public concern regarding patient safety and patients’ health and welfare as to how they were being treated that would cast Winkler County or Winkler County Memorial Hospital or Rolando G. Arafiles, Jr. in a negative light.
This sort of miscarriage of justice should not be allowed to stand. TheTexas Nurses Association has set up a legal defense fund for these nurses (a link is on the TNA home page), and I urger SBM readers to contribute. I have. I also encourage SBM readers to write polite letters of protest to the Winkler County District Attorney’s Office. It is a travesty that this retaliation against nurses just trying to do their duty for their patients has been allowed to continue this long and this far. We should do whatever we can to make sure that this pure power play to put a couple of uppity nurses back in their place does not stand.
September 17th, 2009 by David Kroll, Ph.D. in Better Health Network, Quackery Exposed
Tags: Cancer Center, Evolv, False Advertising, False Claims, Fraud, M.D. Anderson, Misleading, Nutraceuticals, Oncology, Water
No Comments »
 The premier US cancer hospital and research center in Houston released a statement today distancing themselves from a Dallas company claiming an endorsement of their water product by The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center:
The premier US cancer hospital and research center in Houston released a statement today distancing themselves from a Dallas company claiming an endorsement of their water product by The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center:
Recently, you may have heard or read about a company that sells Evolv, a “nutraceutical beverage,” which is being promoted in part based upon testing done at The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, but also is being mistakenly viewed as endorsed by M. D. Anderson. M. D. Anderson conducted limited chemical analysis of the product to evaluate its anti-inflammatory activity for a fee at the request of the manufacturer. No efficacy or toxicity data were generated at M. D. Anderson nor was the product tested on humans. Moreover, M. D. Anderson does not have any involvement with the company, the product is not produced by M. D. Anderson, and M. D. Anderson does not endorse the product or recommend its use.
The current text on Evolv’s website an Evolv fan site is that:
Evolv’s nutraceutical beverage with Archaea Active is tested by M.D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas.
The statement as listed is not exactly wrong; it’s just not complete. Nothing there about what the product was tested for, but the implication is that it gained some healing power by passing through the hallowed halls of M.D. Anderson. I also have no clue as to whether it was tested for archaea (formerly archaebacteria) or if it has the capacity to amplify DNA.
Of course, my blogging about this is going to give the company publicity (a very, very small amount). Evolv is not just water but it is sold by a multi-level marketing company. I already knew to put one hand on my wallet when I dialed up their website. The header has the quote from Mary Kay Ash, “Nothing happens until somebody sells something,” which rotates with others from her and Zig Ziglar who, no doubt, did not authorize their association with the company.
But water? The next multi-level marketing craze?
I don’t think this holds water.
Now if we could only get M.D. Anderson to address this other misuse of their name.
Note added 10 September 2009: This comment from EvolvHealth’s Chief Marketing Officer, Mr Jonathan Gilliam, brought to my attention that I had the incorrect website for the company (as corrected above). The actual website should be http://evolvhealth.com. Currently, their product page lists the M.D. Anderson claim as follows:
Our active ingredient has been tested by the MD Anderson Cancer Center of the University of Texas. Evolv will be released in Fall 2009
*This blog post was originally published at Terra Sigillata*
September 7th, 2009 by Shadowfax in Better Health Network, Quackery Exposed, True Stories
Tags: Complementary And Alternative Medicine, Gerson Protocol, Lymphoma, Oncology, Primary B-Cell Lymphoma
No Comments »
I saw one of the most disturbing things of my career recently — and that is really saying something.
This was a young woman, barely out of her teens, who presented with a tumor in her distal femur, by the knee. This was not a new diagnosis — it had first been noted in January or so, and diagnosed as a Primary B-Cell Lymphoma. By now, the tumor was absolutely huge, and she came to the ER in agonizing pain. Her physical exam was just amazing. The poor thing’s knee (or more precisely, the area just above the knee) was entirely consumed by this massive, hard, immobile mass about the size of a soccer ball. She could not move the knee; it was frozen in a mid-flexed position. She hadn’t been able to walk for months. The lower leg was swollen and red due to blood clots, and the worst of the pain she was having seemed due to compression of the nerves passing behind the knee. It was like something you see out of the third world, or historic medical textbooks. I have never seen its like before.
So we got her pain managed, of course, and I sat down to talk to her and her family.
What I learned was even more amazing. The patient had been seen by the finest oncologists in the region upon diagnosis. They had all recommended the standard treatment of a combined regimen of chemotherapy and radiation. She had, however, steadfastly refused this treatment. She preferred, she said, the “Gerson Protocol.” This is, she continued, “a way for the body to heal itself with a combination of detoxification and boosting the immune system.”
In a less grave situation I might have laughed and asked “So how’s that working for ya?” As it was, the tears from her only partially-controlled pain took any humor out of the situation. She was very frustrated that the Gerson therapy wasn’t working yet, but she did not perceive this as a failure of the treatment. Her theory was that the severity of her uncontrolled pain was keeping her immune system suppressed and preventing it from working. If, she hoped, she could just get her pain under control, she would finally start to get better.
I spent a lot of time with this young lady. Listening as well as explaining. She was dead set against chemo, which to her mind was equated with the “toxins” which had caused her cancer in the first place. She wrote off the oncologists as pushing chemo “because that’s all they know how to do, and it never works.” She had, in fact, burnt all the bridges with the various oncologists who had treated her, and was now left with only a pain specialist and a primary care doctor trying to do what little they could for her. She was equally frustrated by doctors in general, who “won’t do anything to help me.”
I could see why she felt that way; when a patient refuses the only possible effective treatment, there is not really much we can do to help her.
I did what I could. I talked to both her doctors, and I called a new oncologist. The oncologist, a wonderful man, promised to make time to see her in his clinic, even fully forewarned of the “baggage” she would be bringing with her. She was happy to receive the referral, though I warned her that the new oncologist would be recommending more-or-less standard treatments. Ultimately, she went home and I was left to reflect on the futility of the situation and the absolute wickedness of the charlatans and hucksters out there who promote this sort of thinking. From the late Dr Gerson, to his modern-day counterparts Andrew Wakefield and Jenny McCarthy.
Most woo is harmless — but that’s because most woo is directed at chronic, ill-defined, or otherwise incurable conditions. Think chronic fatigue or fibromyalgia. Wave a magnet at somebody, get them to do a lot of enemas and go on a special diet, and you get to write a book and go on Oprah and collect a lot of money. If the subjects of the “magical thinking medicine” think they are better from the intervention, then so much the better.
But the really pernicious thing about allowing fantasy medical theories and treatments into the mainstream is that when they gain enough credence among the masses, they will tend to be used in place of real medical treatments that work. Like vaccines. Even the anti-vaxxers have a limited and indirect harm — of the many thousands of children who go unvaccinated, only a very few get measles and even fewer die. It’s a real harm, but one which is easy to miss if you’re not affected personally. But when woo supplants real medicine against lethal diseases that actually have effective treatments, the harm is so much more severe and so apparent that it cannot be left unrecognized. Because of the practitioners of “alternative” medical treatments who irresponsibly and dishonestly teach people to distrust medicine and embrace unscientific treatments, this young woman is enduring incalculable pain, and may well lose her life.
It’s sad, and it’s an outrage.
*This blog post was originally published at Movin' Meat*
August 27th, 2009 by Kimball Atwood IV, M.D. in Better Health Network, Quackery Exposed
Tags: Complementary And Alternative Medicine, Errors, Misleading, WebMD
No Comments »

Consider this list:
- Sex Matters: tuning in to what turns you on.
- Ticker tune-up tips for guys.
- Manatomy explained.
- Burning down under? It’s time to fess up.
- Pumped Up: ED meds aren’t working? An implant could be the solution.
- When your hoo-ha’s burning, don’t use this common cure!
- Go Om: Meditation can be the healthy answer for type A’s.
- Sexy Seniors: The age-old pleasures and challenges of getting it on.
- Pain: Are your knees at ease?
- Retail Therapy: Four proven ways to battle the call of the mall.
- Detox Diets: The Scary New Skinny
Readers acquainted with popular culture know that such inane, annoying phrases are typical of American women’s magazines. Thus it may be surprising to learn that only three entries were quoted from sources clearly recognizable as such: numbers 3 and 6 from Cosmopolitan, and number 11 from Glamour. The rest were found in WebMD: the Magazine:

The magazine appears to have been introduced in 2005. According to its masthead page,
WebMD’s mission is to provide objective, trustworthy, and timely health information. Our website and magazine provide credible content, tools, and in-depth reference material about health subjects that matter to you. We are committed to providing information on a wide variety of health topics, all of which are reviewed by our board-certified physicians.
Every physician I know receives a “COMPLIMENTARY WAITING ROOM COPY” each month; the 3 or 4 waiting rooms that I’ve perused have been amply stocked. I suspect that most office managers are happy to be provided with free reading material that seems appropriate for patients, and that most physicians haven’t given the magazine more than a passing glance. The problem is that the magazine, like the consumer website of the same name, offers a mixture of accurate-if-mundane information, misleading health claims, exaggerated nutritional advice, unwarranted fear-mongering, and pseudoscientific nonsense. I’ll limit examples and comments to the final four categories.
Misleading Health Claims
In the July/August 2009 issue, which features Jimmy Fallon on the cover, is an article offering five Amazing Facts About Heart Health and Heart Disease. Under ‘fact’ #3 is this assertion:
Health experts now have proof that laughter is good medicine.
The proof?
A good belly laugh can send 20% more blood flowing through your entire body. One study found that when people watched a funny movie, their blood flow increased. That’s why laughter might just be the perfect antidote to stress. When you laugh, the lining of your blood vessel walls relaxes and expands, Krasuski says. So have a good giggle. Your heart will thank you.
Hmmm. I’m willing to believe, even without data, that a good belly laugh can increase cardiac output by 20% (not much compared to, say, exercise or fever). Blood vessel walls (not just the ‘lining’) relax and expand almost continuously, but I’ll grant that such changes are greater during periods of rapid changes in cardiac output than during periods of rest. What doesn’t follow from this is that laughter is an ‘antidote to stress’ (whatever that is); nor, whether it is or isn’t, will ‘your heart’ necessarily ‘thank you’ for laughing.
If your heart is healthy or even moderately diseased, laughing will be of no consequence to it; if it is extremely unhealthy—if you have severe coronary disease with unstable angina, for example, or severe valvular or myocardial (heart muscle) disease such that the slightest increase in demand for blood flow can result in congestive heart failure, laughing might get you into serious trouble. Few people are that fragile, but any magazine that claims to give trustworthy, in-depth health information should make the point.
“Amazing Fact” #3’s main implication, of course, is that laughing ‘might’ reduce your risk of some heart diseases, much as controlling high blood pressure and reducing LDL-cholesterol are known to do, and as regular exercise probably does. The article offers not an iota of credible evidence to support this implication. Nor is there a basis for its implicit corollary, that increasing cardiac output by whatever means is equivalent to the cardiovascular conditioning that occurs with regular exercise.
The article notes, correctly, that the frequency of ‘heart attacks’ is greater in the morning than during the remainder of the 24-hour cycle, but somehow leaps to unrelated and unsupported premises, conclusions and recommendations:
Add in the rise in blood pressure and increased heart rate from the stress of returning to work after the weekend, and you have the perfect recipe for a Monday morning heart attack. That’s why it’s important to reduce your stress levels as much as you can. Practice yoga, meditate, exercise, laugh (see tip No. 3), or spend more quality time with your family — whatever works best for you.
Oh well, at least it throws a bone to poor, sex-starved men:
5. How sex helps the heart
Having an active sex life could cut a man’s risk of dying from heart disease in half. For men, having an orgasm three or four times a week might offer potent protection against a heart attack or stroke, according to one British study.
Whether sex works as well for women’s hearts is unclear, but a healthy love life seems to equate to good overall health. For one thing, sexual activity is an excellent stress buster. It’s also great exercise — burning about 85 calories per half-hour session.
If you find it difficult to have sex, that could be a big red flag that something is wrong with your heart. For example, some researchers think erectile dysfunction might warn of a heart attack up to five years in advance.
A few years ago a friend confided to me that his new girlfriend was convinced of something that he was pretty sure was nonsense, but that he’d no intention of talking her out of: ingesting human semen on a daily basis was good for her health (yup, it’s out there). “Amazing Fact” #5 strikes me as a soft-core version of such a belief. I also wonder how WebMD’s board-certified physicians could stomach the claim that the penis acts as an early-warning system for heart attacks destined to occur five years later. It’s all a bit hard to swallow.
The cover story in the same issue promises to explain “why type A’s (sic) like Fallon tend to get sick on vacation”:
Urban legend, or does the body’s immune system intuitively understand how to sabotage your best-laid plans?
“It seems like we’ve all experienced it,” says Phyllis Kozarsky, MD, travel health expert for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Especially the type A personality, the real go-go-go kind of person who works very hard and takes very few vacations.
“From my 30 years of practice and observing my patients, I think it’s less about a mind-body connection — although I do believe there is one — and more about how stress plays a role in making us sick,” Kozarsky adds. “By the time we are on our so-called ‘break,’ we’re utterly drained and susceptible to catching whatever bug is floating by.”
Ah, but we were never told whether or not it’s an ‘urban legend’ (my guess is that it is). Why offer a theory in search of a phenomenon?
Exaggerated Nutritional Advice
From the June 2009 issue:
Tea Time
One habit you don’t want to bag? Drinking tea. Studies suggest that some teas might help with cancer, heart disease, and diabetes; lower cholesterol; and heighten mental alertness. Tea also appears to have antimicrobial qualities.
Tea is a name given to a lot of brews, but purists consider only green, black, white, oolong, and pu-erh teas the real thing. All are derived from the same plant and contain unique antioxidants called flavenoids. Potential health benefits include:
Green Tea: Its antioxidants could interfere with the growth of bladder, breast, lung, stomach, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers. Green tea might also prevent clogging of the arteries, burn fat, counteract oxidative stress on the brain, reduce risk of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, reduce risk of stroke, and improve cholesterol levels. [etc.]
Phew! But no. Drinking green tea has been associated with reduced mortality due to some of the above but not others, which may or may not have anything to do with the tea: correlation is not causation, whether the topic is tea, orgasms, or anything else. Consumers and board-certified physicians should be wary of panacea claims. After an early period of enthusiasm, trials of antioxidant supplements have been disappointing and worse, in spite of some of the purported benefits having been entirely plausible.
More of the same, from the March/April 2009 issue (pictured above):
[Shallots] also contain flavonoids, a type of antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables that helps protect the body and may reduce the risk of developing cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. (Garlic, leeks, and onions also have great cancer-fighting nutrients, by the way.) Plus, one tablespoon of chopped shallots is high in potassium, vitamin A, and folate.
Groan.
Unwarranted Fear-Mongering
The March/April issue has an article titled “Easy Being Green”:
You don’t need to call in a hazmat team. Try these tips to get rid of the harmful toxins in your home.
What harmful toxins? You’ve probably guessed already:
the products we use every day…cosmetics, antibacterial soaps and cleaners…’plasticizers’ used in plumbing, shower curtains, varnishes, vinyl floors…fragrances.”
Today, a growing group of environmental activists, scientists, and ordinary people is calling attention to the possible real-life risks of the products we swallow, spray, and smear on our bodies every day.
“It’s not in question that many consumer products contain toxins — they do,” says Alan Greene, MD, clinical professor of pediatrics at Stanford University and author of Raising Baby Green: The Earth-Friendly Guide to Pregnancy, Childbirth, and Baby Care. “Most are felt to be in too tiny of a quantity to pose any real risk. But sometimes, very small exposures can have large impacts.”
Spurred by recent research studies, some of which contradict established opinion about what’s safe, environmental advocates now have some of the most commonly used consumer products on their watch lists.
“The irony is, these products’ presumed safety has led them to be produced and consumed almost indiscriminately,” says Rebecca Sutton, PhD, senior scientist with the nonprofit Environmental Working Group. “We’re now all exposed to multiple chemicals on a continuous basis whose long-term health effects aren’t known.”
Certain personal care products have become so popular, they’re literally in our blood. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) now monitors the levels of ingredients from cosmetics and other products in the bloodstream of random Americans, to help guide public health discussions.
Sigh. Don’t get me wrong: I favor elucidating and dealing with real environmental hazards as much as anyone else. What I’m against is the argument from ignorance (also called the “negative proof fallacy”) explicit or implicit in ‘toxin’ hysteria: that since we don’t know that ubiquitous substances that are clearly toxic at certain concentrations are not also toxic at vastly lower ones (perhaps in very subtle or even undetectable ways!), we ought to assume that they are. No: we ought, unless real evidence suggests otherwise, assume that they are not.
The reasons are several, beginning with the obvious problem of all arguments from ignorance: there is no basis for not being afraid of, well, almost everything. Where should people who are trying to live their lives draw the line? ‘Certain personal care products’ have literally been in our blood ever since we started using ‘personal care products’ back in Bedrock. Do WebMD’s board-certified physicians really think that this is a recent phenomenon? Speaking of, an editorial in a real journal notes that asbestos is a naturally occurring substance found in rocks all over the world:
…studies indicate that everyone is exposed to background levels of asbestos in the ambient air. Studies have shown that members of the general (non-occupationally exposed) population have tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of asbestos fibers in each gram of dry lung tissue, which translates into millions of fibers and tens of thousands of asbestos bodies in every person’s lungs. However, the general population does not have an increased risk of asbestos-related lung cancers despite these background levels.
What are these “small exposures that can have large impacts”? Why haven’t I heard of them? Why didn’t the WebMD reviewers insist that they be explained?
A modicum of knowledge and a bit of common sense go a long way here. Famous examples of proven harms from environmental toxins have been distinguished by their clarity: both the sources of exposure and the outcomes have, typically, been discrete and specific to the toxin. The exposures have been substantial, not merely casual. Think: cigarette smoking and lung cancer; asbestos workers and mesothelioma; coal-mining and black-lung disease; eating lead paint and anemia/neurologic/kidney disease; eating radium and anemia/bone-necrosis/cancer; eating mercury and neurologic disease. But NOT, to any measurable extent: ‘passive smoking’ and lung cancer; asbestos in your basement and mesothelioma; a piece of coal on your coffee table and black-lung disease; changing the battery in your car and lead poisoning; mercury preservatives in vaccines and neurologic disease; etc.
Contrary to ‘conventional wisdom’, chemical and biological hazards in the household have become rarer recently, not more common. Popular patent medicines of the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries were likely to contain large amounts of arsenic, mercury, acetanilide, radium, opium, digitalis, cocaine, or other poisons. Smoke from wood and coal stoves and from tobacco has become increasingly rare, as has lead in paint and gasoline. Food can be refrigerated or frozen at any time of the year. Water is safe. Plumbing exists. We know about germs. We know about rusty nails. We know how to kill botulinum spores in the process of canning. We have immunizations. See where this is going?
Sure, there might be some trace substance lurking out there that would be worth worrying about if only we knew what it was. If some people want to waste their own time, drive their family and friends crazy, and turn their children into paranoid neurotics, I suppose that’s their prerogative. What I don’t like is a consumer health magazine, ostensibly reflecting the views of board-certified physicians such as myself, erroneously Hyping Health Risks to every patient in every doctor’s office in the country.
Pseudoscientific Nonsense
And now for the pieces de resistance. Where to begin? Let’s start with an advertisement that ran in both the May and June issues:
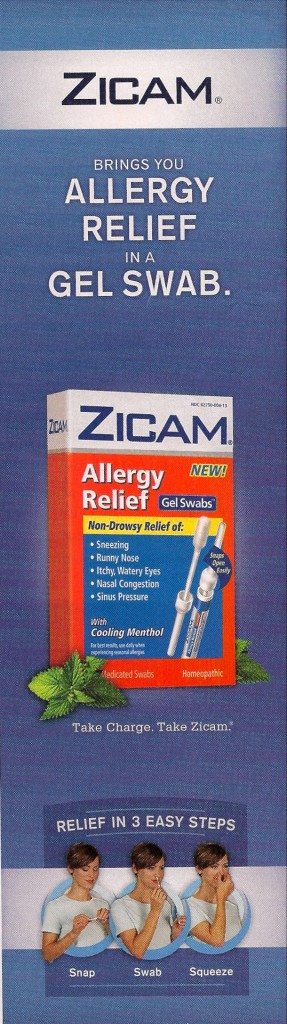
Look familiar? The ad appeared in the very month that the FDA warned consumers not to use another Zicam product because it might destroy their sense of smell. Funny: the following month’s issue of WebMD magazine made no mention of that. The website did report it without mentioning that Matrixx, the maker of Zicam, was one of WebMD’s sponsors. More worrisome to me is how WebMD’s board-certified physician reviewers could have overlooked “Homeopathic”—a sure sign of quackery—printed right on the picture of the Zicam Allergy Relief package.
Could it be that since this was merely an ad, the reviewers either didn’t feel obliged to examine it or were not given the opportunity? Perhaps, but that turns out to be moot. Consider this exchange between the Chief Medical Editor, Michael W. Smith, MD, and Dr. Jordan Josephson, an ear, nose, and throat specialist whom Dr. Smith interviewed about “Sinus Solutions”:
Q: What promise do alternative and complementary therapies hold for those who have spring allergies?
A: Besides irrigation, acupuncture seems to work well for some people through the rebalancing of chi (the energy forces in the body), which can help fortify the immune system to help alleviate the symptoms of sinusitis, allergies, and asthma.
Some of my patients want to try homeopathic remedies, so I send them to doctors who do integrative medicine. A very diluted amount of a particular medicine or combination of medicines is given on the theory that it will boost the immune system. The treatment is individual; each patient is carefully evaluated and receives a specific combination of homeopathic ingredients.
Neither Dr. Smith nor Josephson appeared hesitant to endorse such imaginary healing methods, just as neither appeared to know much about them.
Immune System Inanities
As exemplified above, fanciful statements about the immune system are almost as common in the magazine as are vacuous statements about ’stress’:
Q: Recent research shows that even mild stress or anxiety can worsen allergy symptoms.
A: It’s true: Mild stress or, in today’s economy, major anxiety weakens your resistance. So that does worsen allergies and leave you more susceptible to infections. It’s well known that stress has a relationship to your body’s immunity. —”Sinus Solutions”
…
Health benefits of meditation
Mitchell’s experience is borne out by studies showing that meditation not only lowers blood pressure but also can amp up your immune system — although the mechanism isn’t clear…
Raison participated in a study that indicated that meditation improved both physical and emotional responses to stress. In the study, people who meditated regularly for six weeks showed less activation of their immune systems…
Science hasn’t yet connected the dots between what happens in the meditating brain and the immune system. But a University of Wisconsin study saw increased electrical activity in regions of the left frontal lobe, an area that tends to be more active in optimistic people, after eight weeks of training in meditation. —Go Om
…
A pet is certainly a great friend. After a difficult day, pet owners quite literally feel the love.
In fact, for nearly 25 years, research has shown that living with pets provides certain health benefits. Pets help lower blood pressure and lessen anxiety. They boost our immunity.
… a growing number of studies have suggested that kids growing up in a home with “furred animals” — whether it’s a pet cat or dog, or on a farm and exposed to large animals — will have less risk of allergies and asthma…
If a dog lived in the home, infants were less likely to show evidence of pet allergies — 19% vs. 33%. They also were less likely to have eczema, a common allergy skin condition that causes red patches and itching. In addition, they had higher levels of some immune system chemicals — a sign of stronger immune system activation.
“Dogs are dirty animals, and this suggests that babies who have greater exposure to dirt and allergens have a stronger immune system,” Gern says.
People in stress mode get into a “state of dis-ease,” in which harmful chemicals like cortisol and norepinephrine can negatively affect the immune system, says Blair Justice, PhD, a psychology professor at the University of Texas School of Public Health and author of Who Gets Sick: How Beliefs, Moods, and Thoughts Affect Your Health. —”Animal Instinct“
…
“Like all living organisms, our bodies are making defective cells all the time,” Servan-Schreiber writes. “That’s how tumors are born. But our bodies are also equipped with a number of mechanisms that detect and keep such cells in check.” Supporting the processes that allow the body to recognize and destroy these errant cells is good medicine.—Book Review of Anticancer: A New Way of Life (I can’t find it on the website)
OK, let’s get this straight. “Fortifying” the immune system alleviates the symptoms of allergies and asthma. Even mild stress can worsen allergy symptoms; it weakens your resistance. It’s well known that stress has a relationship to your body’s immunity. So far, so good. Meditation amps up your immune system; that sounds about the same as fortifying or boosting it, no? Makes sense, because meditation improves emotional responses to stress. Oops: people who meditated regularly for six weeks showed less activation of their immune systems. Huh? Isn’t that like, uh, the opposite of amping it up?
Never mind: your pooch will both reduce your stress and boost your immunity, and you’ll have fewer allergies and asthma attacks. Fuggit: science hasn’t connected the dots yet anyway, so who cares?
Seriously, folks, this is a buncha oversimplified baloney. The immune system is a vast complexity of cells, molecules, and signals. It usually works quite well, as long as we aren’t starving or critically ill. It can get us into trouble by being inadequate to meet a challenge if, for example, it is weakened by a disease like AIDS. It can also cause trouble by being ‘overactive’ as is the case, almost by definition, for allergic reactions. Thus “boosting” the immune system seems like a bad idea if the goal is to reduce allergic reactions or to prevent exacerbations of other conditions that have allergic or auto-immune components, such as asthma, rheumatologic diseases, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. But this is also an oversimplifcation, because the immune system is complex and subtle: such diseases almost certainly reflect disturbances in modulations of various processes within it, rather than crude overactivity.
There are so many parts in the immune system that it’s a simple matter to demonstrate some change in the concentration of one or two (serum proteins, typically) after any of numerous interventions. In most instances, we have no idea what such changes mean or whether they have any importance. For an introductory critique of the ‘immune surveillance’ theory of cancer, read this essay.
“Boosting the immune system,” like “detoxification,” “holistic,” “integrative,” “complementary,” and “alternative,” are terms that in the context of popular medical treatises almost always herald pseudoscience and quackery. It’s regrettable that WebMD is chock full of them. On the website are more ads for homeopathic nostrums, numerous fanciful articles about acupuncture and ‘Eastern’ health wisdom, erroneous and misleading statements about naturopathy, chiropractic, and other quackery, and much more.
I wonder why. Is it just that fantasy is easier and more instantly gratifying than reality?
*This blog post was originally published at Science-Based Medicine*