December 27th, 2011 by BarbaraFicarraRN in Health Policy, Opinion
1 Comment »


Bill Crounse, MD, Senior Director, Worldwide Health, Worldwide Public Sector Microsoft Corporation shares his insights and describes four leading trends and technologies that will transform health and health care in 2012 and beyond.
These leading technologies include: cloud computing, health gaming, telehealth services and remote monitoring/mobile health.
Telehealth, Remote Monitoring, Mobile Health
I’d like to focus on telehealth and remote monitoring/mobile health since I feel telehealth is the nucleus of patient care, and telehealth can help reduce health care costs, and improve quality health care for patients. Telehealth technology combined mobile technology such as smartphones will make monitoring patients conditions easier and more efficient, and “cheaper and more scalable.”
Patient Quality Health Care
Through the Accountable Care Organizational Model (ACO), the core concept is to Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Health in 30*
December 21st, 2011 by BarbaraFederOstrov in News, Opinion
No Comments »
 Now that the latest controversial decision over federal “morning after” pill restrictions has faded from the headlines, it’s worth following up on this question: how available is emergency contraception right now in your own community?
Now that the latest controversial decision over federal “morning after” pill restrictions has faded from the headlines, it’s worth following up on this question: how available is emergency contraception right now in your own community?
To recap: last week, HHS Secretary Kathleen Sebelius overruled her own science advisors in a decision preventing the “morning after” contraceptive pill Plan B from being sold over the counter at drugstores and to girls under 17 without a prescription. The election-season decision, largely regarded as highly political, could be reviewed by a federal judge after a legal challenge by a pro-choice group.
Of course, Plan B has been controversial ever since it was first approved by the FDA in 1999 (you can see Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Reporting on Health - Barbara Feder Ostrov's Health Journalism Blog*
December 9th, 2011 by Dr. Val Jones in News, Patient Interviews
1 Comment »
 There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the mHealth Summit yesterday. Jill is a 60 year-old woman from Texas who has been actively concerned for the safety of herself and her daughter over the years.
There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the mHealth Summit yesterday. Jill is a 60 year-old woman from Texas who has been actively concerned for the safety of herself and her daughter over the years.
“My daughter took a self-defense class,” Jill explained, “And she was taught the ‘fight or flight’ response to escape harm. I’m 60 years old. I’m not good at fighting and not very fast at fleeing. So what’s my third option?” Jill created the WatchMe 911 app to provide the solution.
“I first started thinking about a personal alarm system before smart phones even existed. I saw that there were car alarms and house alarms, and wondered why there weren’t personal alarms. At the time I imagined that the personal alarm would go through an answering service system, but since smart phones were created, it can all be tied together in an app format.”
Jill demonstrated the WatchMe 911 app to me during our interview. It contains features such as a panic button that can be armed in advance. Two taps on the smart phone screen and a circle of friends and 9-1-1 are contacted immediately with your GPS location and an alert message. The panic button is a favorite for women who are concerned for their safety when walking late at night or in dimly lit parking lots or alleys. Read more »
December 3rd, 2011 by Elaine Schattner, M.D. in Opinion, Research
No Comments »

The latest issue of the Annals of Internal Medicine contains 2 noteworthy papers on cervical cancer screening. The first, a systematic review of studies commissioned by the USPSTF, looked at 3 methods for evaluating abnormalities in women over 30 years:
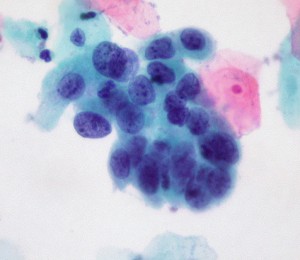
high-grade cervical cell dysplasia (Dr. E. Uthman, Wikimedia Commons)
1. Conventional cytology (as in a Pap smear; the cervix is scraped and cells splayed onto a microscope slide for examination);
2. Liquid-based cytology (for LBC, the NHS explains: the sample is taken as for a Pap test, but the tip of the collection spatula is inserted into fluid rather than applied to slides. The fluid is sent to the path lab for analysis);
3. Testing for high-risk HPV (human papillomavirus). Currently 3 tests have been approved by the FDA in women with atypical cervical cells or for cervical cancer risk assessment in women over the age of 30: Digene Hybrid Capture 2 (manufactured by Quiagen), Cobas 4800 HPV (Roche) and Cervista HR HPV (Hologic); another Roche Diagnostics assay, Amplicor HPV, awaits approval.
These HPV assays use distinct methods to assess DNA of various HPV strains.
There’s a lot of jargon here, and I have to admit some of this was new to me despite my nearly-due diligence as a patient at the gynecologist’s office and my familiarity as an oncologist with the staging, clinical manifestations and treatment of cervical cancer. Who knew so many decisions were made during a routine pelvic exam about which manner of screening? Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Medical Lessons*
November 14th, 2011 by HarvardHealth in Health Tips
No Comments »

I was hiking in the woods recently with a group of women friends when something caught my attention. It wasn’t an interesting bird or plant, but the surprising number of “pit stops” my friends needed to make.
Their frequent detours into the bushes struck me because I had just finished working on Better Bladder and Bowel Control, the latest Special Health Report from Harvard Medical School. According to the report, incontinence is the unintended loss of urine or feces that is significant enough to make it difficult to do ordinary activities without frequent trips to the restroom. In the United States, about 32 million men and women have some degree of incontinence. For women, incontinence is a common but rarely discussed result of childbirth and aging—that could explain the pit stops of my hiking friends, who were all mid-life mothers. For men, incontinence is most often a side effect of treatment for prostate disorders.
Many things can go wrong with the complex system that allows us to control urination. Read more »
*This blog post was originally published at Harvard Health Blog*




 Now that the latest controversial decision over federal “morning after” pill restrictions has faded from the headlines, it’s worth following up on this question: how available is emergency contraception right now in your own community?
Now that the latest controversial decision over federal “morning after” pill restrictions has faded from the headlines, it’s worth following up on this question: how available is emergency contraception right now in your own community? There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the
There aren’t too many grandmothers developing mobile health apps these days, but I met a charming one (Jill Campbell) at the 










