March 9th, 2011 by LouiseHBatzPatientSafetyFoundation in Health Policy, True Stories
No Comments »

This is a guest post by Dr. Julia Hallisy.
Serious infections are becoming more prevalent and more virulent both in our hospitals and in our communities. The numbers are staggering: 1.7 million people will suffer from a hospital-acquired infections each year and almost 100,000 will die as a result.
When our late daughter, Kate, was diagnosed with an aggressive eye cancer in 1989 at five months of age, our life became consumed by doctor visits, MRI scans, radiation treatments, chemotherapy — and fear. My husband and I assumed that our fight was against the ravages of cancer, but almost eight years later we faced another life-threatening challenge we never counted on — a hospital-acquired infection. In 1997, Kate was infected with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the operating room during a “routine” 30-minute biopsy procedure to confirm the reoccurrence of her cancer.
Kate’s hospital-acquired infection led to seven weeks in the pediatric intensive care unit on life support, the amputation of her right leg, kidney damage, and the loss of 70 percent of her lung capacity. While most infections are not this serious, the ones that are often lead to permanent loss of function and lifelong disabilities. In the years since Kate’s infection, resistant strains of the bacteria have emerged and now pose even more of a threat since they can be impossible to treat with our existing arsenal of antibiotics.
Patients afflicted with MRSA will often have to contend with the threat of recurrent infections for the rest of their lives. These patients live in constant fear of re-infection and often struggle with feelings of vulnerability and helplessness. Family members, friends, and co-workers may not fully understand the facts and have nowhere to turn for education about risks and prevention. Loved ones may worry unnecessarily for their own safety, which can cause them to distance themselves from someone who desperately needs their presence and support.
We have the knowledge and the ability to prevent a great number of these frightening infections, but the busy and fragmented system in which healthcare is delivered doesn’t encourage adequate infection control measures, and patients continue to be at risk. A significant part of the problem is that the public doesn’t receive timely and accurate information about the detection and prevention of MRSA and other dangerous organisms, and they aren’t engaged as “safety partners” in the quest to eliminate infections. Read more »
January 29th, 2011 by KevinMD in Health Policy, Opinion
No Comments »

I recently pointed to a BMJ study concluding that pay for performance doesn’t seem to motivate doctors. It has been picking up steam in major media with TIME, for instance, saying: “Money isn’t everything, even to doctors.”
So much is riding on the concept of pay for performance, that it’s hard to fathom what other options there are should it fail. And there’s mounting evidence that it will.
Dr. Aaron Carroll, a pediatrician at the University of Indiana, and regular contributor to KevinMD.com, ponders the options. First he comments on why the performance incentives in the NHS failed:
Perhaps the doctors were already improving without the program. If that’s the case, though, then you don’t need economic incentives. It’s possible the incentives were too low. But I don’t think many will propose more than a 25 percent bonus. It’s also possible that the benchmarks which define success were too low and therefore didn’t improve outcomes. There’s no scientific reason to think that the recommendations weren’t appropriate, however. More likely, it’s what I’ve said before. Changing physician behavior is hard.
So if money can’t motivate doctors, what’s next? Physicians aren’t going to like what Dr. Carroll has to say. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at KevinMD.com*
January 21st, 2011 by DavedeBronkart in Health Tips, Opinion
No Comments »

There are several stages in becoming an empowered, engaged, activated patient — a capable, responsible partner in getting good care for yourself, your family, whoever you’re caring for. One ingredient is to know what to expect, so you can tell when things seem right and when they don’t.
Researching a project today, I came across an article* published in 2006: “Key Learning from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s 10-Year Patient Safety Journey.” This table shows the attitude you’ll find in an organization that has realized the challenges of medicine and is dealing with them realistically:
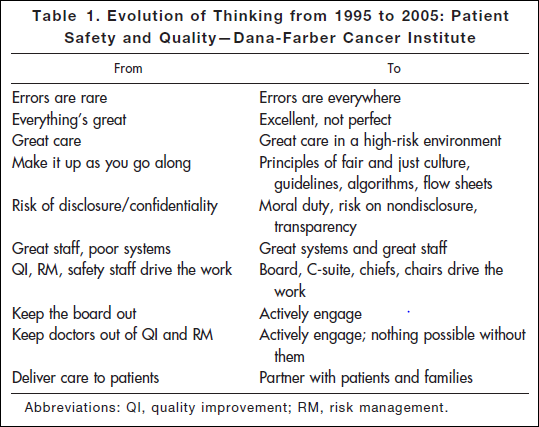
“Errors are everywhere.” “Great care in a high-risk environment.” What kind of attitude is that? It’s accurate.
This work began after the death of Boston Globe health columnist Betsy Lehman. Long-time Bostonians will recall that she was killed in 1994 by an accidental overdose of chemo at Dana-Farber. It shocked us to realize that a savvy patient like her, in one of the best places in the world, could be killed by such an accident. But she was.
Five years later the Institute of Medicine’s report “To Err is Human” documented that such errors are in fact common — 44,000 to 98,000 a year. It hasn’t gotten better: Last November the U.S. Inspector General released new findings that 15,000 Medicare patients are killed in U.S. hospitals every month. That’s one every three minutes. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at e-Patients.net*
January 14th, 2011 by admin in Health Tips, News, Video
No Comments »
 This is a guest post from Dr. Mary Lynn McPherson.
This is a guest post from Dr. Mary Lynn McPherson.
**********
FDA Restricts Acetaminophen In Popular Pain Medications
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) made an announcement yesterday that affects one of the most common pain medications on the market, and as a consequence may affect countless numbers of the 75 million Americans who experience chronic pain (for perspective, that’s more than the number of people suffering from cancer, heart disease and diabetes combined.) The FDA has asked manufacturers of popular prescription pain medications like Vicodin or Percocet to limit the amount of acetaminophen (also known as Tylenol, or APAP) used in these drugs to no more than 325 milligrams per tablet — the equivalent of one regular-strength Tylenol tablet.
The move came because research has shown that acetaminophen can cause liver damage when taken in higher than recommended doses. The problem is that many over-the-counter medications ALSO contain acetaminophen, and patients may take one or more of these common products (like Tylenol) to reduce their fever or get rid of a headache along with their prescription pain relievers.
Before you know it, you could be taking more than the maximum daily dose of acetaminophen which is 4,000 milligrams. I go out of my way to advise people I work with of this warning, but not everyone takes time to talk to the pharmacist and not all pharmacists make themselves readily available. That is why it is critically important that you talk to your pharmacist to make sure that you are not taking more than this amount. The pharmacist is the last stop between you and medication misuse — you could be taking a medication that contains acetaminophen and not even know it. Read more »
December 29th, 2010 by eDocAmerica in Better Health Network, Opinion
No Comments »

Recently, I was involved in a discussion on an email list serve and decided to takes some of my comments on patient autonomy and blog about them. This arose following a debate about whether the term “patient” engendered a sense of passivity and, therefore, whether the term should be dropped in favor of something else, like “client” or something similar.
Having participated in the preparation and dissemination of the white paper on e-patients, I don’t see the need for “factions” or disagreements in the service of advancing Participatory Medicine. As Alan Greene aptly stated: “This is a big tent, with room for all.”
I want all of my patients to be as autonomous as possible. In my view, their autonomy is independent of the doctor-patient relationship that I have with them. They make the choice to enter into, or to activate or deactivate, the relationship with me. They may ignore my input, seek a second opinion, or fire me and seek the care of another physician at any time. They truly are in control in that sense. The only thing I have control over and am responsible for is trying to provide the best advice or consultation I can. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at eDocAmerica*















